Abstract
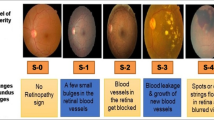
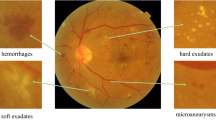
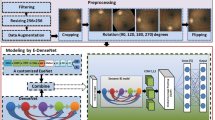
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a severe eye disease which can lead to permanent blindness. Identifying DR in early stages by using computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) systems can help the ophthalmologists to give proper treatment rationally, there by preventing many people from going blind. Due to intra-class variations and imbalanced data distribution, it is highly difficult to design a CAD system for DR severity diagnosis with greater generalizability. In this article, we propose a multi-stage deep learning pipeline, lesion-aware attention with neural support vector machine, for diabetic retinopathy diagnosis. Proposed pipeline consists of a pre-trained convolution base for learning retinal image spatial representations, lesion-aware attention for weighting lesion specific features, convolution autoencoder for learning latent attention representations and a neural support vector machine for discrimination. Convolutional autoencoder and neural support vector machine are jointly trained in end-to-end fashion to obtain category based lesion specific latent attention features by complementing each other in re-constructor and discriminator paths. Proposed approach is validated using two benchmark retinal scan image datasets, Kaggle APTOS 2019 and ISBI 2018 IDRiD, for DR type and severity grade classification tasks. Our experimental studies expose that using lesion-aware attention along with the joint training of autoencoder and neural support vector machine boosted the performance of models used for DR diagnosis, thereby outperforming existing works presented in the literature for DR severity grading. Proposed model achieved the highest accuracy of 90.45%, 84.31% on APTOS dataset and an accuracy of 79.85%, 63.24% on IDRiD dataset for DR type and severity grade classification tasks, respectively.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Antary, M.T., Arafa, Y.: Multi-scale attention network for diabetic retinopathy classification. IEEE Access 9, 54190–54200 (2021)
Albahli, S., Nazir, T., Irtaza, A., Javed, A.: Recognition and detection of diabetic retinopathy using densenet-65 based faster-rcnn. Comput. Mater. Contin. 67, 1333–1351 (2021)
Amin, J., Sharif, M., Yasmin, M.: A review on recent developments for detection of diabetic retinopathy. Scientifica 2016 (2016)
Bhandary, S.V., Rao, K.A.: Automated screening system for retinal health using bi-dimensional empirical mode decomposition and integrated index. Comput. Biol. Med. 75, 54–62 (2018)
Bodapati, J., Shareef, S.N., Naralasetti, V., Mundukur, N.B.: Msenet: Multi-modal squeeze-and-excitation network for brain tumor severity prediction. Int.J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2157005 (2021)
Bodapati, J.D., Shaik, N.S., Naralasetti, V.: Composite deep neural network with gated-attention mechanism for diabetic retinopathy severity classification. J. Ambient Intell. Humanized Comput. (2021)
Bodapati, J.D., Shaik, N.S., Naralasetti, V.: Deep convolution feature aggregation: an application to diabetic retinopathy severity level prediction. Signal Image Video Process., pp. 1–8 (2021)
Bodapati, J.D., Shaik, N.S., Naralasetti, V., Mundukur, N.B.: Joint training of two-channel deep neural network for brain tumor classification. Signal Image Video Process., pp. 1–8 (2020)
Bodapati, J.D., Veeranjaneyulu, N., Shareef, S.N., Hakak, S., Bilal, M., Maddikunta, P.K.R., Jo, O.: Blended multi-modal deep convnet features for diabetic retinopathy severity prediction. Electronics 9(6), 914 (2020)
Chen, M., Shi, X., Zhang, Y., Wu, D., Guizani, M.: Deep features learning for medical image analysis with convolutional autoencoder neural network. IEEE Trans. Big Data (2017)
Chollet, F. Xception: deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2017)
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.-J., Li, K., Fei-Fei, L.: Imagenet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, pp. 248–255 (2009)
Dondeti, V., Bodapati, J.D., Shareef, S.N., Naralasetti, V.: Deep convolution features in non-linear embedding space for fundus image classification deep convolution features in non-linear embedding space for fundus image classification. Revue d’Intell. Artif. 34(3), 307–313 (2020)
Eisenbarth, G.S.: Type I diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 314(21), 1360–1368 (1986)
Fukui, H., Hirakawa, T., Yamashita, T., Fujiyoshi, H.: Attention branch network: learning of attention mechanism for visual explanation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2019)
Gao, Z., Li, J., Guo, J., Chen, Y., Yi, Z., Zhong, J.: Diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy using deep neural networks. IEEE Access 7, 3360–3370 (2019)
Gayathri, S., Gopi, V.P., Palanisamy, P.: A lightweight cnn for diabetic retinopathy classification from fundus images. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 62, 102115 (2020)
Habib, M., Welikala, R., Hoppe, A., Owen, C., Rudnicka, A., Barman, S.: Detection of microaneurysms in retinal images using an ensemble classifier. Inf. Med. Unlocked 9, 44–57 (2017)
He, A., Li, T., Li, N., Wang, K., Fu, H.: Cabnet: category attention block for imbalanced diabetic retinopathy grading. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging (2020)
Hemanth, D.J., Deperlioglu, O., Kose, U.: An enhanced diabetic retinopathy detection and classification approach using deep convolutional neural network. Neural Comput. Appl. 32(3), 707–721 (2020)
Hu, J., Shen, L., Sun, G.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2018)
Kaggle. Aptos 2019 blindness detection challenge. https://www.kaggle.com/c/aptos2019-blindnes-detection. Accessed 30 Dec 2019
Kandel, I., Castelli, M.: Transfer learning with convolutional neural networks for diabetic retinopathy image classification. a review. Appl. Sci. 10(6), 2021 (2020)
Kassani, S.H., Kassani, P.H., Khazaeinezhad, R., Wesolowski, M.J., Schneider, K.A., Deters, R.: Diabetic retinopathy classification using a modified xception architecture. In: 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Signal Processing and Information Technology (ISSPIT), IEEE, pp. 1–6 (2019)
Kaur, N., Chatterjee, S., Acharyya, M., Kaur, J., Kapoor, N., Gupta, S.: A supervised approach for automated detection of hemorrhages in retinal fundus images. In: 2016 5th International Conference on Wireless Networks and Embedded Systems (WECON), IEEE, pp. 1–5 (2016)
Li, X., Hu, X., Yu, L., Zhu, L., Fu, C.-W., Heng, P.-A.: Canet: cross-disease attention network for joint diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema grading. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 39(5), 1483–1493 (2019)
Long, S., Huang, X., Chen, Z., Pardhan, S., Zheng, D.: Automatic detection of hard exudates in color retinal images using dynamic threshold and svm classification: algorithm development and evaluation. BioMed Res. Int. 2019 (2019)
Luong, M.-T., Pham, H., Manning, C.D.: Effective approaches to attention-based neural machine translation. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2015)
Mateen, M., Wen, J., Song, S., Huang, Z., et al.: Fundus image classification using vgg-19 architecture with pca and svd. Symmetry 11(1), 1 (2019)
Mohammedhasan, M., Uğuz, H.: A new early stage diabetic retinopathy diagnosis model using deep convolutional neural networks and principal component analysis. Traitement du Signal 37(5), 711–722 (2020)
Nanni, L., Ghidoni, S., Brahnam, S.: Handcrafted vs. non-handcrafted features for computer vision classification. Pattern Recognit. 71, 158–172 (2017)
Noushin, E., Pourreza, M., Masoudi, K., Ghiasi Shirazi, E.: Microaneurysm detection in fundus images using a two step convolution neural network. Biomed. Eng. Online 18(1), 67 (2019)
Porwal, P., Pachade, S., Kamble, R., Kokare, M., Deshmukh, G., Sahasrabuddhe, V., Meriaudeau, F.: Indian diabetic retinopathy image dataset (idrid): a database for diabetic retinopathy screening research. Data 3(3), 25 (2018)
Porwal, P., Pachade, S., Kokare, M., Deshmukh, G., Son, J., Bae, W., Liu, L., Wang, J., Liu, X., Gao, L., et al.: Idrid: diabetic retinopathy-segmentation and grading challenge. Med. Image Anal.s 59, 101561 (2020)
Prentašić, P., Lončarić, S.: Detection of exudates in fundus photographs using deep neural networks and anatomical landmark detection fusion. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 137, 281–292 (2016)
Qureshi, I., Ma, J., Abbas, Q.: Recent development on detection methods for the diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy. Symmetry 11(6), 749 (2019)
Qureshi, I., Ma, J., Abbas, Q.: Diabetic retinopathy detection and stage classification in eye fundus images using active deep learning. Multimedia Tools Appl. 80(8), 11691–11721 (2021)
Rahim, S.S., Palade, V., Holzinger, A.: Image processing and machine learning techniques for diabetic retinopathy detection: a review. In: Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for Digital Pathology, pp. 136–154 (2020)
Ramasamy, L.K., Padinjappurathu, S.G., Kadry, S., Damaševičius, R.: Detection of diabetic retinopathy using a fusion of textural and ridgelet features of retinal images and sequential minimal optimization classifier. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 7 (2021)
Razzak, M.I., Naz, S., Zaib, A.: Deep learning for medical image processing: Overview, challenges and the future. In: Classification in BioApps. Springer, pp. 323–350 (2018)
Shaban, M., Ogur, Z., Mahmoud, A., Switala, A., Shalaby, A., Abu Khalifeh, H., Ghazal, M., Fraiwan, L., Giridharan, G., Sandhu, H., et al.: A convolutional neural network for the screening and staging of diabetic retinopathy. Plos one 15(6), e0233514 (2020)
Sikder, N., Masud, M., Bairagi, A.K., Arif, A.S.M., Nahid, A.-A., Alhumyani, H.A.: Severity classification of diabetic retinopathy using an ensemble learning algorithm through analyzing retinal images. Symmetry 13(4), 670 (2021)
Srivastava, R.K., Greff, K., Schmidhuber, J.: Training very deep networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 28, Curran Associates, Inc., pp. 2377–2385 (2015)
Sun, R., Li, Y., Zhang, T., Mao, Z., Wu, F., Zhang, Y.: Lesion-aware transformers for diabetic retinopathy grading. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 10938–10947 (2021)
Wang, J., Luo, J., Liu, B., Feng, R., Lu, L., Zou, H.: Automated diabetic retinopathy grading and lesion detection based on the modified r-fcn object-detection algorithm. IET Comput. Vision 14(1), 1–8 (2019)
Xu, K., Ba, J., Kiros, R., Cho, K., Courville, A., Salakhudinov, R., Zemel, R., Bengio, Y.: Show, attend and tell: neural image caption generation with visual attention. In: Proceedings of Machine Learning Research (Lille, France, 09 2015), vol. 37, PMLR, pp. 2048–2057
Zeng, X., Chen, H., Luo, Y., Ye, W.: Automated diabetic retinopathy detection based on binocular siamese-like convolutional neural network. IEEE Access 7, 30744–30753 (2019)
Zheng, Y., He, M., Congdon, N.: The worldwide epidemic of diabetic retinopathy. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 60(5), 428 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shaik, N.S., Cherukuri, T.K. Lesion-aware attention with neural support vector machine for retinopathy diagnosis. Machine Vision and Applications 32, 126 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-021-01253-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-021-01253-y