Abstract
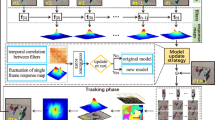
In this study, we concentrate on solving variations in scale, aspect ratio, rotation, visual model and target motion problems for vehicle tracking in low-altitude UAV videos. The contributions of this work are threefold: 1. By introducing a particle rescaling mechanism where each particle is resized with different aspect ratios, tracking under scale and aspect ratio variations is improved. 2. By fully integrating a particle filter with a convolutional neural network, a new structure, which acts as an auxiliary particle filter, is developed. This new structure improves the estimation of the states, namely the location and the velocity of the target, and the dimensions of the bounding boxes, thus enables tracking under fast motion. 3. By introducing a unified multi-part vehicle tracking framework, robust tracking is achieved against scale change, aspect ratio, visual model variations and sudden rotations. The processing of multiple parts, independently, improves the tracking under sudden aspect ratio and rotation changes compared to tracking the vehicle as a whole. In this study, without loss of generality, the number of independent parts is taken as two and the proposed method is tested for image sequences from UAV dataset with various visual problems. The comparisons with the state-of-the-art trackers show that the proposed method achieves good precision and success scores, and outperforms most of the state-of-the-art trackers.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Code Availability
The source codes will be shared at the time of acceptance.
References
Maraş, B., Arica, N., Baytan Ertüzün, A.: Görsel hedef takibi yöntemlerine genel bakış. EMO BİLİMSEL DERGİ 7, 5–16 (2017)
Taufique, A.M.N., Minnehan, B., Savakis, A.: Benchmarking deep trackers on aerial videos, (2020) arXiv:2103.12924v1 [cs.CV]. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20020547
Zhang, S., Zhuo, L., Zhang, H., Li, J.: Object tracking in unmanned aerial vehicle videos via multifeature discrimination and instance-aware attention network. Remote Sensing 12, 2646 (2020)
Wu, Y., Lim, J., Yang, M.-H.: Online object tracking: A benchmark. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2013)
Wu, Y., Lim, J., Yang, M.-H.: Object tracking benchmark. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 37, 1–1 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2388226
Matthias Mueller, N.S., Ghanem, B.: A benchmark and simulator for uav tracking. ECCV (2016)
Fiaz, M., Mahmood, A., Javed, S., Jung, S.K.: Handcrafted and Deep Trackers: Recent Visual Object Tracking Approaches and Trends (2019)
Müller, M., Smith, N., Ghanem, B.: A benchmark and simulator for uav tracking (2016)
Du, D., Qi, Y., Yu, H., Yang, Y., Duan, K., Li, G., Zhang, W., Huang, Q., Tian, Q.: The Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Benchmark: Object Detection and Tracking (2018)
Johansen, Adam M., Doucet, A.: A Note on Auxiliary Particle Filters. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2008)
Kalal, Z., Matas, J., Mikolajczyk, K.: P-n learning: Bootstrapping binary classifiers by structural constraints. In: 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 49–56 (2010)
Baker, S., Matthews, I.: Lucas-kanade 20 years on: A unifying framework. Int. J. Comput. Vision 56(3), 221–255 (2004)
Henriques, J.F., Caseiro, R., Martins, P., Batista, J.: Exploiting the circulant structure of tracking-by-detection with kernels. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pp. 702–715 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-33765-9_50
Henriques, J.F., Caseiro, R., Martins, P., Batista, J.: High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 37(3), 583–596 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/tpami.2014.2345390
Danelljan, M., Häger, G., Khan, F.S., Felsberg, M.: Discriminative scale space tracking. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39, 1561–1575 (2017)
Danelljan, M., Hager, G., Khan, F.S., Felsberg, M.: Learning spatially regularized correlation filters for visual tracking. In: 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/iccv.2015.490
Hare, S., Saffari, A., Torr, P.H.S.: Struck: Structured output tracking with kernels. In: 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/iccv.2011.6126251
Hare, S., Golodetz, S., Saffari, A., Vineet, V., Cheng, M.-M., Hicks, S.L., Torr, P.H.S.: Struck: structured output tracking with kernels. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 38(10), 2096–109 (2016)
Zhang, J., Ma, S., Sclaroff, S.: Meem: Robust tracking via multiple experts using entropy minimization. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 188–203 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10599-4_13
Nam, H., Han, B.: Learning Multi-Domain Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Tracking (2016)
Pu, S., Song, Y., Ma, C., Zhang, H., Yang, M.: Deep attentive tracking via reciprocative learning. arXiv:1810.03851 (2018)
Xia, Y., Qu, S., Goudos, S., Bai, Y., Wan, S.: Multi-object tracking by mutual supervision of cnn and particle filter. Pers. Ubiquit. Comput. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00779-019-01278-1
Danelljan, M., Robinson, A., Shahbaz Khan, F., Felsberg, M.: Beyond correlation filters: Learning continuous convolution operators for visual tracking. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 472–488 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46454-1_29
Danelljan, M., Bhat, G., Khan, F.S., Felsberg, M.: ECO: Efficient Convolution Operators for Tracking (2017)
Li, F., Tian, C., Zuo, W., Zhang, L., Yang, M.-H.: Learning Spatial-Temporal Regularized Correlation Filters for Visual Tracking (2018)
Jalil Mozhdehi, R., Medeiros, H.: Deep convolutional particle filter for visual tracking, pp. 3650–3654 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.2017.8296963
Bertinetto, L., Valmadre, J., Henriques, J.F., Vedaldi, A., Torr, P.H.S.: Fully-Convolutional Siamese Networks for Object Tracking (2016)
Li, B., Yan, J., Wu, W., Zhu, Z., Hu, X.: High performance visual tracking with Siamese region proposal network. In: 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8971–8980 (2018)
Zhu, Z., Wang, Q., Li, B., Wu, W., Yan, J., Hu, W.: Distractor-Aware Siamese Networks for Visual Object Tracking (2018)
Hong, Z., Chen, Z., Wang, C., Mei, X., Prokhorov, D.V., Tao, D.: Multi-store tracker (muster): a cognitive psychology inspired approach to object tracking. In: 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 749–758 (2015)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. CoRR abs/1409.1556 (2015)
Russakovsky, O., Deng, J., Su, H., Krause, J., Satheesh, S., Ma, S., Huang, Z., Karpathy, A., Khosla, A., Bernstein, M., Berg, A.C., Fei-Fei, L.: ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. (IJCV) 115(3), 211–252 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-015-0816-y
Candy, J.V.: Bayesian Signal Processing: Classical, Modern and Particle Filtering Methods. Wiley-Interscience, USA (2009)
Smeulders, A.W.M., Chu, D.M., Cucchiara, R., Calderara, S., Dehghan, A., Shah, M.: Visual tracking: An experimental survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. (2014)
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by TÜBİTAK ARDEB 1001 Program (The Scientific and Technological Research Council Of Turkey Support Program for Scientific and Technological Research Projects) under project number 119E596.
Funding
This study is supported by TÜBİTAK ARDEB 1001 Program under project number 119E596.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Maraş, B., Arica, N. & Ertüzün, A. A robust vehicle tracking in low-altitude UAV videos. Machine Vision and Applications 34, 77 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-023-01427-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-023-01427-w