Abstract
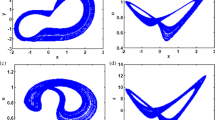
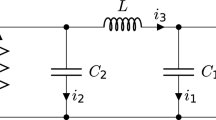
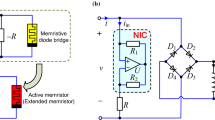
Nonlinear dynamical systems with symmetry have been studied extensively yielding rich and striking bifurcation patterns such as period-doubling sequence, merging crisis, crisis-induced intermittency, spontaneous symmetry breaking, and coexisting pairs of mutually symmetric attractors as well. However, very little is known unfortunately about the behavior of such systems in the presence of an explicit symmetry breaking perturbation. In this work, we evaluate the impact of an explicit symmetry break on the dynamics of a fourth-order autonomous memristive chaotic circuit. The symmetry break is obtained by assuming different electrical properties for the two pairs of diodes forming the generalized memristor. Thus, the generalized memristor exhibits an asymmetric pinched hysteresis loop which induces the asymmetry of the whole jerk circuit. We demonstrate that the symmetry break induces new and extremely complex patterns including critical phenomena, coexisting bubbles of different periodicity, multiple coexisting nonsymmetric attractors, just to name a few. These features are highlighted by using phase portraits, basins of attraction, bifurcation diagrams, and plots of largest Lyapunov exponents as main tools. A series of laboratory experimental tests are carried out to support the theoretical analysis.






















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
S.P. Adhikari, M.P. Sah, H. Kim, L.O. Chua, Three fingerprints of memristor. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regular Papers 60(11), 3008–3021 (2013)
B. Bao, L. Xu, N. Wang, H. Bao, Q. Xu, M. Chen, Third-order RLCM-four-elements-based chaotic circuit and its coexisting bubbles. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 94, 26–35 (2018)
B. Bao, J.P. Xu, G.H. Zhou, Z.H. Ma, L. Zou, Chaotic memristive circuit: equivalent circuit realization and dynamical analysis. Chin. Phys. B 20, 120502 (2011)
B. Bao, J. Yu, F. Hu, Z. Liu, Generalized memristor consisting of diode bridge with first order parallel RC filter. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 24(11), 1450143 (2014)
B. Bao, L. Zhong, J.P. Xu, Transient chaos in smooth memristor oscillator. Chin. Phys. B 19(3), 030510 (2010)
B. Bao, X. Zou, Z. Liu, F. Hu, Generalized memory element and chaotic memory system. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 23(8), 1350135 (2013)
M. Bier, T.C. Bountis, Remerging Feigenbaum trees in dynamical systems. Phys. Lett. A 104, 239–244 (1984)
S.R. Bishop, A. Sofroniou, P. Shi, Symmetry-breaking in the response of the parameterically excited pendulum model. Chaos Solitons Fractals 25(2), 27–264 (2005)
R.K. Budhathoki, M.P. Sah, D. Yang, H. Kim, L.O. Chua, Transient behavior of multiple memristor circuits based on flux charge relationship. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 24(2), 1430006 (2014)
A. Buscarino, L. Fortuna, M. Frasca, L.V. Gambuzza, A gallery of chaotic oscillators based on HP memristor. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 23(5), 1330015 (2013)
H. Cao, Z. Jing, Chaotic dynamics of Josephson equation driven by constant and ac forcings. Chaos Solitons Fractals 12, 1887–1895 (2001)
H. Cao, J.M. Seoane, M.A.F. Sanjuan, Symmetry-breaking analysis for the general Helmholtz-Duffing oscillator. Chaos Solitons Fractals 34, 197–212 (2007)
I. Carro-Pérez, C. Sánchez-López, H.G. González-Hernández, Experimental verification of a memristive neural network. Nonlinear Dyn. 93(4), 1823–1840 (2018)
M. Chen, M. Li, Q. Yu, B. Bao, Q. Xu, J. Wang, Dynamics of self-excited and hidden attractors in generalized memristor-based Chua’s circuit. Nonlinear Dyn. 81(1–2), 215–226 (2015)
M. Chen, J. Yu, Q. Yu, C. Li, B. Bao, A memristive diode bridge-based canonical Chua’s circuit. Entropy 16(12), 6464–6476 (2014)
L. Chua, If it’s pinched it’s a memristor. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 29(10), 1040 (2014)
L.O. Chua, Memristor-The missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuits Theory 18(5), 507–519 (1971)
L.O. Chua, S.M. Kang, Memristive devices and systems. Proc. IEEE 64(2), 209–223 (1976)
L. Chua, G.C. Sirakoulis, A. Adamatzky, Handbook of Memristor Networks (Springer, Cham, 2019)
F. Corinto, A. Ascoli, Memristive diode bridge with LCR filter. Electron. Lett. 48(14), 824–825 (2012)
S.K. Dana, S. Chakraborty, G. Ananthakrishna, Homoclinic bifurcation in Chua’s circuit. Pramana J. Phys. 64(3), 44344 (2005)
S.P. Dawson, Geometric mechanism for antimonotonicity in scalar maps with two critical points. Phys. Rev. E 48, 1676–1680 (1993)
P. Georgios, V. Ioannis, V. Nikolaos, C.S. Georgios, Boolean logic operations and computing circuits based on memristors. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst.-II Exp. Briefs 61, 972–976 (2014)
M.P. Hanias, G. Giannaris, A. Spyridakis, A. Rigas, Time series analysis in chaotic diode resonator circuit. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 27(2), 569–573 (2006)
M. Henrich, T. Dahms, V. Flunkert, S.W. Teitsworth, E. Scholl, Symmetry breaking transitions in networks of nonlinear circuits elements. New J. Phys. 12, 113030 (2010)
M. Hua, S. Yang, Q. Xu, M. Chen, H. Wu, B. Bao, Forward and reverse asymmetric memristor-based jerk circuits. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 123, 153294 (2020)
M. Itoh, L.O. Chua, Memristor oscillators. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 18, 3183–3206 (2008)
C. Kahllert, The effects of symmetry breaking in Chua’s circuit and related piecewise-linear dynamical system. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 3(4), 963–979 (1993)
L. Kamdjeu Kengne, H.T. Kamdem Tagne, A.N. Kengnou Telem, J.R. Mboupda Pone, J. Kengne, A broken symmetry approach for the modeling and analysis of antiparallel diodes-based chaotic circuits: a case study. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 104, 205–227 (2020)
L.K. Kengne, J.R.M. Pone, H.T.K. Tagne, J. Kengne, Dynamics, control and symmetry breaking aspects of a single Opamp-based autonomous LC oscillator. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 118, 153146 (2020)
V.K. Tamba, H.B. Fotsin, J. Kengne, E.B.M. Ngouonkadi, P.K. Talla, Emergence of complex dynamical behaviors in improved Colpitts oscillators: antimonotonicity, coexisting attractors, and metastable chaos. Int. J. Dyn. Control 5(3), 395–406 (2017)
J. Kengne, A.N. Negou, Z.T. Njitacke, Antimonotonicity, chaos and multiple attractors in a novel autonomous jerk circuit. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 27(07), 1750100 (2017)
J. Kengne, A.N. Negou, D. Tchiotsop, Antimonotonicity, chaos and multiple attractors in a novel autonomous memristor-based jerk circuit. Nonlinear Dyn. 88(4), 2589–2608 (2017)
J. Kengne, Z.N. Tabekoueng, H.B. Fotsin, Coexistence of multiple attractors and crisis route to chaos in autonomous third order Duffing-Holmes type chaotic oscillators. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 36, 29–44 (2016)
L.J. Kocarev, K.S. Halle, K. Eckert, L.O. Chua, Experimental observation of antimonotonicity in Chua’s Circuit. Int J Bifurc. Chaos 3, 1051–1055 (1993)
G.A. Leonov, N.V. Kuznetsov, Hidden attractors in dynamical systems, From hidden oscillations in Hilbert Kolmogorov, Aizerman, and Kalman problems to hidden chaotic attractor in Chua circuits. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 23(01), 1330002 (2013)
G.A. Leonov, N.V. Kuznetsov, T.N. Mokaev, Homoclinic orbits, and self-excited and hidden attractors in a Lorenz-like system describing convective fluid motion. Eur. Phys. J. Spl. Topics 224, 1421–1458 (2015)
Z.H. Lin, H.X. Wang, Image encryption based on chaos with PWL memristor in Chua’s circuit In: International conference on communications, circuits and systems, pp. 964–968 (2009)
B. Muthuswamy, Implementing memristor based chaotic circuits. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 20, 1335–1350 (2010)
B. Muthuswamy, L.O. Chua, Simplest chaotic circuit. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 20(5), 1567–1580 (2010)
A.H. Nayfeh, B. Balachandran, Applied Nonlinear Dynamics: Analytical, Computational and Experimental Methods (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1995)
Z.T. Njitacke, H.B. Fotsin, A.N. Negou, D. Tchiotsop, Coexistence of multiple attractors and crisis route to chaos in a novel memristive diode bridge-based Jerk circuit. Chaos Solitons Fractals 91, 180–197 (2016)
V.T. Pham, S. Vaidyanathan, E. Tlelo-Cuautle, T. Kapitaniak, Memory circuit elements: complexity, complex systems, and applications. Complexity (2019). https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4936123
V.T. Pham, C. Volos, S. Jafari, S. Vaidyanathan, Hidden hyperchaotic attractor in a novel simple memristive neural network. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. Rapid Commun. 8(11–12), 1157–1163 (2014)
M.P. Sah, C. Yang, H. Kim, B. Muthuswamy, J. Jevtic, L. Chua, A generic model of memristors with parasitic components. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 62(3), 891–898 (2015)
C. Sánchez-López, A 500 kHz frequency-shift keying modulator based on memductor. Analog Integr. Circ. Sig. Process 100(3), 527–536 (2019)
C. Sánchez-López, V.H. Carbajal-Gómez, M.A. Carrasco-Aguilar, F.E. Morales-López, PID controller design based on memductor. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 101, 9–14 (2019)
C. Sánchez-López, L.E. Aguila-Cuapio, A 860 kHz grounded memristor emulator circuit. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 73, 23–33 (2017)
C. Sánchez-López, J. Mendoza-Lopez, M.A. Carrasco-Aguilar, C. Muñiz-Montero, A floating analog memristor emulator circuit. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Expr. Briefs 61(5), 309–313 (2014)
J.Y. Seok, S.J. Song, J.H. Yoon, K.J. Yoon, T.H. Park, D.E. Kwon, H. Lim, G.H. Kim, D.S. Jeong, C.S. Hwang, A review of three-dimensional resistive switching cross-bar array memories from the integration and materials property points of view. Adv. Funct. Mater. 24, 5316–5339 (2014)
A. Silva-Juárez, E. Tlelo-Cuautle, L.G. de la Fraga, R. Li, Optimization of the Kaplan-Yorke dimension in fractional-order chaotic oscillators by metaheuristics. Appl. Math. Comput. 394, 125831 (2021)
A. Sofroniou, S.R. Bishop, Breaking the symmetry of the parametrically excited pendulum. Chaos Solitons Fractals 28, 673–681 (2006)
S.H. Strogatz, Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos (Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA, 1994)
D.W. Sukov, M.E. Bleich, J. Gauthier, J.E.S. Socolar, Controlling chaos in a fast diode resonator using extended time-delay autosynchronization: experimental observations and theoretical analysis. Chaos 7, 560–576 (1997)
K. Thamilmaran, M. Lakshmanan, Classification of bifurcations and routes to chaos in a variant of Murali–Lakshmanan–Chua circuit. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 12(04), 783–813 (2002)
G.Y. Wang, J.L. He, F. Yuan, C.J. Peng, Dynamical behaviour of a TiO2 memristor oscillator. Chin. Phys. Lett. 30, 110506 (2013)
A. Wolf, J.B. Swift, H.L. Swinney, J.A. Wastano, Determining Lyapunov exponents from time series. Phys. D 16, 285–317 (1985)
H. Wu, J. Zhou, M. Chen, Q. Xu, B. Bao, DC-offset induced asymmetry in memristive diode-bridge-based Shinriki oscillator. Chaos Solitons Fractals 154, 111624 (2021)
L. Zhou, C. Wang, X. Zhang, W. Yao, Various attractors, coexisting attractors and antimonotonicity in a simple fourth-order memristive twin-T oscillator. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 28(04), 1850050 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work is partially funded by Centre for Nonlinear Systems, Chennai Institute of Technology, India, vide funding number CIT/CNS/2022/RD/006. The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their comments and suggestions that helped to greatly improve the content of the present manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kengne, L.K., Ramadoss, J., Kengne, J. et al. Symmetry Breaking-Induced Dynamics for a Fourth-Order Memristor-Based Chaotic Circuit. Circuits Syst Signal Process 41, 3706–3738 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-022-01976-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-022-01976-x