Abstract
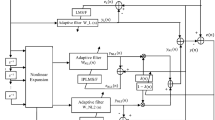
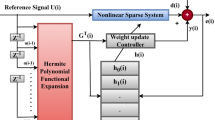
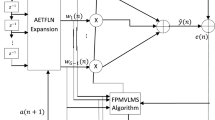
Lately, an adaptive exponential functional link network (AEFLN) involving exponential terms integrated with trigonometric functional expansion is being introduced as a linear-in-the-parameters nonlinear filter. However, they exhibit degraded efficacy in lieu of non-Gaussian or impulsive noise interference. Therefore, to enhance the nonlinear modelling capability, here is a modified logarithmic hyperbolic sine cost function in amalgamation with the adaptive recursive exponential functional link network. In conjugation with this, a sparsity constraint motivated by a curvelet-dependent notion is employed in the suggested approach. Therefore, this paper presents an individually weighted modified logarithmic hyperbolic sine curvelet-based recursive exponential FLN (IMLSC-REF) for robust sparse nonlinear system identification. An individually weighted adaptation gain is imparted to several coefficients corresponding to the nonlinear adaptive model for accelerating the convergence rate. The weight update rule and the maximum criteria for the convergence factor are being further derived. Exhaustive simulation studies profess the effectiveness of the introduced algorithm in case of varied nonlinearity and for identifying as well as modelling the physical path of the acoustic feedback phenomenon of a behind-the-ear (BTE) hearing aid.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.S. Bhattacharjee, M.A. Shaikh, K. Kumar, N.V. George, Robust constrained generalized correntropy and maximum Versoria criterion adaptive filters. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 68(8), 3002–3006 (2021)
S.S. Bhattacharjee, N.V. George, Nonlinear system identification using exact and approximate improved adaptive exponential functional link networks. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 67(12), 3542–3546 (2020)
S.C. Chan, Y.X. Zou, A recursive least M-estimate algorithm for robust adaptive filtering in impulsive noise: fast algorithm and convergence performance analysis. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 52(4), 975–991 (2004)
B. Chen, X. Wang, Y. Li, J.C. Príncipe, Maximum correntropy criterion with variable center. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 26(8), 1212–1216 (2019)
B.D. Chen, L. Xing, Z. Haiquan, Z. Nanning, N. Principe, Generalized correntropy for robust adaptive filtering. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 64(13), 3376–3387 (2015)
Y. Cheng, C. Li, S. Chen, Z. Zhou, An enhanced impulse noise control algorithm using a novel nonlinear function. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 42, 1–20 (2023)
C. Danilo, S. Michele, A. Luis, A.G. Jeronimo, U. Aurelio, Functional link adaptive filters for nonlinear acoustic echo cancellation. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 21(7), 1502–1512 (2013)
C. Danilo, S. Michele, S. Simone. U. Aurelio, Sparse functional link adaptive filter using an \(l_1\)-norm regularization, in 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), pp. 1–5 (2018)
W. Gen, Z. Haiquan, S. Pucha, Robust variable step-size reweighted zero-attracting least mean M-estimate algorithm for sparse system identification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 67, 1149 (2020)
N. George, A. Gonzalez, Convex combination of nonlinear adaptive filters for active noise control. Appl. Acoust. 76, 157–161 (2014)
S.S. Haykin, Adaptive Filter Theory (1991)
F. He, Y. Yang, Nonlinear system identification of neural systems from neurophysiological signals. Neuroscience 458, 213–228 (2021)
F. Huang, Z. Jiashu, Z. Sheng, A family of robust diffusion adaptive filtering algorithms based on the sigmoidal cost. Signal Process. 149, 179 (2018)
F. Huang, Z. Jiashu, Z. Sheng, Maximum Versoria criterion-based robust adaptive filtering algorithm. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 64(10), 1252–1256 (2017)
Y. Huo, T. Xu, Y. Qi, R. Ding, A family of robust diffusion adaptive filtering algorithms based on the Tanh framework. Circuits Syst. Signal Process 43, 1–19 (2023)
R. Isermann, M. Münchhof, Identification of dynamic systems: an introduction with applications (2010)
S. Jain, S. Majhi, Zero-attracting kernel maximum Versoria criterion algorithm for nonlinear sparse system identification. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 29, 1546–1550 (2022)
K. Krishna, M.L.N.S. Karthik, N.V. George, A novel family of sparsity-aware robust adaptive filters based on a logistic distance metric. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 70, 6128 (2022)
K. Krishna, B. Sankha, N. George, Modified Champernowne function based robust and sparsity-aware adaptive filters. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 30, 200 (2023)
K. Kumar, S.S. Bhattacharjee, N.V. George, Joint logarithmic hyperbolic Cosine robust sparse adaptive algorithms. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 68, 526 (2021)
K. Kumar, M.L.N.S. Karthik, N.V. George, Generalized modified blake-Zisserman robust sparse adaptive filters. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 53(1), 647 (2023)
K. Kumar, R. Pandey, S.S. Bhattacharjee, N.V. George, Exponential hyperbolic cosine robust adaptive filters for audio signal processing. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 28, 1410 (2021)
K. Kumar, R. Pandey, S.S. Bora, N.V. George, A robust family of algorithms for adaptive filtering based on the arctangent framework. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 69, 1967 (2022)
L. Li, J. Zhao, Q. Li, L. Tang, H. Zhang, Recursive constrained maximum Versoria criterion algorithm for adaptive filtering. Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. 199(14), 433–445 (2023)
Y. Li, Y. Wang, F. Albu, J. Jiang, general zero attraction proportionate normalized Maximum correntropy criterion algorithm for sparse system identification. Article Symmetry 9, 229 (2017)
Ch. Liu, M. Jiang, Robust adaptive filter with lncosh cost. Signal Process. 168, 107348 (2020)
Z. Mohagheghian Bidgoli, M. Bekrani, A Switching-based variable step-size PNLMS adaptive filter for sparse system identification. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 43, 568 (2023)
V. Patel, V. Gandhi, S. Heda, N.V. George, Design of adaptive exponential functional link network-based nonlinear filters. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I(63), 1434–1442 (2016)
J.C. Patra, A. Kot, Nonlinear dynamic system identification using Chebyshev functional link artificial neural networks. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B Cybern. 32, 505–511 (2002)
S. Peng, S. Wee, B. Chen, L. Sun, Z. Lin, Robust constrained adaptive filtering under minimum error entropy criterion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 65(8), 1119–1123 (2018)
S. Radhika, F. Albu, A. Chandrasekar, Proportionate maximum Versoria criterion-based adaptive algorithm for sparse system identification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 69(3), 1902–1906 (2022)
K. Rao, E. Plotkin, M.N. Swamy, Adaptive blind equalization of nonlinear channels and chaotic systems using coupled EKF and RLS estimator. IETE J. Res. 51(3), 181–192 (2005)
S. Radhika, F. Albu, A. Chandrasekar, Robust exponential hyperbolic sine adaptive filter for impulsive noise environments. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 69(12), 5149–5153 (2022)
J. Sandesh, M. Sudhan, Zero-attracting Kernel maximum Versoria criterion algorithm for nonlinear sparse system identification. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 29, 1546 (2022)
L. Shaohui, Z. Haiquan, Robust diffusion recursive least M-estimate adaptive filtering, and its performance analysis. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 42, 1–24 (2023)
Z. Sheng, Z. Wei, Recursive adaptive sparse exponential functional link neural network for nonlinear AEC in impulsive noise environment. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 29(9), 4314–4323 (2018)
G. Vasundhara Panda, N.B. Puhan, Individual-activation-factor based novel approach for acoustic feedback suppression in hearing aid. Appl. Acoust. 127, 74–79 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2017.05.015
N.B. VasundharaPuhan, G. Panda, De-correlated improved adaptive exponential FLAF-based nonlinear adaptive feedback cancellation for hearing aids. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Reg. Pap. 65(2), 650–662 (2018)
Vasundhara, Re-weighted zero attracting adaptive exponential FLAF with maximum correntropy criterion for robust sparse nonlinear system identification. Digit. Signal Process. 130, 103664 (2022)
Vasundhara, Robust filtering employing bias-compensated M-estimate affine-projection-like algorithm. IET Electron. Lett. 56(5), 241–253 (2020)
Vasundhara, Sparsity aware affine-projection-like filtering integrated with robust set membership and M-estimate approach for acoustic feedback cancellation in hearing aids. Appl. Acoust. 175, 107778 (2021)
S. Wang, W. Wang, K. Xiong, H.H.C. Iu, C.K. Tse, Logarithmic hyperbolic cosine adaptive filter and its performance analysis. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 51(4), 2512–2524 (2021)
F.Y. Wu, Y.C. Song, R. Peng, A Scaled LMS algorithm for sparse system identification with impulsive interference. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 42, 4432 (2023)
Z. Yingying, Z. Haiquan, Z. Xiangping, B.D. Chen, Robust generalized Maximum correntropy criterion algorithms for active noise control. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 28, 1282–1292 (2020)
T. Yu, W. Li, Y. Yu, R.C. de Lamare, Robust adaptive filtering based on exponential functional link network: analysis and application. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 68(7), 2720–2724 (2021)
S. Zandi, M. Korki, Diffusion maximum versoria criterion algorithms robust to impulsive noise. Digit. Signal Process. 126, 103490 (2022)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chikyal, N., Vasundhara, Bhar, C. et al. Individually Weighted Modified Logarithmic Hyperbolic Sine Curvelet Based Recursive FLN for Nonlinear System Identification. Circuits Syst Signal Process 44, 306–337 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-024-02839-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-024-02839-3