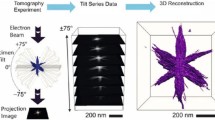
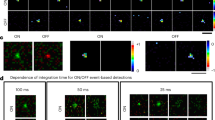
Abstract
The main goal of Nanotechnology is to analyze and understand the properties of matter at the atomic and molecular level. Computer vision is rapidly expanding into this new and exciting field of application, and considerable research efforts are currently being spent on developing new image-based characterization techniques to analyze nanoscale images. Nanoscale characterization requires algorithms to perform image analysis under extremely challenging conditions such as low signal-to-noise ratio and low resolution. To achieve this, nanotechnology researchers require imaging tools that are able to enhance images, detect objects and features, reconstruct 3D geometry, and tracking. This paper reviews current advances in computer vision and related areas applied to imaging nanoscale objects. We categorize the algorithms, describe their representative methods, and conclude with several promising directions of future investigation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguet, F., Van De Ville, D., Unser, M.: Sub-resolution axial localization of nanoparticles in fluorescence microscopy. In: Wilson, T., (ed.) Proceedings of the SPIE European conference on biomedical optics: confocal, multiphoton, and nonlinear microscopic imaging II (ECBO’05), vol. 5860, pp. 103–106. Munich, Germany, June 12–16 (2005)
Aurenhammer F. (1991). Voronoi diagrams – a survey of a fundamental geometric data structure. ACM Comput Surv. 23(3):345–405
Azuma R. (1997). A survey of augmented reality. Presence Teleoperators Virtual Environ. 6(4):355–385
Banks, J, Rothnagel, R., Hankamer, B.: Automated particle picking of biological molecules images by electron microscopy. In: Image and vision computing New Zealand, pp. 269–274, November (2003)
Belge M., Kilmer M., Miller E. (2000). Wavelet domain image restoration with adaptive edge-preserving regularization. Integr. Psychiatry 9(4):597–608
Bera D., Kuiry S.C., McCutchen M., Kruize A., Heinrich H., Seal S., Meyyappan M. (2004). In-situ synthesis of palladium nanoparticles-filled carbon nanotubes using arc discharge in solution. Chem. Phys. Lett. 386(4–6):364–368
Berglund A.J., Mabuchi H. (2005). Tracking-fcs: fluorescence correlation spectroscopy of individual particles. Opt. Express 13:8069–8082
Black M.J., Sapiro G., Marimont D., Heeger D. (1998). Robust anisotropic diffusion. IEEE Trans Image Process. 7(3):421–432
Bonneau S., Dahan M., Cohen L.D. (2005). Single quantum dot tracking based on perceptual grouping using minimal paths in a spatiotemporal volume. IEEE Trans. Image Progress. 14(9):1384–1395
Bovik A.C., Gibson J.D., Bovik A. (eds) (2000). Handbook of Image and Video Processing. Academic, Orlando
Bracewell R. (1999). The Fourier Transform and Its Applications 3rd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Brandt S., Heikkonen J., Engelhardt P. (2001). Automatic alignment of transmission electron microscope tilt series without fiducial markers. J. Struct. Biol. 136:201–213
Brandt S., Heikkonen J., Engelhardt P. (2001). Multiphase method for automatic alignment of transmission electron microscope images using markers. J. Struct. Biol. 133(1):10–22(13)
Brown L.G. (1992) A survey of image registration techniques. ACM Comput. Surv. 24(4):325–376
Chen Y.K., Chu A., Cook J., Green M.L.H., Harris P.J.F., Heesom R., Humphries M., Sloan J., Tsang S.C., Turner J.F.C. (1997). Synthesis of carbon nanotubes containing metal oxides and metals of the d-block and f-block transition metals and related studies. J. Mater. Chem. 7(3):545–549
Chen, Y., Wang, H., Fang, T., Tyan, J.: Mutual information regularized bayesian framework for multiple image restoration. In: IEEE International conference on computer vision (ICCV) (2005)
Comaniciu V., Meer P. (2003). Ker.nel-based object tracking. IEEE Trans. on Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 25(5):564–575
Cornille, N., Garcia, D., Sutton, M., McNeil, S., Orteu, J.: Automated 3-D reconstruction using a scanning electron microscope. In: SEM annual conf. & exp. on experimental and applied mechanics (2003)
Dempster A., Laird N.M., Rubin D.B. (1977). Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 39(1):1–38
Drummond T., Cipolla R. (2002). Real-time tracking of complex structures with on-line camera calibration. Image Vision Comput. 20(5–6):427–433
Duda R.O., Hart P.E. (1972). Use of the hough transformation to detect lines and curves in pictures. Commun. of ACM. 15(1):11–15
Falvo M.R., Clary G., Helser A., Paulson S., Taylor R.M. II, Chi F.P., Brooks V. Jr., Washburn S., Superfine R. (1998). Nanomanipulation experiments exploring frictional and mechanical properties of carbon nanotubes. Micros. Microanal. 4:504–512
Falvo M.R., Taylor R.M. II., Helser A., Chi V., Brooks F.P. Jr., Washburn S., Superfin R. (1999). Nanometre-scale rolling and sliding of carbon nanotubes. Nature 397:236–238
Fang S., Dai Y., Myers F., Tuceryan M., Dunn K. (2000). Three-dimensional microscopy data exploration by interactive volume visualization. Scanning 22:218–226
Farabee, M.: On-line biology book. (http://www.emc. maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBookTOC.html (2001)
Faugeras, O.: Three-dimensional Computer Vision: a Geometric Viewpoint. MIT Press (1993)
Fernandez J., Lawrence A., Roca J., Garcia I., Ellisman M., Carazo J. (2002). High-performance electron tomography of complex biological specimens. J. Struct. Biol. 138:6–20
Fernandez J.-J., Carazo J.-M., Garcia I. (2004). Three-dimensional reconstruction of cellular structures by electron microscope tomography and parallel computing. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 64(2):285–300
Flegler S.L., Heckman J.W., Klomparens K.L. (1995). Scanning and Transmission Electron Microscopy: An Introduction. Oxford Press, Oxford
Gallop J. (2003). SQUIDs: some limits to measurement. Superconduct. Sci. Technol. 16:1575–1582
Garini Y., Vermolen B.J., Young I.T. (2005). From micro to nano: recent advances in high-resolution microscopy. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 16(3):3–12
Goldstein J.I., Newbury D.E., Echlin P., Joy D.C., Fiori C., Lifshin E. (1981). Scanning Electron Microscopy and X-Ray Microanalysis: A Text for Biologists, Materials Scientists, and Geologists. Plenum Publishing Corporation, New York
Grenander U., Srivastava A. (2001). Probability models for clutter in natural images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal Mach. Intell. 23(4):424–429
Grimellec C.L., Lesniewska E., Giocondi M.-C., Finot E., Vie V., Goudonnet J.-P. (1998). Imaging of the surface of living cells by low-force contact-mode atomic force microscopy. Biophys. J. 75:695–703
Guthold M., Liu W., Stephens B., Lord S.T., Hantgan R.R., Erie D.A., Taylor R.M. II, Superfine R. (2004). Visualization and mechanical manipulations of individual fibrin fibers. Biophys. J. 87(6):4226–4236
Haralick R.M., Shapiro L.G. (1992). Computer and Robot Vision. Addison-Wesley Longman Publishing, Boston
Harauz G., Fong-Lochovsky A. (1989). Automatic selection of macromolecules from electron micrographs by component labelling and symbolic processing. Ultramicroscopy 31(4):333–44
Hartley R.I., Zisserman A. (2000). Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Heiler M., Schnörr C. (2005). Natural image statistics for natural image segmentation. Int. J. Comput. Vision, 63(1):5–19
Hell S.W. (2003). Towards fluorescence nanoscopy. Nat Biotechnol. 21(11):1347–1355
Horn B. (1986). Robot Vision. MIT Press, Cambridge
Huang Z., Dikin D.A., Ding W., Qiao Y., Chen X., Fridman Y., Ruoff R.S. (2004). Three-dimensional representation of curved nanowires. J. Micros. 216(3):206–214
Ludtke S.J., Baldwin P., Chiu W. (1999). Eman: semiautomated software for high-resolution single-particle reconstructions. J. Struct. Biol. 128:82–97
Jacob, M., Blu, T., Unser, M.: 3-D reconstruction of DNA filaments from stereo cryo-electron micrographs. In: Proceedings of the first 2002 IEEE international symposium on biomedical imaging: macro to nano (ISBI’02), vol. II, pp. 597–600. Washington, DC, USA, July 7–10 (2002)
Jiang G., Quan L., Tsui H.-T. (2004). Circular motion geometry using minimal data. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 26(6):721–731
Kammerud C., Abidi B., Abidi M. (2005). Computer vision algorithms for 3D reconstruction of microscopic data– a review. Microsc Microanaly. 11:636–637
Kim, D.-H., Kim, T., Kim, B.: Motion planning of an afm-based nanomanipulator in a sensor-based nanorobotic manipulation system. In: Proceedings of 2002 international workshop on microfactory, pp. 137–140 (2002)
Kubota T., Talekar P., Ma X., Sudarshan T.S. (2005). A non-destructive automated defect-detection system for silicon carbide wafers. Mach. Vis. Appl. 16(3):170–176
Kumar, S., Hebert, M.: Discriminative fields for modeling spatial dependencies in natural images. In:Proceedings of advances in neural information processing systems (NIPS), December (2003)
Kumar, S., Chaudhury, K., Sen, P., Guha, S.K.: Atomic force microscopy: a powerful tool for high-resolution imaging of spermatozoa. J. Nanobiotechnol. 3(9), (2005)
Lacroute, P., Levoy, M.: Fast volume rendering using a shear-warp factorization of the viewing transformation. In: SIGGRAPH ’94: proceedings of the 21st annual conference on computer graphics and interactive techniques, pp. 451–458. ACM press, New York, (1994)
Lambert J.H. (1760). Photometria sive de mensure de gratibus luminis, colorum umbrae. Eberhard Klett, Augsburg
Lee A.B., Pedersen K.S., Mumford D. (2003). The nonlinear statistics of high-contrast patches in natural images. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 54(1-3):83–103
Levine Z.H., Kalukin A.R., Kuhn M., Retchi C.C., Frigo P., McNulty I., Wang Y., Lucatorto T.B., Ravel B.D., Tarrio C. (2000). Tomography of integrated circuit interconnect with an electromigration void. J. Appl.Phys. 87(9):4483–4488
Li S.Z. (1995). Markov random field modeling in computer vision. Springer, London
Li G., Xi N., Yu M., Fung W.-K (2004). Development of augmented reality system for afm-based nanomanipulation. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mech. 9(2):358–365
Lucic V., Forster F., Baumeister W. (2005). Structural studies by electron tomography: from cells to molecules.Annu. Rev. Biochem. 74:833–865
Mallick S.P., Xu Y., Kriegman D.J. (2004). Detecting particles in cryo-em micrographs using learned features.J. Struct. Biol. 145(1-2):52–62
Mantooth B.A., Donhauser Z.J., Kelly K.F., Weiss P.S. (2002). Cross-correlation image tracking for drift correction and adsorbate analysis. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 73:313–317
Marco S., Boudier T., Messaoudi C., Rigaud J.-L. (2004). Electron tomography of biological samples. Biochemistry (Moscow) 69(11):1219–1225
McLachlan, G.J., Peel, D.: Robust cluster analysis via mixtures of multivariate t-distributions. InSSPR/SPR pp. 658–666 (1998)
Nicholson W.V., Glaeser R.M. (2001). Review: automatic particle detection in electron microscopy. J. Struc. Biol. 133:90–101
Nicholson W.V., Malladi R. (2004). Correlation-based methods of automatic particle detection in electron microscopy images with smoothing by anisotropic diffusion. J. Micros. 213:119–128
NSRG-Chappel Hill: Nanoscale-Science Research Group. http://www.cs.unc.edu/Research/nano/ (2005)
Ogura T., Sato C. (2001). An automatic particle pickup method using a neural network applicable to low-contrast electron micrographs. J. Struct. Biol. 136(3):227–238
Ong E.W., Razdan A., Garcia A.A., Pizziconi V.B., Ramakrishna B.L., Glaunsinger W.S. (2000). Interactive nano-visualization of materials over the internet. J. Chem. Educa. 77(9):1114–1115
Perona P., Malik J. (1990). Scale-space and edge detection using anisotropic diffusion. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 12(7):629–639
Pohl, D.W.: Scanning near-field optical microscopy. Advances in Optical and Electron Microscopy. In.: Sheppard, C.J.R., Mulvey, T., (eds.) Vol. 12. Academic , London (1990)
Ronneberger O., Schultz E., Burkhardt H. (2002). Automated pollen recognition using 3D volume images from fluorescence microscopy. Aerobiologia 18(2):107–115
Rosenfeld, A., Pfaltz, J.: Distance functions on digital pictures. Pattern Recogn 1(1), 33–61 July (1968).
Rugar, D., Budakian, R., Mamin, H.J., Chui, B.W.: Single spin detection by magnetic resonance force microscopy. Nature, 430, 329–332, July (2004)
Russ J.C. (1998). The Image Processing Handbook. IEEE Press, New York
Ryu, J., Horn, B.K.P., Mermelstein, M.S., Hong, S., Freedam, D.M.: Application of structured illumination in nanoscale vision. In: Proceedings of IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshop: Computer Vision for the Nano Scale, pp. 17–24, June (2003)
Sandberg K., Mastronarde D.N., Beylkina G. (2003). A fast reconstruction algorithm for electron microscope tomography. J. Struct. Biol. 144:61–72
Scharr, H., Black, M., Haussecker, H.: Image statistics and anisotropic diffusion.In: ICCV03, pp. 840–847 (2003)
Scharr, H., Felsberg, M., Forssén, P.-E.: Noise adaptive channel smoothing of low-dose images. In: Proceedings of IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshop: computer vision for the nano scale, June (2003)
Scharr, H., Uttenweiler, D.: 3D anisotropic diffusion filtering for enhancing noisy actin filament fluorescence images. In: Proceedings of the 23rd DAGM-symposium on pattern recognition, pp. 69–75. Springer, London, (2001)
Sharma, G., Mavroidis, C., Ferreira, A.: Virtual reality and haptics in nano and bionanotechnology, vol. X of Handbook of Theoretical and Computational Nanotechnology, chap. 40. American Scientific Publishers, Stevenson Ranch (2005)
Singh V., Marinescu D.C., Baker T.S. (2004). Image segmentation for automatic particle identification in electron micrographs based on hidden markov random field models and expectation maximization. J. Struct. Biol. 145(1-2):123–141
Stoscherk A., Hegerl R. (1997). Automated detection of macromolecules from electron micrographs using advanced filter techniques. J. Micros. 185:76–84
Subramaniam S., d Milne J.L. (2004). Three-dimensional electron microscopy at molecular resolution. Annu. Revi. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 33:141–155
Tan, H.Z., Walker, L., Reifenberger, R., Mahadoo, S., Chiu, G., Raman, A., Helser, A., Colilla, P.: A haptic interface forhuman-in-the-loop manipulation at the nanoscale.In: Proceedings of the 2005 world haptics conference (WHC05): the first joint euro haptics conference and the symposium on haptic interfaces for virtual environment and teleoperator systems, pp. 271–276 (2005)
Tsai R.Y. (1987). A versatile camera calibration technique for high-accuracy 3D machine vision metrology using off-the-shelf TV cameras and lenses. IEEE J. Robot. Autom. RA-3(4):323–344
Valinetti, A., Fusiello, A., Murino, V.: Model tracking for video-based virtual reality. In: ICIAP, pp. 372–377 (2001)
van Heel M., Gowen B., Matadeen R., Orlova E.V., Finn R., Pape T., Cohen D., Stark H., Schmidt R., Schatz M., Patwardhan A. (2000). Single-particle electron cryo-microscopy: towards atomic resolution. Q.Revi. Biophysi. 33(4):307–369
Viola P., Jones M.J. (2004). Robust real-time face detection. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 57(2):137–154
Watt I.M. (1997). The Principles and Practice of Electron Microscopy. Cambridge Press, Cambridge
Weickert J. (1997). Anisotropic Diffusion in Image Processing. Teubner Verlag, Stuttgart
Xiao J., Shah M. (2004). Tri-view morphing. Comput. Vis, Image Understand. 96(3):345–366
Yilmaz A., Shafique K., Shah M. (2003). Target tracking in airborne forward looking infrared imagery. Image Vis. Comput. 21(7):623–635
Yu, Z., Bajaj, C.: A gravitation-based clustering method and its applications in 3D electron microscopy imaging. In:5th International conference on advances in pattern recognition(ICAPR’03), pp. 137–140 (2003)
Yu Z., Bajaj C. (2004). Detecting circular and rectangular particles based on geometric feature detection in electron micrographs. J. Struct. Biol. 145, 168D180
Zhang Z. (2000). A flexible new technique for camera calibration. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 22(11):1330–1334
Zhu Y., Carragher B., Kriegman D., Milligan R.A., Potter C.S. (2001). Automated identification of filaments in cryoelectron microscopy images. J. Struct. Biol. 135:302–321
Zhu Y., Carragher B., Mouche F., Potter C.S. (2003). Automatic particle detection through efficient Hough transforms. IEEE Trans Med Imag. 22(9):1053–1062
Zhu Y., Carragher B., Glaeser R.M., Fellmann D., Bajaj C., Bern M., Mouche F., de Haas F., Hall R.J., Kriegman D.J., Ludtke S.C., Mallick S.P., Penczek P.A., Roseman A.M., Sigworth F.J., Volkmann N., Potter C.S. (2004). Automatic particle selection: Results of a comparative study. J. Struct. Biolo. 145:3–14
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ribeiro, E., Shah, M. Computer Vision for Nanoscale Imaging. Machine Vision and Applications 17, 147–162 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-006-0021-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-006-0021-7