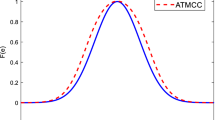
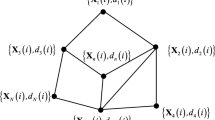
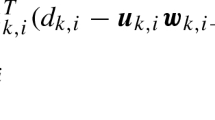Abstract
Distributed estimation algorithms, when based on the mean-square error criterion, often encounter steady-state misalignment in scenarios where the adaptive network experiences impulsive noise. Addressing this challenge, this paper introduces the diffusion combinatoric correntropy algorithm, which employs the combinatoric correntropy as its cost function. Leveraging the inherent robustness of the combinatoric correntropy cost function, this algorithm effectively mitigates the negative impacts caused by impulse noise. A comprehensive analysis, including experimental simulations, is conducted to evaluate the performance of the diffusion combinatoric maximum correntropy criterion algorithm. The simulation outcomes demonstrate that the proposed algorithm surpasses the diffusion maximum correntropy criterion algorithm in terms of convergence speed and steady-state performance. These simulation results align closely with the theoretical analysis, further validating the effectiveness of the diffusion combinatoric correntropy algorithm.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article. Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
M.S.E. Abadi, M.S. Shafiee, Distributed estimation over an adaptive diffusion network based on the family of affine projection algorithms. IEEE Trans Signal Inf Process over Netw 5(2), 234–247 (2018)
F Albu, C Paleologu, J Benesty. A low complexity proportionate affine projection algorithm for echo cancellation. 2010 18th European signal processing conference. IEEE. 6–10(2010)
S. Ashkezari-Toussi, H. Sadoghi-Yazdi, Robust diffusion LMS over adaptive networks. Signal Process. 158, 201–209 (2019)
A. Bajaj, S. Kumar, Design of ECG denoising digital filter under α-stable noisy environment based on morphological signal processing. Circuit Syst Signal Process. 43(5), 3180–3211 (2024)
F.S. Cattivelli, C.G. Lopes, A.H. Sayed, Diffusion recursive least-squares for distributed estimation over adaptive networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 56(5), 1865–1877 (2008)
F. Chen, X. Li, S. Duan, Diffusion generalized maximum correntropy criterion algorithm for distributed estimation over multitask network. Digital Signal Process. 81, 16–25 (2018)
B.L.J. ChenXingLiang, Steady-state mean-square error analysis for adaptive filtering under the maximum correntropy criterion. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 21(7), 880–884 (2014)
B. Chen, L. Xing, H. Zhao, Generalized correntropy for robust adaptive filtering. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 64(13), 3376–3387 (2016)
F. Chen, T. Shi, S. Duan, Diffusion least logarithmic absolute difference algorithm for distributed estimation. Signal Process. 142, 423–430 (2018)
S. Guan, Q. Cheng, Y. Zhao, Diffusion adaptive filtering algorithm based on the fair cost function. Sci rep 11(1), 19715 (2021)
S. Guan, C. Meng, B. Biswal, Diffusion-probabilistic least mean square algorithm. Circuits Syst Signal Process. 40, 1295–1313 (2021)
S. Guan, Y. Zhao, L. Wang, A distributed adaptive algorithm based on the asymmetric cost of error functions. Circuits Syst Signal Process. 42(10), 5811–5837 (2023)
Y. Guo, B. Ma, Y. Li, A kernel-width adaption diffusion maximum correntropy algorithm. IEEE Access. 8, 33574–33587 (2020)
H.J. Hadi, Y. Cao, K.U. Nisa, A comprehensive survey on security, privacy issues and emerging defence technologies for UAVs. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 213, 103607 (2023)
Y. Huo, T. Xu, Y. Qi, A family of robust diffusion adaptive filtering algorithms based on the Tanh framework. Circuits Syst Signal Process. 43, 1938–1956 (2024)
Y. Huo, T. Xu, Y. Xu, Diffusion robust algorithm based on inverse hyperbolic sine and generalized Correntropy. Digital Signal Process. 144, 104289 (2024)
C.T. Kelley, Iterative methods for optimization. SIAM J. Optim. (1999). https://doi.org/10.1137/1.9781611970920
M. Korki, H. Zayyani, Weighted diffusion continuous Combinatoric p-norm algorithm for distributed estimation in non-uniform noise environment. Signal Process. 164, 225–233 (2019)
R. Kranthi, A. Kar, M.G. Christensen, A family of Swish diffusion strategy based adaptive algorithms for distributed active noise control. IEEE Open J Signal Process 5, 503 (2024)
Z. Li, S. Guan, Diffusion normalized Huber adaptive filtering algorithm. J. Franklin Inst. 355(8), 3812–3825 (2018)
X. Li, M. Feng, F. Chen, Robust distributed estimation based on a generalized correntropy logarithmic difference algorithm over wireless sensor networks. Signal Process. 177, 107731 (2020)
X. Long, H. Zhao, X. Hou, A novel combinatoric correntropy algorithm: properties and its performance analysis. IEEE Trans Circuit Syst II Express Brief. 69(12), 5184–5188 (2022)
X. Long, H. Zhao, X. Hou, A novel widely-linear complex-valued diffusion VSS-LMS algorithm for distributed network and its performance analysis. Circuits Syst Signal Process (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-024-02769-0
L. Lu, H. Zhao, W. Wang, Performance analysis of the robust diffusion normalized least mean ${p} $-power algorithm. IEEE Trans. Circuit Syst. II Express Brief. 65(12), 2047–2051 (2018)
C.G. Lopes, A.H. Sayed, Diffusion least-mean squares over adaptive networks: formulation and performance analysis. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 56(7), 3122–3136 (2008)
W. Ma, B. Chen, J. Duan, Diffusion maximum correntropy criterion algorithms for robust distributed estimation. Digital Signal Process. 58, 10–19 (2016)
M. Nautiyal, S.S. Bhattacharjee, N.V. George, Low complexity and robust diffusion affine projection algorithms for distributed estimation. IEEE Trans. Circuit Syst. II Express Brief. 69(3), 1952–1956 (2021)
M. Nautiyal, S.S. Bhattacharjee, N.V. George, Robust and sparse aware diffusion adaptive algorithms for distributed estimation. IEEE Trans. Circuit Syst. II Express Briefs 69(1), 239–243 (2021)
J. Ni, Diffusion sign subband adaptive filtering algorithm for distributed estimation. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 22(11), 2029–2033 (2015)
J. Ni, J. Chen, X. Chen, Diffusion sign-error LMS algorithm: Formulation and stochastic behavior analysis. Signal Process. 128, 142–149 (2016)
L. Peng, T. Zhang, S. Wang, Diffusion adagrad minimum kernel risk sensitive mean p-power loss algorithm. Signal Process. 202, 1938–1956 (2024)
Z. Qing, J. Ni, J. Chen, Diffusion least mean kurtosis algorithm and its performance analysis. Inf. Sci. 638, 118982 (2023)
S. Lv, H. Zhao, Robust diffusion recursive least M-estimate adaptive filtering and its performance analysis. Circuits Syst Signal Process. 42(8), 4929–4952 (2023)
A.N. Sadigh, H. Zayyani, A proportionate robust diffusion recursive least exponential hyperbolic cosine algorithm for distributed estimation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 69(4), 2381–2385 (2022)
S.P. Talebi, S. Werner, D.P. Mandic, Distributed adaptive filtering of alpha-stable signals. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 25(10), 1450–1454 (2018)
F. Wang, Y. He, S. Wang, Maximum total correntropy adaptive filtering against heavy-tailed noises. Signal Process. 141, 84–95 (2017)
Y. Wang, Y. Li, F. Albu, Group-constrained maximum correntropy criterion algorithms for estimating sparse mix-noised channels. Entropy 19(8), 432 (2017)
F. Wen, Diffusion least-mean P-power algorithms for distributed estimation in alpha-stable noise environments. Electron. Lett. 49(21), 1355–1356 (2013)
Y. Yu, H. Zhao, W. Wang, Robust diffusion Huber-based normalized least mean square algorithm with adjustable thresholds. Circuits Syst Signal Process. 39, 2065–2093 (2020)
S. Zandi, M. Korki, Diffusion maximum versoria criterion algorithms robust to impulsive noise. Digital Signal Process. 126, 103490 (2022)
H. Zayyani, M. Korki, Adaptive-width generalized correntropy diffusion algorithm for secure distributed estimation. IEEE Trans. Circuit Syst. II Express Briefs 70(7), 2700–2704 (2023)
J. Zhang, J. Tian, A.M. Alcaide, Lifetime extension approach based on the Levenberg–Marquardt neural network and power routing of DC–DC converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 38(8), 10280–10291 (2023)
J. Zhang, J. Tian, P. Yan, Multi-hop graph pooling adversarial network for cross-domain remaining useful life prediction: a distributed federated learning perspective. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 244, 109950 (2024)
H. Zhao, Y. Chen, S. Lv, Robust diffusion total least mean M-estimate adaptive filtering algorithm and its performance analysis. IEEE Trans. Circuit Syst. II Express Brief. 69(2), 654–658 (2021)
Z. Zheng, Z. Liu, M. Huang, Diffusion least mean square/fourth algorithm for distributed estimation. Signal Process. 134, 268–274 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This research was jointly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32360434), and the Gansu Provincial Department of Education: Industry Support Program Project, China (2023CYZC-11).
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China,32360434,shengwei Wang,Gansu Provincial Department of Education: Industry Support Program Project,2023CYZC-11,shengwei Wang
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors disclosed on relevant relationships.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Xu, Y., Xu, T. et al. Diffusion Combinatoric Correntropy Algorithm for Distributed Estimation. Circuits Syst Signal Process 44, 889–910 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-024-02826-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-024-02826-8