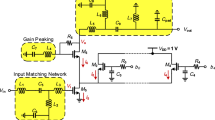
Abstract
A 160 MHz bandwidth 90° active RC–CR phase shifter with integrated on-line amplitude locked loop (ALL) calibration targeted to 802.11ac 5 GHz wireless local area network (WLAN) applications is presented in this paper. The quadrature phase shifter is a key component for transceivers employing the Hartley image rejection architecture. The passive RC–CR phase shifter generates the required two quadrature outputs with an accurate 90° phase shift over the required bandwidth but lack the required accuracy in amplitude matching. A 90 nm CMOS microelectronic implementation of an RC–CR phase shifter is proposed with active resistors that are adjusted by an integrated on-line ALL calibration system to maintain matching amplitudes of the quadrature outputs over the required bandwidth. The on-line ALL calibration system employs peak detectors, comparators, digital logic control, and charge pump to incrementally adjust the active resistors while converging to matched amplitudes similar to the operation of phase-locked loop with a phase-frequency detector and charge pump. The resulting 90 nm implementation supports − 40db to − 70db image rejection ratios (IMMRs) over the IF 170 MHz to 330 MHz bandwidth. The 90 nm CMOS implementation is fully functional considering process variations based on 200 Monte Carlo simulations.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.K. Cavers, M.W. Liao, Adaptive compensation for imbalance and offset losses in direct conversion transceivers. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 42(4), 581–588 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1109/25.260752
M. Elmala, G. Ibrahim, Calibration study of dual-band Weaver-Hartley receiver architecture. Microelectr. J. 46(6), 439–446 (2015)
M. Elmala, S. Embabi, Calibration of phase and gain mismatches in Weaver image-reject receiver. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 39(2), 283–289 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSSC.2003.821779
H. Ghonoodi, H.M. Naimi, A series-coupled LC quadrature oscillator using phase/amplitude calibration. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 45(5), 613–624 (2016)
A. Hamidia, M. Honarbar, B. Virdee, Multi-way and poly-phase wideband differential phase shifter based on metamaterial technology. AEU Int. J. Electr. Commun. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeue.2019.152872
B. Jackson, C. Saavedra, A CMOS Ku-band 4x subharmonic mixer. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 43(6), 1351–1359 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSSC.2008.922738
M.F. Lan, A. Tammineedi, R. Geiger, Current mirror layout strategies for enhancing matching performance. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 28, 9–26 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011237602078
A. Li, Y. Ding, Z. Chen, B. Chi, 1.15GHz image rejection filter with 45 dB image rejection ratio and 8.4 mW DC power in 90 nm CMOS. Microelectr. J. 84, 48–53 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mejo.2018.12.003
S. Li, X. Zhang, H. Xue, S. Ren, On-chip self-calibration system for CMOS active inductor band pass filter. AEU Int. J. Electr. Commun. 92, 64–68 (2018)
S. Li, H. Xue, X. Zhang, S. Ren, A low power CMOS amplitude peak detector for on-chip self-calibration applications. IEEE NAECON (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/NAECON.2017.8268794
C. Meng, T. Wu, J. Syu, S. Yu, K. Tsung, Y. Teng, 2.4/5.7-GHz CMOS dual-band low-IF architecture using Weaver-Hartley image-rejection techniques. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Techn. 57(3), 552–561 (2009)
D. Ozis, J. Paramesh, D. Allstot, A CMOS 5GHz image-reject receiver front-end architecture. IEEE RFIC Symp. (2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/RFIC.2007.380892
S. Ren, J. Emmert, R. Siferd, Design and performance of a robust 180 nm CMOS standalone VCO and the integrated PLL. Analog Integr. Circ. Sig. Process. 68(3), 285–298 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-011-9644-3
M. Sarkezeh, A. Safarian, An S-band 6-bit full 360° phase shifter using wideband quadrature generation with pole-zero manipulation. AEU Int. J. Electr. Commun. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeue.2019.153027
A. Szymanski, E. Kurjata-Pfitzner, J. Lesinski, J. Wasowski, The self-calibration method of IR mixer with low IF. Syst. Signal Process. 55, 115–124 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-008-9141-5
P. Tsai, P. Lo, F. Shih, W. Jau, M. Huang, Z. Huang, A 4×4 MIMO-OFDM baseband receiver with 160MHz bandwidth for indoor gigabit wireless communications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst I 62(12), 2929–2939 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSI.2015.2495740
M. Yaghoobi, M. Yavari, H. Ghafoorifard, A 17-to-24 GHz low-power variable-gain low-noise amplifier in 65-nm CMOS for phased-array receivers. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 38, 5448–5466 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-019-01169-z
J. Yu, F.F. Dai, R.C. Jaeger, A 12-bit Vernier ring time-to-digital converter in 0.13 um CMOS technology. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 45(4), 830–842 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSSC.2010.2040306
X. Zhang, S. Li, R. Siferd, S. Ren, High-sensitivity high-speed dynamic comparator with parallel input clocked switches. AEU Int. J. Electr. Commun. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeue.2020.153236
D. Zhu, W. Chen, S. Pan, Photonics-enabled balanced Hartley architecture for broadband image-reject microwave mixing. Opt. Express (2018). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.26.028022
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XZ: Circuit design, simulation, layout, and paper preparation. PhD. SL: Circuit simulation and reference searching. PhD. RS: Advising and paper revision. PhD. SR: Advising and paper revision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Li, S., Siferd, R. et al. A 170 MHz to 330 MHz Wideband 90 nm CMOS RC–CR Phase Shifter with Integrated On-Line Amplitude Locked Loop Calibration for Hartley Image Rejection Transceiver. Circuits Syst Signal Process 40, 5249–5263 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-021-01722-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-021-01722-9