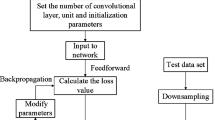
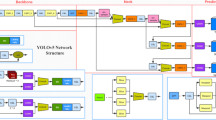
Abstract
In ship classification, selecting distinctive features and designing a proper classifier are two key points of the process. As a lack of most of the studies, these two essential points are considered separately. In this study, our proposal includes joint feature extraction, selection, and classifier design framework to build a novel deep cascade network for ship classification. We propose a transfer learning-based deep feature extraction using cascade Convolutional Neural Network architecture to convert the input image to multi-dimensional feature maps. The distributions of the MUTual Information (MUTInf) based feature selection algorithm compose a distinctive feature set originated for a public ship imagery dataset. The dataset consists of five specific classes of ships most existed in the maritime domain. A quadratic kernel-based non-linear Support Vector Machine is the designed classifier. Extensive experiments on the benchmark dataset indicate that the proposed framework can integrate the optimal feature set and a well-designed classifier to increase the performance of the classification process in ship imagery. In the experiments, the proposed method achieves an overall accuracy of 95.06%. The ship classes are also performed high classification performances into cargo, military, carrier, cruise, and tanker with an accuracy of 88.26%, 98.38%, 98.38%, 98.78%, and 91.50%, respectively. In addition, MUTInf feature selection reduces the features at a rate of 50.04%. These results show that the proposed method provides the highest performance value with less number of elements and outperforms state-of-the-art methods.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The processed dataset is already available in public and properly referenced in the bibliography list.
References
Leclerc, M., Tharmarasa, R., Florea, M.C., Boury-Brisset, A.C., Kirubarajan, T., Duclos-Hindié, N.: Ship classification using deep learning techniques for maritime target tracking. In: 2018 21st International Conference on Information Fusion, FUSION 2018. pp. 737–744. ISIF (2018)
Kumlu, D.: Autonomous Ship Recognition from Color Images (2012)
Ucar, F., Korkmaz, D.: A ship detector design based on deep convolutional neural networks for satellite ımages. Sak. Univ. J. Sci. 24, 197–202 (2020). https://doi.org/10.16984/saufenbilder.587731
Bentes, C., Velotto, D., Tings, B.: Ship classification in TerraSAR-X images with convolutional neural networks. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 43, 258–266 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/JOE.2017.2767106
Du, Y., Song, W., He, Q., Huang, D., Liotta, A., Su, C.: Deep learning with multi-scale feature fusion in remote sensing for automatic oceanic eddy detection. Inf. Fusion 49, 89–99 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2018.09.006
Prasad, D.K., Rajan, D., Rachmawati, L., Rajabally, E., Quek, C.: Video processing from electro-optical sensors for object detection and tracking in a maritime environment: a survey. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 18, 1993–2016 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2016.2634580
Shi, Q., Li, W., Zhang, F., Hu, W., Sun, X., Gao, L.: Deep CNN with multi-scale rotation invariance features for ship classification. IEEE Access 6, 38656–38668 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2853620
Xu, Y., Lang, H., Niu, L., Ge, C.: Discriminative adaptation regularization framework-based transfer learning for ship classification in SAR ımages. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. PP, 1–5 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/lgrs.2019.2907139
Wang, C., Zhang, H., Wu, F., Jiang, S., Zhang, B., Tang, Y.: A novel hierarchical ship classifier for COSMO-SkyMed SAR data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 11, 484–488 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2013.2268875
Gundogdu, E., Solmaz, B., Yücesoy, V., Koç, A.: MARVEL: a large-scale image dataset for maritime vessels. In: Computer Vision—ACCV 2016, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pp. 165–180. Springer, Cham (2017)
Lin, H., Song, S., Yang, J.: Ship classification based on MSHOG feature and task-driven dictionary learning with structured incoherent constraints in SAR images. Remote Sens. (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020190
Jiang, M., Yang, X., Dong, Z., Fang, S., Meng, J.: Ship classification based on superstructure scattering features in SAR images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 13, 616–620 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2016.2514482
Dong, Y., Zhang, H., Wang, C., Wang, Y.: Fine-grained ship classification based on deep residual learning for high-resolution SAR images. Remote Sens. Lett. 10, 1095–1104 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/2150704x.2019.1650982
Gao, J.Q., Fan, L.Y., Li, L., Xu, L.Z.: A practical application of kernel-based fuzzy discriminant analysis. Int. J. Appl. Math. Comput. Sci. 23, 887–903 (2013). https://doi.org/10.2478/amcs-2013-0066
Gao, J.Q., Fan, L.Y., Xu, L.Z.: Median null(Sw)-based method for face feature recognition. Appl. Math. Comput. 219, 6410–6419 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2013.01.005
Oliveau, Q., Sahbi, H.: Learning attribute representations for remote sensing ship category classification. IEEE J Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 10, 2830–2840 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2665346
Wang, H., Ran, Y., Liu, S., Deng, Y., Su, D.: Analysis of the ship target detection in high-resolution SAR images based on information theory and harris corner detection. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 291, 685–694 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-6504-1_83
Wei, Z., Ding, S., Duan, M., Liu, S., Huang, L., Zhou, F.: FeSTwo, a two-step feature selection algorithm based on feature engineering and sampling for the chronological age regression problem. Comput. Biol. Med. 125, 104008 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.104008
Xu, Y., Lu, L., Xu, Z., He, J., Zhou, J., Zhang, C.: Dual-channel CNN for efficient abnormal behavior identification through crowd feature engineering. Mach. Vis. Appl. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-018-0971-6
Zhang, X., Wu, J., Meng, M., Sun, Y., Sun, W.: Feature-transfer network and local background suppression for microaneurysm detection. Mach. Vis. Appl. 32, 1–13 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-020-01119-9
Nikbakhsh, N., Baleghi, Y., Agahi, H.: A novel approach for unsupervised image segmentation fusion of plant leaves based on G-mutual information. Mach. Vis. Appl. 32, 1–12 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-020-01130-0
Solorio-Fernández, S., Carrasco-Ochoa, J.A., Martínez-Trinidad, J.F.: A review of unsupervised feature selection methods. Artif. Intell. Rev. 53, 907–948 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-019-09682-y
Vergara, J.R., Estévez, P.A.: A Review of Feature Selection Methods Based on Mutual İnformation (2014). https://link.springer.com/article/https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-013-1368-0
Zaffalon, M., Hutter, M.: Robust Feature Selection by Mutual Information Distributions. (2002)
Peng, H., Long, F., Ding, C.: Feature selection based on mutual information: criteria of max-dependency, max-relevance, and min-redundancy. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 27, 1226–1238 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2005.159
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems—Volume 1. pp. 1097–1105. Curran Associates Inc. (2012)
Yao, Y., Yang, Y., Wang, Y., Zhao, X.: Artificial intelligence-based hull structural plate corrosion damage detection and recognition using convolutional neural network. Appl. Ocean Res. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apor.2019.05.008
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In: 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2015. pp. 1–14 (2015)
Iandola, F.N., Han, S., Moskewicz, M.W., Ashraf, K., Dally, W.J., Keutzer, K.: SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and <0.5MB model size. Arxiv 1602.07360, pp. 1–13 (2016)
Zhang, X., Zhou, X., Lin, M., Sun, J.: ShuffleNet: an extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6848–6856. IEEE Computer Society (2018)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778. IEEE Computer Society (2016)
Sandler, M., Howard, A., Zhu, M., Zhmoginov, A., Chen, L.C.: MobileNetV2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4510–4520. IEEE Computer Society (2018)
Shen, S., Yang, H., Li, J., Xu, G., Sheng, M.: Auditory inspired convolutional neural networks for ship type classification with raw hydrophone data. Entropy (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/e20120990
Li Mou, L., Liu, Q., Wang, Y., Zhu, X.X.: HSF-Net: Multiscale deep feature embedding for ship detection in optical remote sensing imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 56, 7147–7161 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2018.2848901
Zhang, M.M., Choi, J., Daniilidis, K., Wolf, M.T., Kanan, C.: VAIS: a dataset for recognizing maritime imagery in the visible and infrared spectrums. In: IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 10–16 (2015)
Suykens, J.A.K., Van Gestel, T., De Brabanter, J., De Moor, B., Vandewalle, J.: Least Squares Support Vector Machines (2002)
Cıbuk, M., Budak, U., Guo, Y., Cevdet Ince, M., Sengur, A.: Efficient deep features selections and classification for flower species recognition. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 137, 7–13 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2019.01.041
Jain, A.: Game of Deep Learning: Ship datasets (Kaggle). https://www.kaggle.com/arpitjain007/game-of-deep-learning-ship-datasets
Cheng, G., Wang, Y., Xu, S., Wang, H., Xiang, S., Pan, C.: Automatic road detection and Centerline extraction via cascaded end-to-end convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 55, 3322–3337 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2017.2669341
Lin, H., Shi, Z., Zou, Z.: Fully convolutional network with task partitioning for inshore ship detection in optical remote sensing images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 14, 1665–1669 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2017.2727515
Chen, C., He, C., Hu, C., Pei, H., Jiao, L.: A deep neural network based on an attention mechanism for SAR ship detection in multiscale and complex scenarios. IEEE Access. 7, 104848–104863 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2019.2930939
Yang, X., Sun, H., Fu, K., Yang, J., Sun, X., Yan, M., Guo, Z.: Automatic ship detection in remote sensing images from google earth of complex scenes based on multiscale rotation dense feature pyramid networks. Remote Sens. 10, 1–14 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10010132
Wu, Y., Liu, B., Wu, W., Lin, Y., Yang, C., Wang, M.: Grading glioma by radiomics with feature selection based on mutual information. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 9, 1671–1682 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-018-0883-3
Rahmaninia, M., Moradi, P.: OSFSMI: online stream feature selection method based on mutual information. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 68, 733–746 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.08.034
Vapnik, V.N.: Statistical Learning Theory (1998)
Thirumala, K., Pal, S., Jain, T., Umarikar, A.C.: A classification method for multiple power quality disturbances using EWT based adaptive filtering and multiclass SVM. Neurocomputing 334, 265–274 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.NEUCOM.2019.01.038
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ucar, F., Korkmaz, D. A novel ship classification network with cascade deep features for line-of-sight sea data. Machine Vision and Applications 32, 73 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-021-01198-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-021-01198-2