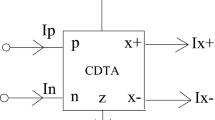
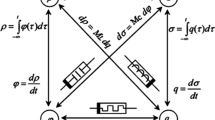
Abstract
Unlike the memristor element, the unavailability of any physical architectures for other memelements (memcapacitor and meminductor) has enhanced the significance of emulation of these elements through analogue circuit implementation. The proposed work aims to present a charge-controlled memelement emulator using a VDCC (voltage differencing current conveyor) and an OTA (operational transconductance Amplifier) with grounded passive elements. The developed emulator can be used to implement the behaviour of memristor and memcapacitor elements through the proper selection of passive elements. The proposed emulator circuit offers the advantage of adjustability of realized behaviour electronically and through employed passive elements as well. In the open research repertoire, the presented memelement emulator is the most optimized as compared to any other emulator ever reported for the realization of charge-dependent dual memelement functions with single-circuit architecture. It is due to the non-employment of any external memristor or bulky passive inductor and no use of any analogue multiplier in the circuit structure. The performance of the circuit has been checked through PSPICE-generated simulations for the use of 0.18um CMOS technology. The paper also discusses the application of realized memcapacitor in the modelling of Amoeba behaviour, and the results have been presented. We have also shown the commercial IC-based realization of the proposed memelement emulator and discussed the generated results through macro-model-based simulations as well as experimental.




































Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
https://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/data-sheets/AD844.pdf
M.T. Abuelma’atti, Z.J. Khalifa, A new memristor emulator and its application in digital modulation. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 80, 577–584 (2014)
M.T. Abuelma’atti, Z.J. Khalifa, A continuous-level memristor emulator and its application in a multivibrator circuit. AEU—Int. J. Electron. Commun. 69, 771–775 (2015)
K. Agashe, N. Sarwade, S. Joshi, P. Soman, Comprehensive study of current controlled memristor models. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 7, 1–6 (2016)
A.G. Alharbi, Z.J. Khalifa, M.E. Fouda, M.H. Chowdhury, A new simple emulator circuit for current controlled memristor. In 2015 IEEE Int. Conf. Electron. Circuits, Syst. (IEEE, 2015)
A.G. Alharbi, Z.J. Khalifa, M.E. Fouda, M.H. Chowdhury, Memristor emulator based on single CCII. In 2015 27th Int. Conf. Microelectron. (IEEE, 2015)
A.F. Arbel, L. Goldminz, Output stage for current-mode feedback amplifiers, theory and applications. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2, 243–255 (1992)
Y. Babacan, An operational transconductance amplifier-based memcapacitor and meminductor. Istanb. Univ.—J. Electr. Electron. Eng. 18, 36–38 (2018)
Y. Babacan, A. Yesil, F. Kacar, Memristor emulator with tunable characteristic and its experimental results. AEU—Int. J. Electron. Commun. 81, 99–104 (2017)
D. Biolek, Z. Biolek, V. Biolkova, SPICE modeling of memristive, memcapacitative and meminductive systems. In 2009 Eur. Conf. Circuit Theory Des. (IEEE, 2009).
D. Biolek, V. Biolková, Z. Kolka, J. Dobeš, Analog emulator of genuinely floating memcapacitor with piecewise-linear constitutive relation. Circuits, Syst. Signal Process. 35, 43–62 (2016)
D. Biolek, R. Senani, V. Biolkova, Z. Kolka, Active elements for analog signal processing: classification, review, and new proposals. Radioengineering 17, 15–32 (2008)
Z.G. Cam, H. Sedef, A new floating memristance simulator circuit based on second generation current conveyor. J. Circuits, Syst. Comput. 26, 1750029 (2017)
L. Chua, Memristor-the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 18, 507–519 (1971)
E. Demir, A. Yesil, Y. Babacan, T. Karacali, Operational transconductance amplifier-based electronically controllable memcapacitor and meminductor emulators. J. Circuits, Syst. Comput. 30, 2150222 (2021)
A.S. Elwakil, M.E. Fouda, A.G. Radwan, A simple model of double-loop hysteresis behavior in memristive elements. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 60, 487–491 (2013)
M.E. Fouda, A.G. Radwan, Charge controlled memristor-less memcapacitor emulator. Electron. Lett. 48, 1454–1455 (2012)
A. I. Hussein and M. E. Fouda, A simple MOS realization of current controlled memristor emulator. In 2013 25th Int. Conf. Microelectron. (IEEE, 2013).
H. Kim, M.P. Sah, C. Yang, S. Cho, L.O. Chua, Memristor emulator for memristor circuit applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 59, 2422–2431 (2012)
M. Konal, F. Kacar, Electronically tunable memcapacitor emulator based on operational transconductance amplifiers. J. Circuits, Syst. Comput. 30, 2150082 (2021)
M. Konal, F. Kacar, Y. Babacan, Electronically controllable memcapacitor emulator employing VDCCs. AEU—Int. J. Electron. Commun. 140, 153932 (2021)
Y. Liu, H.H.-C. Iu, Novel floating and grounded memory interface circuits for constructing mem-elements and their applications. IEEE Access 8, 114761–114772 (2020)
Y. Pershin, S. La Fontaine, M. Di Ventra, Memristive model of amoeba learning. Nat. Preced. 80, 021926 (2008)
Y.V. Pershin, M. Di Ventra, Emulation of floating memcapacitors and meminductors using current conveyors. Electron. Lett. 47, 243–244 (2011)
D. Prasad, A. Ahmad, A. Shukla, A. Mukhopadhyay, B.B. Sharma, M. Srivastava, Novel VDCC based low-pass and high-pass Ladder filters. In 2015 Annu. IEEE India Conf. (IEEE, 2015)
D. Prasad, D.R. Bhaskar, M. Srivastava, New single VDCC-based explicit current-mode SRCO employing all grounded passive components. Electron. ETF 18, 81–88 (2014)
S.S. Prasad, P. Kumar, R.K. Ranjan, Resistorless memristor emulator using CFTA and its experimental verification. IEEE Access 9, 64065–64075 (2021)
N. Raj, R.K. Ranjan, F. Khateb, M. Kumngern, Mem-elements emulator design with experimental validation and its application. IEEE Access 9, 69860–69875 (2021)
R.K. Ranjan, N. Raj, N. Bhuwal, F. Khateb, Single DVCCTA based high frequency incremental/decremental memristor emulator and its application. AEU—Int. J. Electron. Commun. 82, 177–190 (2017)
R.K. Ranjan, N. Rani, R. Pal, S.K. Paul, G. Kanyal, Single CCTA based high frequency floating and grounded type of incremental/decremental memristor emulator and its application. Microelectron. J. 60, 119–128 (2017)
R.K. Ranjan, S. Sagar, S. Roushan, B. Kumari, N. Rani, F. Khateb, High-frequency floating memristor emulator and its experimental results. IET Circuits, Devices Syst. 13, 292–302 (2019)
R.K. Ranjan, P.K. Sharma, R. Sagar, N. Raj, B. Kumari, F. Khateb, Memristor emulator circuit using multiple-output OTA and its experimental results. J. Circuits, Syst. Comput. 28, 1950166 (2019)
F.J. Romero, D.P. Morales, A. Godoy, F.G. Ruiz, I.M. Tienda-Luna, A. Ohata, N. Rodriguez, Memcapacitor emulator based on the Miller effect. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 47, 572–579 (2019)
F.J. Romero, A. Ohata, A. Toral-Lopez, A. Godoy, D.P. Morales, N. Rodriguez, Memcapacitor and meminductor circuit emulators: a review. Electronics 10, 1225 (2021)
C. Sánchez-López, L.E. Aguila-Cuapio, A 860kHz grounded memristor emulator circuit. AEU—Int. J. Electron. Commun. 73, 23–33 (2017)
C. Sánchez-López, M.A. Carrasco-Aguilar, C. Muñiz-Montero, A 16Hz–160kHz memristor emulator circuit. AEU—Int. J. Electron. Commun. 69, 1208–1219 (2015)
F. Setoudeh, M.M. Dezhdar, A new design and implementation of the floating-type charge-controlled memcapacitor emulator. Majlesi J. Telecommun. Devices 9, 1–15 (2020)
V.K. Sharma, M.S. Ansari, T. Parveen, Tunable memristor emulator using off-the-shelf components. Proc. Comput. Sci. 171, 1064–1073 (2020)
P.K. Sharma, R.K. Ranjan, F. Khateb, M. Kumngern, Charged controlled mem-element emulator and its application in a chaotic system. IEEE Access 8, 171397–171407 (2020)
A. Singh, S.K. Rai, VDCC-based memcapacitor/meminductor emulator and its application in adaptive learning circuit. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Electr. Eng. 45, 1151–1163 (2021)
M. Srivastava, D. Prasad, VDCC based dual-mode quadrature sinusoidal oscillator with outputs at appropriate impedance levels. Adv. Electr. Electron. Eng. 14, 168–177 (2016)
D.B. Strukov, G.S. Snider, D.R. Stewart, R.S. Williams, The missing memristor found. Nature 453, 80–83 (2008)
Z.G.Ç. Taşkıran, M. Sağbaş, U.E. Ayten, H. Sedef, A new universal mutator circuit for memcapacitor and meminductor elements. AEU—Int. J. Electron. Commun. 119, 153180 (2020)
M. Di Ventra, Y.V. Pershin, L.O. Chua, Circuit elements with memory: memristors, memcapacitors, and meminductors. Proc. IEEE 97, 1717–1724 (2009)
J. Vista, A. Ranjan, Design of memcapacitor emulator using DVCCTA. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1172, 012104 (2019)
J. Vista, A. Ranjan, Simple charge controlled floating memcapacitor emulator using DXCCDITA. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 104, 37–46 (2020)
F.Z. Wang, L.O. Chua, X. Yang, N. Helian, R. Tetzlaff, T. Schmidt, C. Li, J.M.G. Carrasco, W. Chen, D. Chu, Adaptive neuromorphic architecture (ANA). Neural Netw. 45, 111–116 (2013)
A. Yesil, Y. Babacan, Electronically controllable memcapacitor circuit with experimental results. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 68, 1443–1447 (2021)
A. Yeşil, Y. Babacan, F. Kaçar, A new DDCC based memristor emulator circuit and its applications. Microelectron. J. 45, 282–287 (2014)
A. Yesil, F. Kacar, H. Kuntman, New simple CMOS realization of voltage differencing transconductance amplifier and its RF filter application. Radioengineering 20, 632–637 (2011)
D. Yu, X. Zhao, T. Sun, H.H.C. Iu, T. Fernando, A simple floating mutator for emulating memristor, memcapacitor, and meminductor. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 67, 1334–1338 (2020)
F. Yuan, Y. Li, G. Wang, G. Dou, G. Chen, Complex dynamics in a memcapacitor-based circuit. Entropy 21, 188 (2019)
F. Yuan, G. Wang, X. Wang, Chaotic oscillator containing memcapacitor and meminductor and its dimensionality reduction analysis. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 27, 033103 (2017)
Q. Zhao, C. Wang, X. Zhang, A universal emulator for memristor, memcapacitor, and meminductor and its chaotic circuit. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 29, 013141 (2019)
Y.Y. Zhen, T. Heng, H.C. Guan, L.O. Chua, What are memristor, memcapacitor, and meminductor? IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 62, 402–406 (2015)
H. Zhiheng, L. Yingxiang, J. Li, Y. Juebang, Chaos in a charge-controlled memcapacitor circuit. In 2010 Int. Conf. Commun. Circuits Syst. (IEEE, 2010)
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhardwaj, K., Srivastava, M. New Multiplier-Less Compact Tunable Charge-Controlled Memelement Emulator Using Grounded Passive Elements. Circuits Syst Signal Process 41, 2429–2465 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-021-01895-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-021-01895-3