Abstract
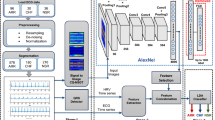
Classification of cardiac diseases from electrocardiogram signals is essential for enhancing patient results to minimize healthcare costs, early detection and accurate diagnosis. This research investigates the integration of dimensionality reduction methods with various deep learning classifiers to improve the accuracy and efficient classification of cardiac disease. Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection combined with Principal Component Analysis is used for dimensionality reduction, that captures both global and local data structures. Deep learning classifiers with convolutional neural networks, capsule networks, recurrent neural networks, graph neural networks, deep long short-term memory and automatical attention-based convolutional neural networks are employed for classification. The Adaptive spiral Flying Sparrow Search algorithm optimizes classifier parameters for enhance accuracy. Performance is evaluated through various metrics, with area under the receiver operating characteristic curve, accuracy, F1-Score, precision and recall. The proposed method's outcomes are compared with and without optimization to demonstrate the efficiency and attains 92.16%, 96.15%, 91.95%, 94.65%, 91.45% and 92.85% accuracy respectively for each classification method.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
S.R. Breesha, S.S. Vinsley, Automated extraction of fetal ECG signal features using twinned filter and integrated methodologies. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 43(2), 661–683 (2024)
S.S. Dambal, M.K. Doddananjedevaru, S.B. Gopalakrishna, A hybrid feature dimension reduction and SVM for a classification of heart rate variability. Int. J. Intell. Eng. Syst. 16, 104–112 (2023)
S. Daphin Lilda, R. Jayaparvathy, A. Balaji, An efficient machine learning based ventricular late potential detection and classification technique for cardiac healthcare. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/cpe.7279
S. Das, M. Sultana, S. Bhattacharya, D. Sengupta, D. De, Xai–reduct: accuracy preservation despite dimensionality reduction for heart disease classification using explainable AI. J. Supercomput. 79, 18167–18197 (2023)
B. Dhananjay, J. Sivaraman, Analysis and classification of heart rate using CatBoost feature ranking model. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 68, 102610 (2021)
C. Ding, S. Wang, X. Jin, Z. Wang, J. Wang, A novel transformer-based ECG dimensionality reduction stacked auto-encoders for arrhythmia beat detection. Med. Physics. 50, 5897–5912 (2023)
L.T. Duong, T.T.H. Doan, C.Q. Chu, P.T. Nguyen, Fusion of edge detection and graph neural networks to classifying electrocardiogram signals. Expert Syst. Appl. 225, 120107 (2023)
Y. Fang, J. Shi, Y. Huang, T. Zeng, Y. Ye, L. Su, D. Zhu, J. Huang, Electrocardiogram signal classification in the diagnosis of heart disease based on RBF neural network. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2022, 1–9 (2022)
A.L. Golande, T. Pavankumar, Optical electrocardiogram based heart disease prediction using hybrid deep learning. J. Big Data. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-023-00820-6
S. Jamil, M. Rahman, A novel deep-learning-based framework for the classification of cardiac arrhythmia. J. Imaging 8, 70 (2022)
Y. Jiao, H. Qi, J. Wu, Capsule network assisted electrocardiogram classification model for smart healthcare. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 42, 543–555 (2022)
P. Jyothi, G. Pradeepini, HDPSANN: an efficient heart disease prediction system using a soft swish artificial neural network based on ECG signals. Int. J. Intell Syst. Appl. Eng. 11, 671–684 (2023)
S. Karthik, M. Santhosh, M.S. Kavitha, A.C. Paul, Automated deep learning based cardiovascular disease diagnosis using ECG signals. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 42, 183–199 (2022)
S. Kuila, N. Dhanda, S. Joardar, Feature extraction and classification of ECG signals through Dimension Reduction. Lecture Notes Electrical Eng. 223–233 (2022)
S. Kuila, N. Dhanda, S. Joardar, ECG signal classification and arrhythmia detection using ELM-RNN. Multimed. Tools Appl. 81, 25233–25249 (2022)
M.A. Kumar, A. Chakrapani, Classification of ECG signal using FFT based improved Alexnet classifier. PLoS ONE 17, e0274225 (2022)
S. Kusuma, K.R. Jothi, Heart disease classification using multiple K-PCA and hybrid deep learning approach. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 41, 1273–1289 (2022)
X. Liu, H. Wang, Z. Li, L. Qin, Deep learning in ECG diagnosis: a review. Knowl. Based Syst. 227, 107187 (2021)
M. Malik, T. Dua, Snigdha, Biomedical signal processing: ECG signal analysis using machine learning in matlab. Recent Adv. Metrology. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-2468-2_14
R. Nagulapalli, K. Hayatleh, S. Barker, P. Georgiou, F.J. Lidgey, A high value, linear and tunable cmos pseudo-resistor for biomedical applications. J. Circ. Syst. Comput. 28(06), 1950096 (2019)
R. Nagulapalli, K. Hayatleh, S. Barker, S. Zourob, N. Yassine, S. Raparthy, A. Tammam, A novel high CMRR trans-impedance instrumentation amplifier for biomedical applications. Analog Integr. Circ. Signal Process. 98, 233–241 (2019)
R. Nagulapalli, K. Hayatleh, S. Barker, S. Zourob, N. Yassine, S. Sridevi, A PVT insensitive programmable amplifier for biomedical applications. in 2017 International Conference Microelectronic Devices, Circuits and Systems, (ICMDCS). IEEE, pp. 1–5 (2017)
C. Ouyang, Y. Qiu, D. Zhu, Adaptive spiral flying sparrow search algorithm. Sci. Programm. 2021, 1–16 (2021)
K. Ramasamy, K. Balakrishnan, D. Velusamy, Detection of cardiac arrhythmias from ECG signals using FBSE and jaya optimized ensemble random subspace K-nearest neighbor algorithm. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 76, 103654 (2022)
K. Ramasamy, K. Balakrishnan, D. Velusamy, Classification of inter-patient’s cardiac arrhythmias in ECG signals with enhanced JAYA optimized TQWT parameters and stacked ensemble algorithm. Soft. Comput. 27, 11341–11356 (2023)
M. Rashed-Al-Mahfuz, M.A. Moni, P. Lio, S.M.S. Islam, S. Berkovsky, M. Khushi, J.M. Quinn, Deep convolutional neural networksbased ECG beats classification to diagnose cardiovascular conditions. Biomed. Eng. Let. 11, 147–162 (2021)
A. Rath, D. Mishra, G. Panda, S.C. Satapathy, K. Xia, Improved heart disease detection from ECG signal using deep learning based ensemble model. Sustain. Comput. Info. Syst. 35, 100732 (2022)
M. Roy, S. Majumder, A. Halder, U. Biswas, ECG-net: a deep LSTM autoencoder for detecting anomalous ECG. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 124, 106484 (2023)
S. Schmitz, U. Weidner, H. Hammer, A. Thiele, Evaluating uniform manifold approximation and projection for dimension reduction and visualization of polinsar features. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Info. Sci. 1, 39–46 (2021)
M.G. Shankar, C.G. Babu, H. Rajaguru, Classification of cardiac diseases from ECG signals through bio inspired classifiers with adam and R-adam approaches for hyperparameters updation. Measurement 194, 111048 (2022)
A. Tyagi, R. Mehra, Intellectual heartbeats classification model for diagnosis of heart disease from ECG signal using hybrid convolutional neural network with Goa. SN Appl. Sci. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-021-04185-4
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors have contributed equally to the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no potential conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All applicable institutional and/or national guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Informed Consent
For this type of analysis formal consent is not needed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Karthikeyani, S., Sasipriya, S. & Ramkumar, M. An Evaluation of Dimensionality Reduction and Classification Techniques for Cardiac Disease Diagnosis from ECG Signals with Various Deep Learning Classifiers. Circuits Syst Signal Process 44, 416–446 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-024-02845-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-024-02845-5