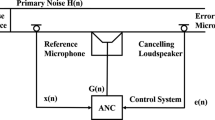
Abstract
This paper provides a detailed overview of active impulsive noise control (AINC) technology of α-stable distribution noise. The second-order moment of the non-Gaussian impulsive noise does not exist, so the adaptive algorithms based on second-order statistics would lead to poor noise reduction performance. On account of this defect, a series of AINC algorithms have been proposed over the past 25 years. In this paper, we briefly classified the AINC algorithms into the classic algorithms and the expanded algorithms depending on different criteria, and both the classic AINC algorithms and the expanded AINC algorithms are further divided. Afterward, we introduced the principles and characteristics of different AINC algorithms and listed the weights update formulas of those algorithms. Finally, the computational complexity comparisons of common AINC algorithms and further recommendations are given, and a brief review about the experimental testing of AINC systems is provided in order to assist related scholars to carry out AINC researches more conveniently.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
K. Ahuja, J. Stevens, Recent advances in active noise control. AIAA J. 1, 1058–1067 (1990)
M.T. Akhtar, A. Nishihara, Data-reusing-based filtered-reference adaptive algorithms for active control of impulsive noise sources. Appl. Acoust. 92, 18–26 (2015)
M.T. Akhtar, Binormalized data-reusing adaptive filtering algorithm for active control of impulsive sources. Digit. Signal Process. 49, 56–64 (2016)
M.T. Akhtar, W. Mitsuhashi, Improved adaptive algorithm for active noise control of impulsive noise, in 2008 9th International Conference on Signal Processing, 26–29 Oct 2008 (2008), pp. 2669–2672
M. Akhtar, A normalized filtered-x generalized fractional lower order moment adaptive algorithm for impulsive ANC systems (2018)
M. Akhtar, W. Mitsuhashi, A modified normalized FxLMS algorithm for active control of impulsive noise, in European Signal Processing Conference (2010)
M.T. Akhtar, M.A. Raja, Fractional processing-based active noise control algorithm for impulsive noise, in 2015 IEEE China Summit and International Conference on Signal and Information Processing (ChinaSIP), 12–15 July 2015 (2015), pp. 10–14
S. Ambike, J. Ilow, D. Hatzinakos, Detection for binary transmission in a mixture of Gaussian noise and impulsive noise modeled as an alpha-stable process. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 1(3), 55–57 (1994)
I.T. Ardekani, W.H. Abdulla, Theoretical convergence analysis of FxLMS algorithm. Signal Process. 90(12), 3046–3055 (2010)
M. Aslam, P. Shi, C.C. Lim, Variable threshold-based selective updating algorithms in feed-forward active noise control systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 66(2), 782–795 (2018)
E. Atmaca, I. Peker, A. Altin, Industrial noise and its effects on humans. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 14(6), 721–726 (2005)
R.T. Bambang, Adjoint EKF learning in recurrent neural networks for nonlinear active noise control. Appl. Soft Comput. 8(4), 1498–1504 (2008)
R.F. Barron, Industrial Noise Control and Acoustics (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2002)
M. Basner, W. Babisch, A. Davis, M. Brink, C. Clark, S. Janssen, S. Stansfeld, Auditory and non-auditory effects of noise on health. Lancet 383, 1325–1332 (2013)
J.M. Bedout, M. Franchek, R.J. Bernhard, L. Mongeau, Adaptive-passive noise control with self-tuning Helmholtz resonators. J. Sound Vib. 202, 109–123 (1997)
T. Bein, S. Herold, D. Mayer, Recent advances in active noise and vibration control, in 10th European Congress and Exposition on Noise Control Engineering, Euronoise 2015, June 1, 2015–June 3, 2015, Maastricht, Netherlands 2020. Euronoise (2015), pp. 2195–2200
L.H. Bell, D.H. Bell, Industrial Noise Control: Fundamentals and Applications (Marcel Dekker, New York, 1994)
M. Bergamasco, L. Piroddi, Active noise control of impulsive noise using online estimation of an alpha-stable model, in 49th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), 15–17 Dec 2010 (2010), pp. 36–41
M. Bergamasco, F. Della Rossa, L. Piroddi, Active noise control with on-line estimation of non-Gaussian noise characteristics. J. Sound Vib. 331(1), 27–40 (2012)
R.J. Bernhard, H.R. Hall, J.D. Jones, Adaptive-passive noise control. Inter-Noise 92, 427–430 (1992)
S. Bianchi, A. Corsini, A. Sheard, A critical review of passive noise control techniques in industrial fans. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 136(4), 044001 (2014)
M. Bouchard, Multichannel affine and fast affine projection algorithms for active noise control and acoustic equalization systems. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 11(1), 54–60 (2003)
J. Burgess, Active adaptive sound control in a duct: a computer simulation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 70, 715–726 (1981)
M. Calton, S. Sommerfeldt, Modeling systems of acoustic resonators for application in passive noise control. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 139, 2205–2205 (2016)
A. Carini, G.L. Sicuranza, Transient and steady-state analysis of filtered-x affine projection algorithms. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 54(2), 665–678 (2006)
D.P. Das, G. Panda, Active mitigation of nonlinear noise Processes using a novel filtered-s LMS algorithm. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 12(3), 313–322 (2004)
D.P. Das, D.J. Moreau, B.S. Cazzolato, Adjoint nonlinear active noise control algorithm for virtual microphone. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 27, 743–754 (2012)
S.J. Elliott, P.A. Nelson, Active noise control. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 10(4), 12–35 (1993)
M. Ferrer, M. de-Diego, A. Gonzalez, G. Pinero, Convex combination of adaptive filters for ANC, in Proceedings of the 16th International Congress on Sound and Vibration (ICSV'09) (2009)
M. Ferrer, A. Gonzalez, M.D. Diego, G. Pinero, Convex combination filtered-X algorithms for active noise control systems. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 21(1), 156–167 (2013)
N. George, G. Panda, Advances in active noise control: a survey, with emphasis on recent nonlinear techniques. Signal Process. 93, 363–377 (2013)
N.V. George, A. Gonzalez, Convex combination of nonlinear adaptive filters for active noise control. Appl. Acoust. 76, 157–161 (2014)
N.V. George, G. Panda, A robust filtered-s LMS algorithm for nonlinear active noise control. Appl. Acoust. 73(8), 836–841 (2012)
P.G. Georgiou, P. Tsakalides, C. Kyriakakis, Alpha-stable modeling of noise and robust time-delay estimation in the presence of impulsive noise. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 1(3), 291–301 (1999)
F. Gu, S. Chen, Z. Zhou, Y. Jiang, An enhanced normalized step-size algorithm based on adjustable nonlinear transformation function for active control of impulsive noise. Appl. Acoust. 176, 107853 (2021)
H. Guo, Y.S. Wang, N.N. Liu, R.P. Yu, H. Chen, X.T. Liu, Active interior noise control for rail vehicle using a variable step-size median-LMS algorithm. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 109, 15–26 (2018)
X. Guo, J. Jiang, L. Tan, S. Du, Improved adaptive recursive even mirror Fourier nonlinear filter for nonlinear active noise control. Appl. Acoust. 146, 310–319 (2019)
T. Habib, M. Kepesi, Open IEN issues of active noise control applications (2007)
Z.C. He, H.H. Ye, E. Li, An efficient algorithm for nonlinear active noise control of impulsive noise. Appl. Acoust. 148, 366–374 (2019)
J. Hong, J.C. Akers, R. Venugopal, L. Miin-Nan, A.G. Sparks, P.D. Washabaugh, D.S. Bernstein, Modeling, identification, and feedback control of noise in an acoustic duct. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 4(3), 283–291 (1996)
L. Hui, Z. Ming, S. Wee, A weight-constrained FxLMS algorithm for feedforward active noise control systems. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 9(1), 1–4 (2002)
Y. Ji, S. Chen, W. Zhu, The effect of pore numbers in the cell walls of soybean oil polyurethane foam on sound absorption performance. Appl. Acoust. 157, 107010 (2020)
J. Jiang, Y. Li, Review of active noise control techniques with emphasis on sound quality enhancement. Appl. Acoust. 136, 139–148 (2018)
Y. Jiang, S. Chen, F. Gu, H. Meng, Y. Cao, A modified feedforward hybrid active noise control system for vehicle. Appl. Acoust. 175, 107816 (2021)
R.S. Job, Community response to noise: a review of factors influencing the relationship between noise exposure and reaction. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 83, 991–1001 (1988)
Y. Kajikawa, W. S. Gan, S. Kuo, Recent advances on Active noise control: open issues and innovative applications. APSIPA Trans. Signal Inf. Process. 1, E3 (2012)
Y. Kajikawa, W. Gan, S.M. Kuo, Recent applications and challenges on active noise control, in 2013 8th International Symposium on Image and Signal Processing and Analysis (ISPA), 4-6 Sept 2013 (2013), pp. 661–666
B. Krstajic, Z. Zecevic, Z. Uskokovic, Increasing convergence speed of FxLMS algorithm in white noise environment. AEU-Int. J. Electron. C. 67, 848–853 (2013)
S. Kuo, D. Morgan, Active noise control: a tutorial review. Proc. IEEE 87, 943–973 (1999)
S. Kuo, D. Morgan, Active Noise Control Systems: Algorithms and DSP Implementations (John Wiley & Sons, Inc, New York, 1996)
P. Lara, F. Igreja, L.D.T.J. Tarrataca, D.B. Haddad, M.R. Petraglia, Exact expectation evaluation and design of variable step-size adaptive algorithms. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 26(1), 74–78 (2018)
R. Leahy, Z. Zhou, Y.C. Hsu, Adaptive filtering of stable processes for active attenuation of impulsive noise, vol 5 (1995)
H.M. Lee, Z. Wang, K. Lim, H. Lee, A review of active noise control applications on noise barrier in three-dimensional/open space: myths and challenges. Fluct. Noise Lett. 18, 1930002 (2019)
P. Li, X. Yu, Comparison study of active noise cancelation algorithms for impulsive noise (2011)
C.E. Lin, C. Wen-Chih, H. An-Chih, W. Jon-Bi, A CFXLMS algorithm with selection detector for active noise control system, in 2005 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology, 14–17 Dec 2005 (2005), pp. 137–141
L. Liu, S. Gujjula, P. Thanigai, S.M. Kuo, Still in womb: intrauterine acoustic embedded active noise control for infant incubators. Adv. Acoust. Vib. 2008, 495317 (2008)
L. Lu, H. Zhao, Adaptive Volterra filter with continuous lp-norm using a logarithmic cost for nonlinear active noise control. J. Sound Vib. 364, 14–29 (2016)
L. Lu, H. Zhao, Active impulsive noise control using maximum correntropy with adaptive kernel size. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 87, 180–191 (2017)
P. Lueg, Verfahren zur Dämpfung von Schallschwingungen. Ger Pat 508 (1933)
P. Leug, Process of silencing sound oscillations. U.S. Patent 2043416 (1936)
S. Marburg, Developments in structural-acoustic optimization for passive noise control. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 9, 291–370 (2002)
H. Meng, S. Chen, Particle swarm optimization based novel adaptive step-size FxLMS algorithm with reference signal smoothing processor for feedforward active noise control systems. Appl. Acoust. 174, 107796 (2021)
H. Meng, S. Chen, A modified adaptive weight-constrained FxLMS algorithm for feedforward active noise control systems. Appl. Acoust. 164, 107227 (2020)
D. Morgan, History, applications, and subsequent development of the FXLMS algorithm [DSP history]. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 30, 172–176 (2013)
W. Niu, C. Zou, B. Li, W. Wang, Adaptive vibration suppression of time-varying structures with enhanced FxLMS algorithm. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 118, 93–107 (2019)
A.M. Al Omour, A. Zidouri, N. Iqbal, A. Zerguine, Filtered-X least mean fourth (FXLMF) and leaky FXLMF adaptive algorithms. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2016(1), 39 (2016)
T. Padhi, M. Chandra, D.A. Kar, M.N.S. Swamy, A new adaptive control strategy for hybrid narrowband active noise control systems in a multi-noise environment. Appl. Acoust. 146, 355–367 (2018)
T. Padhi, M. Chandra, Cascading time-frequency domain filtered-x LMS algorithm for active control of uncorrelated disturbances. Appl. Acoust. 149, 192–197 (2019)
A. Panda, K. Das, A survey on actively controlling mixture of impulsive and Gaussian noise (2019)
M. Pawelczyk, W. Wierzchowski, L. Wu, X. Qiu, An extension to the filtered-x LMS algorithm with logarithmic transformation, in 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Signal Processing and Information Technology (ISSPIT), 7–10 Dec 2015 (2015), pp. 454–459
R.J. Peppin, Industrial noise and vibration control, by J. D. Irwin and E. R. Graf. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 67(5), 1850–1851 (1980)
F. Pfander, Danger of auditory impairment from impulse noise: a comparative study of the CHABA damage-risk criteria and those of the Federal Republic of Germany. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 67, 628 (1980)
G. Pinte, B. Stallaert, P. Sas, W. Desmet, J. Swevers, A novel design strategy for iterative learning and repetitive controllers of systems with a high modal density: theoretical background. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 24(2), 432–443 (2010)
R.M. Reddy, I.M.S. Panahi, R. Briggs, Hybrid FxRLS-FxNLMS adaptive algorithm for active noise control in fMRI application. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 19(2), 474–480 (2011)
M. Rupp, A.H. Sayed, Robust FxLMS algorithms with improved convergence performance. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 6(1), 78–85 (1998)
F.H. Schmitz, Y.H. Yu, Helicopter impulsive noise: theoretical and experimental status, in Recent Advances in Aeroacoustics. ed. by A. Krothapalli, C.A. Smith (Springer, New York, 1986), pp. 149–243
B.A. Schnaufer, W.K. Jenkins, New data-reusing LMS algorithms for improved convergence, in Proceedings of 27th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, 1–3 Nov 1993, vol 1582 (1993), pp. 1584–1588
M. Shao, C.L. Nikias, Signal processing with fractional lower order moments: stable processes and their applications. Proc. IEEE 81(7), 986–1010 (1993)
G.L. Sicuranza, A. Carini, On the accuracy of generalized hammerstein models for nonlinear active noise control, in 2006 IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference Proceedings, 24–27 April 2006 (2006), pp. 1411–1416
A. Smith, A review of the non-auditory effects of noise on health. Work Stress. 5(1), 49–62 (1991)
S.D. Snyder, N. Tanaka, Active control of vibration using a neural network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 6(4), 819–828 (1995)
S.A. Stansfeld, M.P. Matheson, Noise pollution: non-auditory effects on health. Br. Med. Bull. 68(1), 243–257 (2003)
P. Song, H. Zhao, Filtered-x least mean square/fourth (FXLMS/F) algorithm for active noise control. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 120, 69–82 (2019)
P. Song, H. Zhao, Filtered-x generalized mixed norm (FXGMN) algorithm for active noise control. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 107, 93–104 (2018)
B. Stallaert, G. Pinte, P. Sas, W. Desmet, J. Swevers, A novel design strategy for iterative learning and repetitive controllers of systems with a high modal density: application to active noise control. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 24(2), 444–454 (2010)
G. Sun, M. Li, T.C. Lim, Enhanced filtered-x least mean M-estimate algorithm for active impulsive noise control. Appl. Acoust. 90, 31–41 (2015)
G. Sun, M. Li, T.C. Lim, A family of threshold based robust adaptive algorithms for active impulsive noise control. Appl. Acoust. 97, 30–36 (2015)
X. Sun, S.M. Kuo, G. Meng, Adaptive algorithm for active control of impulsive noise. J. Sound Vib. 291(1), 516–522 (2006)
L. Tan, J. Jiang, Active control of impulsive noise using a nonlinear companding function. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 58–59, 29–40 (2015)
P. Thanigai, S.M. Kuo, R. Yenduri, Nonlinear active noise control for infant incubators in neo-natal intensive care units, in 2007 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing - ICASSP '07, 15–20 April 2007 (20070, pp. I-109–I-112
L. Thiery, C. Meyer-Bisch, Hearing loss due to partly impulsive industrial noise exposure at levels between 87 and 90 dB(A). J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 84, 651–659 (1988)
H. Wang, H. Sun, Y. Sun, M. Wu, J. Yang, A narrowband active noise control system with a frequency estimation algorithm based on parallel adaptive notch filter. Signal Process. 154, 108–119 (2018)
L. Wu, X. Qiu, Y. Guo, A simplified adaptive feedback active noise control system. Appl. Acoust. 81, 40–46 (2014)
L. Wu, X. Qiu, Y. Guo, A generalized leaky FxLMS algorithm for tuning the waterbed effect of feedback active noise control systems. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 106, 13–23 (2018)
L. Wu, X. Qiu, Active impulsive noise control algorithm with post adaptive filter coefficient filtering. IET Signal Proc. 7(6), 515–521 (2013)
L. Wu, X. Qiu, An M-estimator based algorithm for active impulse-like noise control. Appl. Acoust. 74(3), 407–412 (2013)
L. Wu, H. He, X. Qiu, An active impulsive noise control algorithm with logarithmic transformation. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 19(4), 1041–1044 (2011)
W. Xia, Y. Wang, A variable step-size diffusion LMS algorithm over networks with noisy links. Signal Process. 148, 205–213 (2018)
L. Xiao, M. Wu, J. Yang, A new efficient filtered-x affine projection sign algorithm for active control of impulsive noise. Signal Process. 120, 456–461 (2016)
F. Yang, Y. Cao, M. Wu, F. Albu, J. Yang, Frequency-domain filtered-x LMS algorithms for active noise control: a review and new insights. Appl. Sci. 8, 2313 (2018)
G. Yang, J. Wang, G. Yue, S. Li, Complex baseband myriad filtering and maximum likelihood MSK demodulation under symmetric alpha-stable noise, in 2016 IEEE 83rd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), 15–18 May 2016 (2016), pp. 1–5
K. Yin, H. Zhao, L. Lu, Functional link artificial neural network filter based on the q-gradient for nonlinear active noise control. J. Sound Vib. 435, 205–217 (2018)
N. Yu, Z. Li, Y. Wu, R. Feng, B. Chen, Convex combination-based active impulse noise control system. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control 39(1), 190–202 (2019)
H. Zayyani, Continuous mixed $p$-norm adaptive algorithm for system identification. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 21(9), 1108–1110 (2014)
A. Zeb, A. Mirza, Q.U. Khan, S.A. Sheikh, Improving performance of FxRLS algorithm for active noise control of impulsive noise. Appl. Acoust. 116, 364–374 (2017)
J. Zhang, T.D. Abhayapala, Samarasinghe, P.N., Zhang, W., Jiang, S., Sparse complex FxLMS for active noise cancellation over spatial regions, in 2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 20–25 March 2016 (2016), pp. 524–528
Q.Z. Zhang, W.S. Gan, Active noise control using a simplified fuzzy neural network. J. Sound Vib. 272(1), 437–449 (2004)
S. Zhang, Y.S. Wang, H. Guo, C. Yang, X.L. Wang, N.N. Liu, A normalized frequency-domain block filtered-x LMS algorithm for active vehicle interior noise control. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 120, 150–165 (2019)
S. Zhang, W.X. Zheng, Recursive adaptive sparse exponential functional link neural network for nonlinear AEC in impulsive noise environment. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 29(9), 4314–4323 (2018)
H. Zhao, X. Zeng, Z. He, S. Yu, B. Chen, Improved functional link artificial neural network via convex combination for nonlinear active noise control. Appl. Soft Comput. 42, 351–359 (2016)
T.L. Zhe, J. Jean, Filtered-X second-order Volterra adaptive algorithms. Electron. Lett. 33(8), 671–672 (1997)
D. Zhou, V. DeBrunner, Efficient adaptive nonlinear filters for nonlinear active noise control. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 54(3), 669–681 (2007)
Y. Zhou, Y. Yin, Q. Zhang, Active control of SαS impulsive noise based on a sigmoid transformation algorithm, vol 1 (2012)
Y. Zhou, Q. Zhang, Y. Yin, Active control of impulsive noise with symmetric α-stable distribution based on an improved step-size normalized adaptive algorithm. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 56–57, 320–339 (2015)
Y.L. Zhou, Y.X. Yin, Q.Z. Zhang, Active control of repetitive impulsive noise in a non-minimum phase system using an optimal iterative learning control algorithm. J. Sound Vib. 332(18), 4089–4102 (2013)
T. Zhu, S. Chen, W. Zhu, Y. Wang, Optimization of sound absorption property for polyurethane foam using adaptive simulated annealing algorithm. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 135, 46426 (2018)
C. Zou, Adaptive vibration suppression of time-varying structures with enhanced FxLMS algorithm. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 118, 93–107 (2018)
Funding
This work was supported by the Jilin Provincial Natural Science Foundation Project (20180101070JC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SC was involved in data curation, writing-reviewing and editing, and project administration. FG was involved in conceptualization, methodology, and writing-original draft preparation. CL was involved in validation, visualization, and investigation. HM was involved in validation and resources. KW was involved in supervision and investigation. ZZ was involved in supervision and investigation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest exists in the submission of this manuscript, and the manuscript is approved by all authors for publication. I would like to declare on behalf of my co-authors that the work described is original research and has not been published previously, in whole or in part. All the authors listed have approved the manuscript that is enclosed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Gu, F., Liang, C. et al. Review on Active Noise Control Technology for α-Stable Distribution Impulsive Noise. Circuits Syst Signal Process 41, 956–993 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-021-01814-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-021-01814-6