Abstract
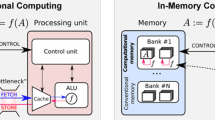
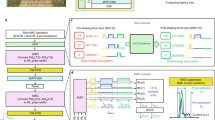
The von Neumann computing architecture faces considerable challenges (e.g., high throughput and improving energy efficiency) in developing artificial intelligence (AI) edge devices. In-memory computation (IMC) is a new computing paradigm to improve the energy efficiency and the throughput of dot product operations for AI edge devices. In this paper, a 6T2M hybrid SRAM (HSRAM)-based IMC macro is proposed that supports non-volatile storage and in-memory dot product (IMDP) operation. The HSRAM bit cell is designed using NMOS and memristor devices, which reduces the area overhead and improves the energy efficiency compared to prior SRAM-based IMC macro due to non-volatile storage capability. A 128 x 128 IMC macro based on HSRAM is designed in 65 nm technology. For normal memory operation, the read margin of the proposed HSRAM bit cell is improved by 84.1% compared to 4T2R ReRAM, and the write margin is enhanced by 44.01% compared to 8T SRAM. For IMDP operation, it can compute 128 parallel dot products on binary input and binary weight values with 500 MHz frequency and achieves the energy efficiency of 134.5 TOPS/W at VDD = 1V. According to Monte Carlo simulations, the IMDP operation has a standard deviation of 4.24 percent in accumulation, which equates to a classification accuracy of 96.71% on the MNIST dataset and an 82.51% on the CIFAR-10 dataset.





















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
With appropriate request, the relevant author will make accessible the datasets used and/or created during the present work.
References
A. Agrawal, A. Jaiswal, C. Lee, K. Roy, X-SRAM: enabling in-memory Boolean computations in CMOS static random access memories. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 65(12), 4219–4232 (2018)
A. Biswas, A.P. Chandrakasan, CONV-SRAM: an energy-efficient SRAM with in-memory dot-product computation for low-power convolutional neural networks. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 54(1), 217–230 (2019)
P.F. Chiu, M.F. Chang, C.W. Wu, C.H. Chuang, S.S. Sheu, Y.-S. Chen, M.J. Tsai, Low store energy, low VDDmin, 8T2R nonvolatile latch and SRAM with vertical-stacked resistive memory (Memristor) devices for low power mobile applications. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 47(6), 1483–1496 (2012)
L. Chua, Memristor-the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuits Theory 18(5), 507–519 (1971)
M.F. Chang, L.Y. Huang, W.Z. Lin, Y.N. Chiang, C.C. Kuo, C.H. Chuang, K.H. Yang, H.J. Tsai, T.F. Chen, S.S. Sheu, A ReRAM-based 4T2R nonvolatile TCAM using rc-filtered stress-decoupled scheme for frequent-OFF instant-ON search engines used in IoT and big-data processing. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 51(11), 2786–2798 (2016)
W.H. Chen, K.X. Li, W.Y. Lin, K.H. Hsu, P.Y. Li, C.H. Yang, C.X. Xue, E.Y. Yang, Y.K. Chen, Y.S. Chang, T.H. Hsu, Y.C. King, C.J. Lin, R.S. Liu, C.C. Hsieh, K.T. Tang, M.F. Chang, A 65nm 1Mb nonvolatile computing-in-memory ReRAM macro with sub-16ns multiply-and-accumulate for binary DNN AI edge processors. in 2018 IEEE International Solid State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), IEEE
Y. Chen, L. Lu, B. Kim, T.T.H. Kim, A reconfigurable 4T2R ReRAM computing in-memory macro for efficient edge applications. IEEE Open J. Circ. Syst. 2, 210–222 (2021)
Q. Dong, S. Jeloka, M. Saligane, Y. Kim, M. Kawaminami, A. Harada, S. Miyoshi, M. Yasuda, D. Blaauw, D. Sylvester, A 4+ 2T SRAM for searching and in-memory computing With 0.3-V \(V_{DDmin}\). IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 53, 1006–1015 (2018)
K. Eshraghian, K.R. Cho, O. Kavehei, S.K. Kang, D. Abbott, S.M.S. Kang, Memristor MOS content addressable memory (MCAM): Hybrid architecture for future high performance search engines. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. VLSI Syst. 19(8), 407–1417 (2010)
R. Guo, Y. Liu, S. Zheng, S. Y. Wu, P. Ouyang, W. S. Khwa, X. Chen, J. J. Chen, X. Li, L. Liu, M. F. Chang, S. Wei, S. Yin, A 5.1pJ/Neuron 127.3us/Inference RNN-based speech recognition processor using 16 computing-in-memory SRAM macros in 65nm CMOS. in 2019 Symposium on VLSI Circuits,IEEE, C120-C121 (2019)
M. Horowitz, 1.1 Computing’s energy problem (and what we can do about it), in 2014 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference Digest of Technical Papers (ISSCC), IEEE, 10–14 (2014)
M.Y. Hsu, C.F. Liao, Y.H. Shih, C.J. Lin, Y.C. King, A RRAM integrated 4T SRAM with self-inhibit resistive switching load by pure CMOS logic process. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 12(1), 1–9 (2017)
S. Jeloka, N.B. Akesh, D. Sylvester, D. Blaauw, A 28 nm configurable memory (TCAM/BCAM/SRAM) using push-rule 6T bit cell enabling logic-in-memory. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 51(4), 1009–1021 (2016)
C.J. Jhang, C.X. Xue, J.M. Hung, F.C. Chang, M.F. Chang, Challenges and trends of SRAM-based computing-in-memory for AI edge devices. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 68(5), 1773–1786 (2021)
S. Kvatinsky, E.G. Friedman, A. Kolodny, U.C. Weiser, Team: threshold adaptive memristor model. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 60(1), 211–221 (2013)
M. Kang, S.K. Gonugondla, A. Patil, N.R. Shanbhag, A multi-functional in-memory inference processor using a standard 6t sram array. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 53(2), 642–655 (2018)
S. Kvatinsky, K. Talisveyberg, D. Fliter, E. G. Friedman, A. Kolodny, U. C. Weiser, Verilog-A for memristor models, CCIT Technical Report, Textbf801 (2011)
W. S. Khwa, J. J. Chen, J. F. Li, X. Si, E. Y. Yang, X. Sun, R. Liu, P. Y. Chen, Q. Li, S. Yu, M. F. Chang, A 65nm 4Kb algorithm-dependent computing-in-memory SRAM unit-macro with 2.3ns and 55.8TOPS/W fully parallel product-sum operation for binary DNN edge processors, in 2018 IEEE International Solid State Circuits Conference (ISSCC),IEEE, 496–498 (2018)
R. Liu, X. Peng, X. Sun, W. S. Khwa, X. Si, J. J. Chen, J. F. Li, M. F. Chang, S. Yu, Parallelizing SRAM arrays with customized bit-cell for binary neural networks, in 2018 55th ACM/ESDA/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC),IEEE, 1–6 (2018)
L. Lu, T. Yoo, V.L. Le, T.T.H. Kim, A 0.506-pJ 16-kb 8T SRAM with vertical read wordlines and selective dual split power lines. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. VLSI Syst. 28(6), 1345–1356 (2020)
S. Majumdar, S. K. Kingra, M. Suri, M. Tikyani, Hybrid CMOS-OxRAM based 4T-2R NVSRAM with efficient programming scheme, in 2016 16th Non-Volatile Memory Technology Symposium (NVMTS), IEEE, 1–4 (2016)
Y. Ma, Y. Du, L. Du, J. Lin, Z. Wang, In-memory computing: the next-generation AI computing paradigm, in Proceedings of the 2020 on Great Lakes Symposium on VLSI, ser. GLSVLSI ’20, Association for Computing Machinery, 265–270 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1145/3386263.3407588
S. Majumdar, Single bit-line differential sensing based real-time NVSRAM for low power applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Exp. Briefs 64(7), 2623–2627 (2021)
V.T. Nguyen, J.S. Kim, J.W. Lee, 10T SRAM computing-in-memory macros for binary and multibit mac operation of DNN edge processors. IEEE Access 9, 262–276 (2021)
A.K. Rajput, M. Pattanaik, G. Kaushal, Local bit-line shared pass-gate 8T SRAM based energy efficient and reliable in-memory computing architecture. Microelectron. J. 129, 105569 (2022)
A. K. Rajput , M. Pattanaik, Energy efficient 9T SRAM with R/W margin enhanced for beyond Von-Neumann computation, in 2020 24th International Symposium on VLSI Design and Test (VDAT), IEEE, 1–4 (2020)
A. Sebastian, T. Tuma, N. Papandreou, M. Le Gallo, L. Kull, T. Parnell, E. Eleftheriou, Temporal correlation detection using computational phase-change memory. Nat. Commun. 8(1), 1115 (2017)
X. Si, W.S. Khwa, J.J. Chen, J.F. Li, X. Sun, R. Liu, S. Yu, H. Yamauchi, Q. Li, M.F. Chang, A dual-split 6T SRAM-based computing-in-memory unit-macro with fully parallel product-sum operation for binarized DNN edge processors. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 66(11), 4172–4185 (2019)
V. Sharma, H. Kim, T.T.H. Kim, A 64 Kb reconfigurable full-precision digital ReRAM-based compute-in-memory for artificial intelligence applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 69(8), 3284–3296 (2022)
D. Strukov, M. Prezioso, F. Merrik-Bayat, B. Hoskins, Memristors and method for fabricating memristors, US Patent 9899450 (2018)
J. Singh, B. Raj, Comparative analysis of memristor models and memories design. J. Semicond. 39(7), 074006 (2018)
T. Yoo, H. Kim, Q. Chen, T. T. H. Kim, B. Kim, A logic compatible 4T dual embedded DRAM array for in-memory computation of deep neural networks, in 2019 IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Low Power Electronics and Design (ISLPED),IEEE, 1–6 (2019)
C. Yu, T. Yoo, T. T. H. Kim, K. C. Tshun Chuan, B. Kim, A 16K current-based 8T SRAM compute-in-memory macro with decoupled read/write and 1-5bit column ADC, in 2020 I EEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC),IEEE, 1–4 (2020)
S. Yin, Z. Jiang, J.S. Seo, M. Seok, XNOR-SRAM: in-memory computing SRAM macro for binary/ternary deep neural networks. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 55(6), 1733–1743 (2020)
Y. Zha, E. Nowak, J. Li, Liquid silicon: a nonvolatile fully programmable processing-in-memory processor with monolithically integrated ReRAM for big data/machine learning applications, in 2019 Symposium on VLSI Circuits,IEEE, C206–C207 (2019)
J. Zhang, Z. Wang, N. Verma, In-memory computation of a machine-learning classifier in a standard 6T SRAM array. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 52(4), 915–924 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The tool used in this work is supported by SMDP-C2SD project MeitY, Government of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rajput, A.K., Tiwari, A.K. & Pattanaik, M. An Energy-Efficient Hybrid SRAM-Based In-Memory Computing Macro for Artificial Intelligence Edge Devices. Circuits Syst Signal Process 42, 3589–3616 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-022-02284-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-022-02284-0