Abstract
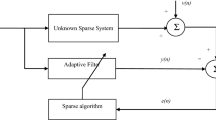
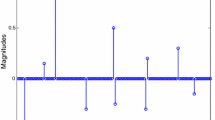
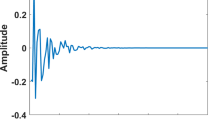
A new LMS algorithm is proposed to improve the accuracy of the sparse system identification with impulse interference. The algorithm adopts a scaler to filter impulse interference, the scalar is also used for identifying sparse systems. The adaptive iteration can avoid significant changes since the abrupt impulsive interference in the channel estimation. Furthermore, the proposed method searches the sparse solution by considering the system sparsity and using an approximated \(\ell _0\) norm constraint. Because the proposed method combines sparse constraint and impulse interference, it gradually adjusts the step size according to the gradient. The effectiveness and superiority of the proposed algorithm are confirmed for sparse system identification with impulse interference in simulations.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated. This article describes entirely theoretical research during the current study.
References
R.C. de Lamare, R. Sampaio-Neto, Sparsity-aware adaptive algorithms based on alternating optimization and shrinkage. IEEE Signal Process. 21(2), 225–229 (2014)
D.L. Duttweiler, Proportionate normalized least-mean-squares adaptation in echo cancelers. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 8(5), 508–518 (2000)
Y. Gu, J. Jin, S. Mei, \(\ell _0\) norm constraint LMS algorit hm for sparse system identification. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 16(9), 774–777 (2009)
S.H. Hosseini, M.G. Shayesteh, A. Ebrahimi, Adaptive sparse system identification in compressed space. Wire. Per. Commun. 96(1), 925–937 (2017)
F. Huang, J. Zhang, S. Zhang, NLMS algorithm based on a variable parameter cost function robust against impulsive interferences. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II, Exp. Briefs 64(5), 600–604 (2017)
J. Jin, Y. Gu, S. Mei, A stochastic gradient approach on compressive sensing signal reconstruction based on adaptive filtering framework. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 4(2), 409–420 (2010)
K. Kumar, R. Pandey, M.L.N.S. Karthik, S.S. Bhattacharjee, N.V. George, Robust and sparsity-aware adaptive filters: a review. Signal Process. 189, 1–25 (2021)
L. Luo, W.Z. Zhu, An optimized zero-attracting LMS algorithm for the identification of sparse system. IEEE-ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. 30, 3060–3073 (2022)
Q. Nasir, Wireless channel tracking based on optimum predictive LMS. Wire. Per. Commun. 48(4), 511–519 (2009)
M. S. Salman, F. El-Sayed, A. Youssef, A sparse variable step-size LMS algorithm for impulsive noise, 2019 3rd International Conference on Bio-engineering for Smart Technologies (BioSMART). 1–4(2019)
K. Shi, P. Shi, Convergence analysis of sparse LMS algorithms with \(\ell _1\)-norm penalty based on white input signal. Signal Process. 90(12), 3289–3293 (2010)
I. Song, P. Park, R.W. Newcomb, A normalized least mean squares algorithm with a step-size scaler against impulsive measurement noise. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II, Exp. Briefs 60(7), 442–445 (2013)
G. Su, J. Jin, Y. Gu, J. Wang, Performance analysis of \(\ell _0\) norm constraint least mean square algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 60(5), 2223–2235 (2012)
G. Wang, H. Zhao, P. Song, Robust variable step-size reweighted zero-attracting least mean M-estimate algorithm for sparse system identification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Exp. Briefs 67(6), 1149–1153 (2020)
F.Y. Wu, F. Tong, Non-uniform norm constraint LMS algorithm for sparse system identification. IEEE Commun. Lett. 17(2), 385–388 (2013)
F.Y. Wu, K. Yang, R. Duan, T. Tian, Compressive sampling and reconstruction of acoustic signal in underwater wireless sensor networks. IEEE Sens. J. 18(14), 5876–5884 (2018)
F.Y. Wu, K. Yang, F. Tong, T. Tian, Compressed sensing of delay and Doppler spreading in underwater acoustic channels. IEEE Access 6, 36031–36038 (2018)
J. Zeng, Y. Lin, L. Shi, A normalized least mean squares algorithm based on the arctangent cost function robust against impulsive interference. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 35(8), 3040–3047 (2015)
Y. Zong, J. Ni, Cluster-sparsity-induced affine projection algorithm and its variable step-size version. Signal Process 195, 1–6 (2022)
Y. Zou, S.C. Chan, T.S. Ng, A recursive least M-estimate (RLM) adaptive filter for robust filtering in impulse noise. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 7(11), 324–326 (2000)
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 62171369,61701405).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, FY., Song, YC. & Peng, R. A Scaled LMS Algorithm for Sparse System Identification with Impulsive Interference. Circuits Syst Signal Process 42, 4432–4441 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-023-02307-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-023-02307-4