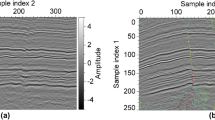
Abstract.
In this paper, we present an automatic horizon-picking algorithm, based on a surface detection technique, to detect horizons in 3D seismic data. The surface detection technique, and the use of 6-connectivity, allows us to detect fragments of horizons that are afterwards combined to form full horizons. The criteria of combining the fragments are similarity of orientation of the fragments, as expressed by their normal vectors, and proximity using 18-connectivity. The identified horizons are interrupted at faults, as required by the experts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bondar I (1992) Seismic horizon detection using image processing algorithms. Geophys Prospect 40:785-800
Frangi AF, Niessen WJ, Vincken KL, Viergever MA (1998) Multiscale vessel enhancement filtering. In: Proceedings of medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention - MICCAI’98, 1496:130-137
Keskes N, Boulanouar A, Faugeras O (1982) Application of image analysis techniques to seismic data. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing, pp 855-858
Keskes N, Zaccagnino P, Rether D, Mermey P (1983) Automatic extraction of 3-D seismic horizons. In: Society of Exploration Geophysicists (SEG), Annual Meeting Expanded Abstracts, pp 557-559
Lavest P, Chipot Y (1993) Building complex horizons for 3-D seismic. In: Society of Exploration Geophysicists (SEG), Annual Meeting Expanded Abstracts, pp 159-161
Lindeberg T (1998) Edge detection and ridge detection with automatic scale selection. Int J Comput Vision 30(2):77-116
Maroni C, Quinquis A, Vinson S (2001) Horizon picking on subbottom profiles using multiresolution analysis. Digital Signal Process 11:269-287
Petrou M (1993) Optimal convolution filters and an algorithm for the detection of wide linear features. IEE Proc 140:331-339
Pieper S, Berlage T (2002) Enhancing volume visualisation of 3-D seismic data by exploitation of 3-D texture features. In: Proceedings of 64th European Association of Geoscientists and Engineers (EAGE) annual conference and exhibition
Pitas I, Kotropoulos C (1992) A texture-based approach to the segmentation of seismic images. Pattern Recog 25:929-945
Pitas I, Venetsanopoulos AN (1987) AGIS: An expert system for automated geophysical interpretation of seismic images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing, pp 2256-2259
Roberto V, Peron A, Fumis PL (1989) Low-level processing techniques in geophysical image interpretation. Pattern Recog Lett 10:111-122
Sato Y, Nakajima S, Shiraga N (1998) 3D multi-scale line filter for segmentation and visualisation of curvilinear structures in medical images. Med Image Anal 2(2):143-168
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received: 16 August 2003, Accepted: 4 May 2004, Published online: 17 August 2004
Correspondence to: Maria Petrou
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faraklioti, M., Petrou, M. Horizon picking in 3D seismic data volumes. Machine Vision and Applications 15, 216–219 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-004-0151-8
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-004-0151-8