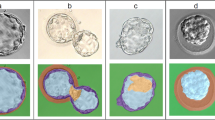
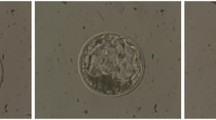
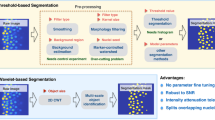
Abstract
Detailed and accurate characteristics of preimplantation embryos are fundamental for a deep understanding of their development. Recent studies indicate that various geometric features of cells, such as size, shape, volume, and position play a significant role in embryo growth. However, a quantitative assessment of these characteristics first needs a segmentation of the individual cells. The manual separation and labeling of cells is extremely inefficient, and an automated approach is highly desirable. This paper presents an automatic method for early stage embryo segmentation into its constituent cells and membranes using three-dimensional (3D) data. The input data consist of two Z-stacks of fluorescence microscope images containing nuclei and membranes. The method uses a 3D level set segmentation algorithm. Its evaluation is based on a dataset composed of 20 mouse embryos, each with 4–32 blastomeres. Segmentation accuracy was evaluated by calculating F-scores with ground truth obtained by manually labeling desired regions. We also compared output of our method with the one acquired with a watershed algorithm. The proposed approach was able to achieve more than \(90\%\) accuracy for embryos with 4 and 8 cells, while for embryos with higher number of cells it was lower, reaching \(75\%\) for 32-cell embryo.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adalsteinsson, D., Sethian, J.A.: A fast level set method for propagating interfaces. J. Comput. Phys. 118, 269–277 (1995). doi:10.1006/jcph.1995.1098
Al-Kofahi, Y., Lassoued, W., Lee, W., Roysam, B.: Improved automatic detection and segmentation of cell nuclei in histopathology images. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 57(4), 841–52 (2010). doi:10.1109/TBME.2009.2035102
Altman, D.G.: Practical Statistics for Medical Research. Chapman Hall, London (1991)
Bedzhov, I., Graham, S.J.L., Leung, C.Y., Zernicka-Goetz, M.: Developmental plasticity, cell fate specification and morphogenesis in the early mouse embryo. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 369(1657) (2014). doi:10.1098/rstb.2013.0538
Brox, T., Weickert, J.: Level set segmentation with multiple regions. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 15(10), 3213–3218 (2006). doi:10.1109/TIP.2006.877481
Caselles, V., Kimmel, R., Sapiro, G.: Geodesic active contours. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 22(1), 61–79 (1997). doi:10.1023/A:1007979827043
Cremers, D., Rousson, M., Deriche, R.: A review of statistical approaches to level set segmentation: integrating color, texture, motion and shape. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 72(2), 195–215 (2007). doi:10.1007/s11263-006-8711-1
Dard, N., Louvet-Valle, S., Maro, B.: Orientation of mitotic spindles during the 8- to 16-cell stage transition in mouse embryos. PLoS ONE 4(12), 1–8 (2009). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008171
Dufour, A., Shinin, V., Tajbakhsh, S., Guillen-Aghion, N., Olivo-Marin, J.C.: Segmenting and tracking fluorescent cells in dynamic 3-D microscopy with coupled active surfaces. IEEE Signal Process. Soc. 14, 1396–1410 (2005). doi:10.1109/TIP.2005.852790
Dzyubachyuk, O., van Cappellen, W.A., Essers, J., Nissen, W.J.: Advanced level-set-based cell tracking in time-lapse fluorescence microscopy. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 29, 852–867 (2010). doi:10.1109/TMI.2009.2038693
Fernandez, R., Das, P., Mirabet, V., Moscardi, E., Traas, J., Verdeil, J.L., Malandain, G., Godin, C.: Imaging plant growth in 4D: robust tissue reconstruction and lineaging at cell resolution. Nat. Methods 7(7), 547–553 (2001). doi:10.1038/nmeth.1472
Gharipour, A., Wee-Chung Liew, A.: Segmentation of cell nuclei in fluorescence microscopy images: an integrated framework using level set segmentation and touching-cell splitting. Pattern Recognit. 58, 1–11 (2016). doi:10.1016/j.patcog.2016.03.030
Giusti, A., Corani, G., Gambardella, L., Magli, C., Gianaroli, L.: Blastomere segmentation and 3D morphology measurements of early embryos from Hoffman modulation contrast image stacks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, Rotterdam, pp. 13–17 (2010). doi:10.1109/ISBI.2010.5490225
Goldenberg, R., Kimmel, R., Rivlin, E., Rudzsky, M.: Fast geodesic active contours. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 10(10), 1467–1475 (2001). doi:10.1109/83.951533
Hillman, N., Sherman, M.I., Graham, C.: The effect of spatial arrangement on cell determination during mouse development. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol. 28, 263–278 (1972)
Huang, X., Metaxas, D., Chen, T.: Metamorphs: Deformable shape and texture models. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 496–503 (2004). doi:10.1109/CVPR.2004.1315072
Kong, J., Wang, F., Teodoro, G., Liang, Y., Zhu, Y., Tucker-Burden, C., Brat, D.J.: Automated cell segmentation with 3D fluorescence microscopy images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, pp. 1212–1215 (2015). doi:10.1109/ISBI.2015.7164091
Li, G., Liu, T., Tarokh, A., Nie, J., Guo, L., Mara, A., Holley, S., Wong, S.T.: 3D cell nuclei segmentation based on gradient flow tracking. BMC Cell Biol. 8, 40 (2007). doi:10.1186/1471-2121-8-40
Lou, X., Kang, M., Muoz-Descalzo, S., Hadjantonakis, A.K.: A rapid and efficient 2D/3D nuclear segmentation method for analysis of early mouse embryo and stem cell image data. Stem Cell Rep. 11, 382–397 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.stemcr.2014.01.010
Mandar, D.M., Bosiljka, T., Kazunari, M., Ling, L., Liqun, L.: A global double-fluorescent cre reporter mouse. Genesis 45, 593–605 (2007). doi:10.1002/dvg.20335
Mansouri, A.R., Mitiche, A., Vazquez, C.: Multiregion competition: a level set extension of region competition to multiple region image partitioning. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 101(3), 137–150 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.cviu.2005.07.008
Meyer, F.: Topographic distance and watershed lines. Signal Process. 38(1), 113–125 (1994). doi:10.1016/0165-1684(94)90060-4
Nandy, K., Chellappa, R., Kumar, A.A.: Size-invariant cell nucleus segmentation in 3-D microscopy. In: 2012 IEEE Southwest Symposium on Image Analysis and Interpretation (SSIAI), pp. 37–40 (2012). doi:10.1109/SSIAI.2012.6202447
Nandy, K., Chellappa, R., Kumar, A.: Segmentation of nuclei from 3D microscopy images of tissue via graphcut optimization. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 10(1), 140–150 (2016). doi:10.1109/JSTSP.2015.2505148
Niakan, K.K., Han, J., Pedersen, R.A., Simon, C., Pera, R.A.: Human pre-implantation embryo development. Development 139, 829–841 (2012). doi:10.1242/dev.060426
Nowotschin, S., Hadjantonakis, A.K.: Live imaging mouse embryonic development: seeing is believing and revealing. Methods Mol. Biol. 1092, 405–420 (2014). doi:10.1007/978-1-60327-292-6_24
Ohnishi, Y., Huber, W., Tsumura, A., Kang, M., Xenopoulos, P., Kurimoto, K., Oles, A.K., Arazo-Bravo, M.J., Saitou, M., Hadjantonakis, A.K., Hiiragi, T.: Cell-to-cell expression variability followed by signal reinforcement progressively segregates early mouse lineages. Nat. Cell Biol. 16, 27–37 (2014). doi:10.1038/ncb2881
Olivier, N., Luengo-Oroz, M.A., Duloquin, L., Faure, E., Savy, T., Veilleux, I., Solinas, X., Débarre, D., Bourgine, P., Santos, A., Peyriéras, N., Beaurepaire, E.: Cell lineage reconstruction of early zebrafish embryos using label-free nonlinear microscopy. Science 329(5994), 967–971 (2010). doi:10.1126/science.1189428
Ortiz De Solorzano, C., Malladi, R., Lelivre, S.A., Lockett, S.J.: Segmentation of nuclei and cells using membrane related protein markers. J. Microsc. 201(3), 404–415 (2001). doi:10.1046/j.1365-2818.2001.00854.x
Osher, S., Sethian, J.A.: Fronts propagating with curvature dependent speed: algorithms based on Hamilton–Jacobi formulations. J. Comput. Phys. 79, 12–49 (1988). doi:10.1016/0021-9991(88)90002-2
Pedersen, U.D., Fogh, O.O., Holm, N.O.: A multiphase variational level set approach for modelling human embryos. In: Proceedings of the Workshop on Variational, Geometric and Level Set Methods in Computer Vision, pp. 25–32 (2003)
Rijsbergen, C.J.V.: Information Retrieval, 2nd edn. Butterworth, London (1979)
Rossant, J., Tam, P.P.: Emerging asymmetry and embryonic patterning in early mouse development. Dev. Cell 7, 155–164 (2004). doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2004.07.012
Sethian, J.A.: A fast marching level set method for monotonically advancing fronts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci 93(4), 1591–1595 (1996). doi:10.1073/pnas.93.4.1591
Shi, Y., Clem, W.K.: A fast implementation of the level set method without solving partial differential equations. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, pp. 97–100 (2005)
Singh, A., Buonassisi, J., Saeedi, P., Havelock, J.: Automatic blastomere detection in day 1 to day 2 human embryo images using partitioned graphs and ellipsoids. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Paris, pp. 917–921 (2014). doi:10.1109/ICIP.2014.7025184
Stephenson, R.O., Yamanaka, Y., Rossant, J.: Disorganized epithelial polarity and excess trophectoderm cell fate in preimplantation embryos lacking E-cadherin. Development 137(20), 3383–3391 (2010). doi:10.1242/dev.050195
Strnad, P., Gunther, S., Reichmann, J., Krzic, U., Balazs, B., de Medeiros, G., Norlin, N., Hiiragi, T., Hufnagel, L., Ellenberg, J.: Inverted light-sheet microscope for imaging mouse pre-implantation development. Nat. Methods 13(2), 139–142 (2016). doi:10.1038/nmeth.3690
Tarkowski, A.K., Wróblewska, J.: Development of blastomeres of mouse eggs isolated at the 4- and 8-cell stage. Development 18(1), 155–180 (1967)
Wahlby, C., Sintorn, I.M., Erlandsson, F., Borgefors, G., Bengtsson, E.: Combining intensity, edge and shape information for 2D and 3D segmentation of cell nuclei in tissue sections. J. Microsc. 215(1), 67–76 (2004). doi:10.1111/j.0022-2720.2004.01338.x
Wennekamp, S., Mesecke, S., Nedelec, F., Hiiragi, T.: A self-organization framework for symmetry breaking in the mammalian embryo. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 14, 452–459 (2013). doi:10.1038/nrm3602
Zernicka-Goetz, M., Morris, S.A., Bruce, A.W.: Making a firm decision: multifaceted regulation of cell fate in the early mouse embryo. Nat. Rev. Genet. 10, 467–477 (2009). doi:10.1038/nrg2564
Zhu, S.C., Yuille, A.: Region competition: unifying snakes, region growing, and Bayes/MDL for multiband image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Computer Vision, 1995, Cambridge, MA, pp. 416–423 (1995). doi:10.1109/ICCV.1995.466909
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grushnikov, A., Niwayama, R., Kanade, T. et al. 3D level set method for blastomere segmentation of preimplantation embryos in fluorescence microscopy images. Machine Vision and Applications 29, 125–134 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-017-0880-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-017-0880-0