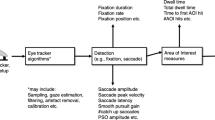
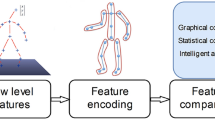
Abstract
This work is focused on the field of automatic hearing assessment for patients presenting cognitive decline or severe communication difficulties. Audiometry is a test of behavior requiring intense interaction between patient and audiologist, so it is extremely difficult to properly assess patients with severe communication disorders. However, patients with cognitive decline often make some eye gestures in reaction to auditory stimuli. These reactions are interpreted by expert audiologists. On the other hand, a manual assessment of the patient creates problems such as subjectivity or low reproducibility, to name but two. Bearing this in mind, this paper introduces a novel methodology to analyze video recordings acquired during audiometric evaluations and characterize movements of the eye so they can be interpreted as a positive gestural reaction to sound. Motion analysis in the eye region helps the human expert to establish the existence of a reaction to sound, thus increasing the reproducibility and objectivity of the test.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acton, Q.: Dementia: New Insights for the Healthcare Professional: 2013 Edition. Scholarly Editions (2013). http://books.google.es/books?id=pkE0Yv1MfOQC
Audiology, B.S.: Recommended Procedure Pure-tone Air-conduction and Bone-conduction Threshold Audiometry With and Without Masking (2015). http://www.thebsa.org.uk/resources/pure-tone-air-bone-conduction-threshold-audiometry-without-masking/
Australian Hearing Annual Report (2009). http://www.hearing.com.au/australian-hearing-annual-reports
Bolón-Canedo, V., Fernández, A., Alonso, A., Ortega, M., Penedo, M.G.: On the use of machine learning techniques for the analysis of spontaneous reactions in automated hearing assessment. In: European Symposium on Artificial Neural Networks, pp. 355–360 (2015)
Boraston, Z., Blakemore, S.J.: The application of eye-tracking technology in the study of autism. J. Physiol. 581(3), 893–898 (2007)
Bouguet, J.Y.: Pyramidal Implementation of the Lucas–Kanade Feature Tracker: Description of the Algorithm. Intel Corporation, Microprocessor Research Labs, Santa Clara (2000)
Chawla, N.V., Bowyer, K.W., Hall, L.O., Kegelmeyer, W.P.: SMOTE: synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 16(1), 321–357 (2002)
Collins, J.G., National Center for Health Statistics (U.S.): Prevalence of selected chronic conditions: United States, 1986–1988. DHHS Publication. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics (1993). http://books.google.es/books?id=fYbFnQEACAAJ
Davis, A.: Prevalence of hearing impairment. In: Hearing in Adults, Chapter 3, pp. 46–45. Whurr Ltd, London (1995)
Davis, A.: The prevalence of hearing impairment and reported hearing disability among adults in great britain. Int. J. Epidemiol. 18, 911–917 (1989)
De Santi, L., Lanzafame, P., Spanò, B., D’Aleo, G., Bramanti, A., Bramanti, P., Marino, S.: Pursuit ocular movements in multiple sclerosis: a video-based eye-tracking study. Neurol. Sci. 32(1), 67–71 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-010-0395-1
del Río, S., López, V., Benítez, J.M., Herrera, F.: On the use of MapReduce for imbalanced big data using Random Forest. Inf. Sci. 285, 112–137 (2014)
Fernández, A., de Moura, J., Ortega, M., Penedo, M.G.: Detection and characterization of the sclera: evaluation of eye gestural reactions to auditory stimuli. In: 10th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP) Vol.2, pp. 313–320 (2015)
Fernández, A., Ortega, M., Gonzalez, Penedo M., Vazquez, C., Gigirey, L.: A methodology for the analysis of spontaneous reactions in automated hearing assessment. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 20(1), 376–387 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2014.2360061
Fukushima, K., Fukushima, J., Barnes, G.R.: Clinical application of eye movement tasks as an aid to understanding parkinsons disease pathophysiology. Exp. Brain Res. 235(5), 1309–1321 (2017)
IMSERSO: Las personas mayores en España. In: Instituto de Mayores y Servicios Sociales (2008)
IMSERSO: Libro blanco del envejecimiento activo (in Spanish) (2010)
Jain, V., Learned-Miller, E.: Fddb: A benchmark for face detection in unconstrained settings. University of Massachusetts, Amherst, Technical Report UM-CS-2010-009 2(7):8 (2010)
Kothari, R., Mitchell, J.: Detection of eye locations in unconstrained visual images. In: Image Processing, 1996. Proceedings., International Conference on, Vol. 3, pp. 519–522 (1996)
Li, D., Winfield, D., Parkhurst, D.: Starburst: A hybrid algorithm for video-based eye tracking combining feature-based and model-based approaches. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition-Workshops, 2005. CVPR Workshops. IEEE Computer Society Conference on, pp. 79–79 (2005)
Lin, F.R.: Hearing loss and cognition among older adults in the united states. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 66, 1131–1136 (2011)
Lucas, B.D., Kanade, T.: An iterative image registration technique with an application to stereo vision. In: Proceedings of the 7th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence Volume 2, IJCAI’81, pp. 674–679. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., San Francisco (1981)
Lusa, L., et al.: Smote for high-dimensional class-imbalanced data. BMC Bioinform. 14(1), 106 (2013)
Marandi, R.Z., Sabzpoushan, S.H.: Using eye movement analysis to study auditory effects on visual memory recall. Basic Clin. Neurosci. 5(1), 55–65 (2014)
Murlow, C., Aguilar, C., Endicott, J., Velez, R., Tuley, M., Charlip, W., Hill, J.: Asociation between hearing impairment and the quality of life of elderly individuals. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 38, 45–50 (1990)
National Institute of Deafness and Other Communication Disorders: Quick statistics (2014). https://www.nidcd.nih.gov/health/statistics/quick-statistics-hearing
Pereira, M.L., Camargo, M.V., Aprahamian, I., Forlenza, O.V.: Eye movement analysis and cognitive processing: detecting indicators of conversion to Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 10, 1273–1285 (2014)
Raney, G.E., Campbell, S.J., Bovee, J.C.: Using eye movements to evaluate the cognitive processes involved in text comprehension. J. Vis. Exp. 83, e50780 (2014)
Shi, J., Tomasi, C.: Good features to track. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 1994. Proceedings CVPR ’94., 1994 IEEE Computer Society Conference on, pp. 593–600 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.1994.323794
Timm, F., Barth, E.: Accurate eye centre localisation by means of gradients. In: Mestetskiy, L., Braz, J. (eds.) VISAPP, pp. 125–130. SciTePress, Setúbal (2011)
Viola, P., Jones, M.: Robust real-time object detection. In: International Journal of Computer Vision (2001)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Government of Spain and FEDER funds of the European Union through the PI14/02161 and the DTS15/00153 research projects. Also, this work has received financial support from the European Union (European Regional Development Fund-ERDF) and the Xunta de Galicia, Centro singular de investigación de Galicia accreditation 2016-2019, Ref. ED431G/01, and Grupos de Referencia Competitiva, Ref. ED431C 2016-047.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernández, A., Ortega, M., de Moura, J. et al. Detection of reactions to sound via gaze and global eye motion analysis using camera streaming. Machine Vision and Applications 29, 1069–1082 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-018-0952-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-018-0952-9