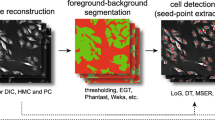
Abstract
The detection and segmentation of adherent eukaryotic cells from brightfield microscopy images represent challenging tasks in the image analysis field. This paper presents a free and open-source image analysis package which fully automates the tasks of cell detection, cell boundary segmentation, and nucleus segmentation in brightfield images. The package also performs image registration between brightfield and fluorescence images. The algorithms were evaluated on a variety of biological cell lines and compared against manual and fluorescence-based ground truths. When tested on HT1080 and HeLa cells, the cell detection step was able to correctly identify over 80% of cells, whilst the cell boundary segmentation step was able to segment over 75% of the cell body pixels, and the nucleus segmentation step was able to correctly identify nuclei in over 75% of the cells. The algorithms for cell detection and nucleus segmentation are novel to the field, whilst the cell boundary segmentation algorithm is contrast-invariant, which makes it more robust on these low-contrast images. Together, this suite of algorithms permit brightfield microscopy image processing without the need for additional fluorescence images. Finally our sephaCe application, which is available at http://www.sephace.com, provides a novel method for integrating these methods with any motorised microscope, thus facilitating the adoption of these techniques in biological research labs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali, R.: Applications of microscopy image analysis and modelling in characterising the mechanisms of hypoxia-mediated drug resistance. Ph.D thesis, University of Oxford, Oxford (2009)
Ali, R., Gooding, M., Christlieb, M., Brady, M.: Phase-based segmentation of cells from brightfield microscopy. In: Proceedings of the International Symposium Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), pp 57–60 (2007)
Ali, R., Gooding, M., Christlieb, M., Brady, M.: Advanced phase-based segmentation of multiple cells from brightfield microscopy images. In: Proceedings of the International Symposium Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), pp 181–184 (2008)
Ali, R., Szilagyi, T., Gooding, M., Christlieb, M., Brady, M.: On the use of lowpass filters for image processing with inverse laplacian models. J. Math. Imag. Vis. Under Rev. (2010)
Barber, P.R., Locke, R.J., Pierce, G.P., Rothkamm, K., Vojnovic, B.: Gamma-H2AX focicounting: image processing and control software for high-content screening. In: Proceedings of SPIE, San Jose, CA,USA, pp 64, 411M–64, 411M–10 (2007)
Boukerroui M., Noble D., Brady A.: On the choice of band-pass quadraturefilters. J. Math. Imag. Vis. 21, 53–80 (2004)
Bradbury, L.: Segmentation of bright-field cell images. Ph.D thesis, University of Waterloo, Ontario, Canada (2009)
Carpenter A.E., Jones T.R., Lamprecht M.R., Clarke C., Kang I.H., Friman O., Guertin D.A., Chang J.H., Lindquist R.A., Moffat J., Golland P., Sabatini D.M.: CellProfiler: image analysis software for identifying and quantifying cell phenotypes. Genome Biol. 7(10), R100 (2006)
Cates J., Lefohn A., Whitaker R.: GIST: an interactive, GPU-Based level set segmentation tool for 3D medical images. Med. Imag. Anal. 8, 217–231 (2004)
Curl C., Harris T., Harris P., Allman B., Bellair C., Stewart A., Delbridge L.: Quantitative phase microscopy: a new tool for measurement of cell culture growth and confluency in situ. Eur. J. Physiol. 448, 462–468 (2004)
Dice, L. (1945) Measures of the amount of ecologic association between species. Ecology 26:297–302
Felsberg M., Sommer G.: The monogenic signal. IEEE Trans. Sig. Proc. 49(12), 3136–3144 (2001)
Felsberg M., Kalkan S., Krüger N.: Continuous dimensionality characterization of image structures. Imag. Vis. Comput. 27(6), 628–636 (2009)
Folkard M., Prise K.M., Grime G., Kirkby K., Vojnovic B.: The use of microbeamsto investigate radiation damage in living cells. Appl. Rad. Isot. 67(3), 436–439 (2009)
Gooding M., Kennedy S., Noble J.: Volume segmentation and reconstruction from freehand 3D ultrasound data with application to ovarian follicle measurement. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 34(2), 183–195 (2008)
Gordon A., Colman-Lerner A., Chin T., Benjamin K., Yu R., Brent R.: Single-cell quantification of molecules and rates using open-source microscope-based cytometry. Nat. Methods 4, 175–181 (2007)
Korzynska A., Stronjy W., Hoppe A., Wertheim D., Hoser P.: Segmentation of microscope images of living cells. Pattern Anal. Appl. 10(4), 301–319 (2007)
Mellor M., Brady M.: Phase mutual information as a similarity measure for registration. Med. Image Anal. 9(4), 330–343 (2005)
Nilsson B., Heyden A.: A fast algorithm for level set-like active contours. Pattern Rec. Lett. 24, 1331–1337 (2003)
Otsu N.: A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 9, 62–66 (1979)
Paganin D., Nugent K.: Noninterferometric phase imaging with partially coherent light. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80(12), 2586–2589 (1998)
Paganin D., Barty A., McMahon P., Nugent K.: Quantitative phase-amplitude microscopy. III. The effects of noise. J. Microsc. 214, 51–61 (2004)
Rittscher J., Machiraju R., Wong S.T.C.: Microscopic Image Analysis for Life Science Applications, 1st edn. Artech House Publishers, USA (2008)
Rote G.: Computing the minimum Hausdorff distance between two point sets on a line under translation. Inf. Process. Lett. 38, 123–127 (1991)
Selinummi, J., Ruusuvuori, P., Podolsky, I., Ozinsky, A., Gold, E., Yli-Harja, O., Aderem, A., Shmulevich, I.: Bright field microscopy as an alternative to whole cell fluorescence in automated analysis of macrophage images 4(10):e7497 (2009). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0007497
Styner M., Brehbuhler C., Szekely G., Gerig G.: Parametric estimate of intensity homogeneities applied to MRI. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 19(3), 153–165 (2000)
Teague M.: Deterministic phase retrieval: a green’s function solution. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 73, 1434–1441 (1983)
Tscherepanow M., Zollner F., Kummert F.: Classification of segmented regions in brightfield microscope images. ICPR 06(3), 972–975 (2006)
Tscherepanow M., Nickels N., Kummert F.: Recognition of unstained live drosophila cells in microscope image, pp. 169–176. IMVIP, Los Alamitos (2007)
Veselov O., Polak W., Ugenskiene R., Lebed K., Lekki J., Stachura Z., Styczen J.: Development of the IFJ single ion hit facility for cell irradiation. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 122, 316–319 (2006)
Volkov V., Zhu Y., Graef M.D.: A new symmetrized solution for phase retrieval using the transport of intensity equation. Micron. 33(5), 411–416 (2002)
Wang K., Chang A., Kale L., Dantzig A.: Parallelization of a level set method for simulating dendritic growth. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 11, 1379–1386 (2006)
Wu K., Gauthier D., Levine M.: Live cell image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 42(1), 1–12 (1995)
Xu C., Prince J.: Snakes, shapes and gradient vector flow. IEEE Trans. Image. Proc. 7, 359–369 (1998)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, R., Gooding, M., Szilágyi, T. et al. Automatic segmentation of adherent biological cell boundaries and nuclei from brightfield microscopy images. Machine Vision and Applications 23, 607–621 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-011-0337-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-011-0337-9