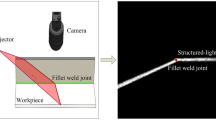
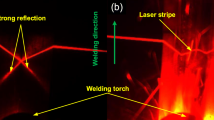
Abstract
In the process of vision-assisted robot automatic welding, splash and arc noise will interfere with the useful information in the image, which has a serious impact on the subsequent vision-based weld seam recognition and tracking algorithm. Although various methods have been proposed to achieve noise reduction, those are implemented from a perspective of image processing or intelligent algorithm. In this paper, we propose a pairwise response noise reduction model (PRNM) from the imaging perspective of seam tracking camera, which provides an image processing-free method to suppress welding splash and arc. Inverse response law and the loss function is established and solved by using singular value decomposition, and then the irradiance of reference scene is restored. A tone mapping approach is proposed based on the advantages of full-range compression and joint estimator, followed by mapping the obtained irradiance distribution to a high dynamic range (HDR) image. The grayscale correspondences of two reference images and the HDR image are reflected in the form of a two-dimensional lookup table (LUT). For welding noise characteristics, an alignment strategy is proposed to further correct the LUT to form a PRNM, which responds to all pairwise inputs with high computational efficiency. A batch of PRNMs have potential to form imaging solutions serving a welding process library. Experimental results reveal that the proposed model has a good effect in noise reduction, and the real-time performance is suitable for weld seam tracking.
























Similar content being viewed by others
References
He, Y., Chen, Y., Xu, Y., Huang, Y., Chen, S.: Autonomous detection of weld seam profiles via a model of saliency-based visual attention for robotic arc welding. J. Intell. Rob. Syst. 81(3), 395–406 (2016)
Wang, B., Hu, S.J., Sun, L., Freiheit, T.: Intelligent welding system technologies: state-of-the-art review and perspectives. J. Manuf. Syst. 56, 373–391 (2020)
Ge, J., Zhu, Z., He, D., Chen, L.: A vision-based algorithm for seam detection in a PAW process for large-diameter stainless steel pipes. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 26(9), 1006–1011 (2005)
Shao, W., Liu, X., Wu, Z.: A robust weld seam detection method based on particle filter for laser welding by using a passive vision sensor. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 104(5), 2971–2980 (2019)
Jin, Z., Li, H., Zhang, C., Wang, Q., Gao, H.: Online welding path detection in automatic tube-to-tubesheet welding using passive vision. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 90(9), 3075–3084 (2017)
Xiao, R., Xu, Y., Hou, Z., Chen, C., Chen, S.: An adaptive feature extraction algorithm for multiple typical seam tracking based on vision sensor in robotic arc welding. Sens. Actuat. A 297, 111533 (2019)
Muhammad, J., Altun, H., Abo-Serie, E.: Welding seam profiling techniques based on active vision sensing for intelligent robotic welding. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 88(1), 127–145 (2017)
Xiao, R., Xu, Y., Hou, Z., Chen, C., Chen, S.: An automatic calibration algorithm for laser vision sensor in robotic autonomous welding system. J. Intell. Manuf. 33, 1–14 (2021)
Ii’yashchenko, D.P., Sapozhkov, S.B.: Splashing in manual arc coated electrode welding and methods of reducing splashing. Weld. Int. 22(12), 874–877 (2008)
He, Y., Yu, Z., Li, J., Yu, L., Ma, G.: Discerning weld seam profiles from strong arc background for the robotic automated welding process via visual attention features. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 33(1), 1–12 (2020)
Photonfocus.: User Manual MV1-D1312(IE/C) Camera Series[EB/OL] (2018). https://www.photonfocus.com/support/manuals/. Accessed 1 Feb 2022
Gritchenko, A.S., Eremchev, I.Y., Naumov, A.V., Melentiev, P.N., Balykin, V.I.: Single quantum emitters detection with amateur CCD: comparison to a scientific-grade camera. Opt. Laser Technol. 143, 107301 (2021)
Oliveira, J.P., Curado, T.M., Zeng, Z., Lopes, J.G., Rossinyol, E., Park, J.M., Kim, H.S.: Gas tungsten arc welding of as-rolled CrMnFeCoNi high entropy alloy. Mater. Des. 189, 108505 (2020)
Paskual, A., Álvarez, P., Suárez, A.: Study on arc welding processes for high deposition rate additive manufacturing. Procedia Cirp 68, 358–362 (2018)
Kaplan, A.F.H., Powell, J.: Spatter in laser welding. J. Laser Appl. 23(3), 032005 (2011)
Huang, Y., Hua, X., Li, F., Shen, C., Mou, G., Tang, B.: Spatter feature analysis in laser welding based on motion tracking method. J. Manuf. Process. 55, 220–229 (2020)
Erkan, U., Enginoğlu, S., Thanh, D.N.: Adaptive frequency median filter for the salt and pepper denoising problem. IET Image Proc. 14(7), 1291–1302 (2020)
Khan, S., Lee, D.H.: An adaptive dynamically weighted median filter for impulse noise removal. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2017(1), 1–14 (2017)
Zhuang, C., Liao, P.: An improved empirical wavelet transform for noisy and non-stationary signal processing. IEEE Access 8, 24484–24494 (2020)
Shen, J.Z.: Research on Seam Image Processing for CO2 Horizontal Position Welding Based on Laser Vision Sensing. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Materials Processing Engineering, Tianjin University (2010)
Du, R., Xu, Y., Hou, Z., Shu, J., Chen, S.: Strong noise image processing for vision-based seam tracking in robotic gas metal arc welding. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 101(5), 2135–2149 (2019)
Wang, H., Xie, Q., Zhao, Q., Meng, D.: A model-driven deep neural network for single image rain removal. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3103–3112 (2020)
Zou, Y., Chen, J., Wei, X.: Research on a real-time pose estimation method for a seam tracking system. Opt. Lasers Eng. 127, 105947 (2020)
Bhola, A., Sharma, T., Verma, N.K.: DCNet: dark channel network for single-image dehazing. Mach. Vis. Appl. 32(3), 1–11 (2021)
Debevec, P.E., Malik, J.: Recovering high dynamic range radiance maps from photographs. ACM SIGGRAPH 2008 Classes, pp. 1–10 (2008)
Ali, M.A., Mann, S.: Comparametric image compositing: Computationally efficient high dynamic range imaging. In: 2012 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). IEEE (2012)
Keerativittayanun, S., Kondo, T., Kotani, K., Phatrapornnant, T., Karnjana, J.: Two-layer pyramid-based blending method for exposure fusion. Mach. Vis. Appl. 32(2), 1–18 (2021)
Eilertsen, G., Kronander, J., Denes, G., Mantiuk, R.K., Unger, J.: HDR image reconstruction from a single exposure using deep CNNs. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 36(6), 1–15 (2017)
Bacioiu, D., et al.: Automated defect classification of Aluminium 5083 TIG welding using HDR camera and neural networks. J. Manuf. Process. 45, 603–613 (2019)
Mann, S., et al.: Realtime HDR (high dynamic range) video for eyetap wearable computers, FPGA-based seeing aids, and glasseyes (eyetaps). In: 2012 25th IEEE Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering (CCECE). IEEE (2012)
Mann, S.: Comparametric equations with practical applications in quantigraphic image processing. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 9(8), 1389–1406 (2000)
Chinchuluun, A., Pardalos, P.M., Migdalas, A., Pitsoulis, L.: Pareto Optimality, Game Theory and Equilibria. Springer, Berlin (2008)
Wall, M.E., Rechtsteiner, A., Rocha, L.M.: Singular value decomposition and principal component analysis. In: A Practical Approach to Microarray Data Analysis, pp. 91–109. Springer, Boston (2003)
Grossberg, M.D., Nayar, S.K.: Modeling the space of camera response functions. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 26(10), 1272–1282 (2004)
Ma, K., Liu, W., Zhang, K., Duanmu, Z., Wang, Z., Zuo, W.: End-to-end blind image quality assessment using deep neural networks. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 27(3), 1202–1213 (2017)
Vega, M.T., Mocanu, D.C., Stavrou, S., Liotta, A.: Predictive no-reference assessment of video quality. Signal Process. Image Commun. 52, 20–32 (2017)
Huang, W., Jing, Z.: Evaluation of focus measures in multi-focus image fusion. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 28(4), 493–500 (2007)
Her, L., Yang, X.: Research of image sharpness assessment algorithm for autofocus. In: 2019 IEEE 4th International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing (ICIVC), pp. 93–98. IEEE (2019)
Yang, C., Chen, M., Zhou, F., Li, W., Peng, Z.: Accurate and rapid auto-focus methods based on image quality assessment for telescope observation. Appl. Sci. 10(2), 658 (2020)
Johnson, D.H.: Signal-to-noise ratio. Scholarpedia 1(12), 2088 (2006)
Sara, U., Akter, M., Uddin, M.S.: Image quality assessment through FSIM, SSIM, MSE and PSNR—a comparative study. J. Comput. Commun. 7(3), 8–18 (2019)
Hore, A., Ziou, D.: Image quality metrics: PSNR vs. SSIM. In: 2010 20th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, pp. 2366–2369. IEEE (2010)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Key Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province 2020 B090928002, National Natural Science Foundation of China (62176072) and Self-Planned Task NO.SKLRS20 2111B of State Key Laboratory of Robotics and System (HIT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, Z., Wang, K. & Li, R. Welding splash and arc noise reduction imaging model based on computationally efficient pairwise response serving welding process library. Machine Vision and Applications 33, 93 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-022-01342-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-022-01342-6