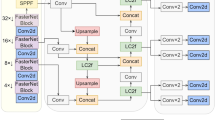
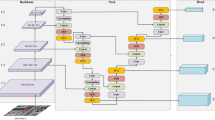
Abstract
An emergency risk assessment by collecting disaster-affected images via unmanned aerial vehicles is the current norm. Reasonable rescue planning and resource allocation depend on a quick and precise semantic interpretation of natural disaster images. However, the poor image quality produced by various technological and environmental factors and complex scenarios associated with disaster-affected regions makes the classification operation challenging. In order to get in-depth spatial features for decoding the intricate textures associated with catastrophe images, this study proposes an implementation of the CNN-based multibranch feature extraction technique. An advanced mixed-attention mechanism is exploited to extract the highly essential features. This mixed-attention mechanism effectively overcomes the flaws generated by traditional convolution by neglecting the global information and focusing on local key features. An SRGAN-based super-resolution method is utilized to acquire high-resolution images with rich spatial details to enhance the quality of aerial images. Besides, we experiment with several existing image classification algorithms, such as the ensemble model of pre-trained networks, the capsule network model, and the stacked autoencoder. Finally, we perform a comparative analysis between all the deployed models to obtain the best-performing classifier. Our proposed multibranch feature extraction with mixed-attention mechanism-based network performs more superiorly among the four models due to its ability to extract highly relevant features from disaster images. Generated super-resolution images effectively increase the classification performance. Our research findings and approaches accommodate quality resources for disaster image quality enhancement and classification activities.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Salluri, D., Bade, K., Madala, G.: Object detection using convolutional neural networks for natural disaster recovery. Int. J. Saf. Secur. Eng. 10(2), 285 (2020)
Akram, T., Awais, M., Naqvi, R., Ahmed, A., Naeem, M.: Multicriteria uav base stations placement for disaster management. IEEE Syst. J. 14(3), 3475–3482 (2020)
Aamir, M., Ali, T., Irfan, M., Shaf, A., Azam, M.Z., Glowacz, A., Brumercik, F., Glowacz, W., Alqhtani, S., Rahman, S.: Natural disasters intensity analysis and classification based on multispectral images using multi-layered deep convolutional neural network. Sensors 21(8), 2648 (2021)
Lopez-Fuentes, L., van de Weijer, J., Gonz’alez-Hidalgo, M., Skinnemoen, H., Bagdanov, A.D.: Review on computer vision techniques in emergency situations. Multimedia Tools Appl. 77(13), 17069–17107 (2018)
Kyrkou, C., Theocharides, T.: Deep-learning-based aerial image classification for emergency response applications using unmanned aerial vehicles. In: CVPR Workshops, pp. 517–525 (2019)
Munawar, H.S., Ullah, F., Qayyum, S., Khan, S.I., Mojtahedi, M.: Uavs in disaster management: Application of integrated aerial imagery and convolutional neural network for flood detection. Sustainability 13(14), 7547 (2021)
Osco, L.P., Junior, J.M., Ramos, A.P.M., Jorge, L.A.d.C., Fatholahi, S.N., Silva, J.d.A., Matsubara, E.T., Pistori, H., Gon¸calves, W.N., Li, J.: A review on deep learning in uav remote sensing. arXiv preprint arXiv:2101.10861 (2021)
Wang, T., Sun, W., Qi, H., Ren, P.: Aerial image super resolution via wavelet multiscale convolutional neural networks. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 15(5), 769–773 (2018)
Vetrivel, A., Gerke, M., Kerle, N., Vosselman, G.: Identification of structurally damaged areas in airborne oblique images using a visual-bagof-words approach. Remote Sens. 8(3), 231 (2016)
Gonz’alez, D., Patricio, M.A., Berlanga, A., Molina, J.M.: A super-resolution enhancement of uav images based on a convolutional neural network for mobile devices. Personal Ubiquit. Comput. 26, 1–12 (2019)
Vetrivel, A., Gerke, M., Kerle, N., Vosselman, G.: Identification of damage in buildings based on gaps in 3d point clouds from very high resolution oblique airborne images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 105, 61–78 (2015)
Xiong, Y., Guo, S., Chen, J., Deng, X., Sun, L., Zheng, X., Xu, W.: Improved srgan for remote sensing image super-resolution across locations and sensors. Remote Sens. 12(8), 1263 (2020)
Ma, W., Pan, Z., Guo, J., Lei, B.: Super-resolution of remote sensing images based on transferred generative adversarial network. In: IGARSS 2018–2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, pp. 1148–1151. IEEE (2018)
Yang, J.-J., Li, J., Shen, R., Zeng, Y., He, J., Bi, J., Li, Y., Zhang, Q., Peng, L., Wang, Q.: Exploiting ensemble learning for automatic cataract detection and grading. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 124, 45–57 (2016)
Erdelj, M., Kr’ol, M., Natalizio, E.: Wireless sensor networks and multiuav systems for natural disaster management. Comput. Netw. 124, 72–86 (2017)
Vetrivel, A., et al.: Disaster damage detection through synergistic use of deep learning and 3D point cloud features derived from very high resolution oblique aerial images, and multiple-kernel-learning. ISPRS J. Photogram. Remote Sens. 140, 45–59 (2018)
Li, S., Yan, Q., Liu, P.: An efficient fire detection method based on multiscale feature extraction, implicit deep supervision and channel attention mechanism. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 29, 8467–8475 (2020)
Hong, Z., et al.: Classification of building damage using a novel convolutional neural network based on post-disaster aerial images. Sensors 22(15), 5920 (2022)
Ma, Z., et al.: Triple-strip attention mechanism-based natural disaster images classification and segmentation. Vis. Comput. 38(9), 3163–3173 (2022)
Li, Y., et al.: Unsupervised domain adaptation with self-attention for post-disaster building damage detection. Neurocomputing 415, 27–39 (2020)
Peng, X., et al.: Optical remote sensing image change detection based on attention mechanism and image difference. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 59(9), 7296–7307 (2020)
Szegedy, C., et al.: Going deeper with convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2015)
Kumar, A.D.: Novel deep learning model for traffic sign detection using capsule networks. arXiv:1805.04424 (2018)
Pourashraf, P., Tomuro, N., Apostolova, E.: Genre-based image classification using ensemble learning for online flyers. In: Seventh International Conference on Digital Image Processing (ICDIP 2015), vol. 9631, p. 96310. International Society for Optics and Photonics (2015)
Feng, S., Zhou, H., Dong, H.: Using deep neural network with small dataset to predict material defects. Mater. Des. 162, 300–310 (2019)
Zhou, S., Xue, Z., Du, P.: Semisupervised stacked autoencoder with cotraining for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 57(6), 3813–3826 (2019)
Lv, F., Han, M., Qiu, T.: Remote sensing image classification based on ensemble extreme learning machine with stacked autoencoder. IEEE Access 5, 9021–9031 (2017)
Khamparia, A., Saini, G., Pandey, B., Tiwari, S., Gupta, D., Khanna, A.: Kdsae: chronic kidney disease classification with multimedia data learning using deep stacked autoencoder network. Multimedia Tools Appl. 79(47), 35425–35440 (2020)
Kyrkou, C., Theocharides, T.: Emergencynet: efficient aerial image classification for drone-based emergency monitoring using atrous convolutional feature fusion. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 13, 1687–1699 (2020)
Erdelj, M., Natalizio, E., Chowdhury, K.R., Akyildiz, I.F.: Help from the sky: leveraging uavs for disaster management. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 16(1), 24–32 (2017)
Quaritsch, M., Kruggl, K., Wischounig-Strucl, D., Bhattacharya, S., Shah, M., Rinner, B.: Networked uavs as aerial sensor network for disaster management applications. e & I Elektrotechnik und Informationstechnik 127(3), 56–63 (2010)
Dong, C., Loy, C.C., He, K., Tang, X.: Learning a deep convolutional network for image super-resolution. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 184–199. Springer (2014)
Kim, J., Lee, J.K., Lee, K.M.: Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1646–1654 (2016)
Ledig, C., Theis, L., Husz'ar, F., Caballero, J., Cunningham, A., Acosta, A., Aitken, A., Tejani, A., Totz, J., Wang, Z., et al.: Photorealistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4681–4690 (2017)
Burdziakowski, P.: Increasing the geometrical and interpretation quality of unmanned aerial vehicle photogrammetry products using super-resolution algorithms. Remote Sens. 12(5), 810 (2020)
Risojevi'c, V., Momi'c, S., Babi'c, Z.: Gabor descriptors for aerial image classification. In: International Conference on Adaptive and Natural Computing Algorithms, pp. 51–60. Springer (2011)
Cao, Q.D., Youngjun, C.: Building damage annotation on post-hurricane satellite imagery based on convolutional neural networks. Nat. Hazards 103(3), 3357–3376 (2020)
Zhang, D.Y., et al.: Crowd-assisted disaster scene assessment with human-ai interactive attention. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 34. No. 03. (2020)
Phung, V.H., Rhee, E.J., et al.: A high-accuracy model average ensemble of convolutional neural networks for classification of cloud image patches on small datasets. Appl. Sci. 9(21), 4500 (2019)
Xue, D., Zhou, X., Li, C., Yao, Y., Rahaman, M.M., Zhang, J., Chen, H., Zhang, J., Qi, S., Sun, H.: An application of transfer learning and ensemble learning techniques for cervical histopathology image classification. IEEE Access 8, 104603–104618 (2020)
Liu, X., Hu, Q., Cai, Y., Cai, Z.: Extreme learning machine-based ensemble transfer learning for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 13, 3892–3902 (2020)
Walambe, R., Marathe, A., Kotecha, K.: Multiscale object detection from drone imagery using ensemble transfer learning. Drones 5(3), 66 (2021)
Lei, R., Zhang, C., Liu, W., Zhang, L., Zhang, X., Yang, Y., Huang, J., Li, Z., Zhou, Z.: Hyperspectral remote sensing image classification using deep convolutional capsule network. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 14, 8297–8315 (2021)
Li, W., Fu, H., Yu, L., Gong, P., Feng, D., Li, C., Clinton, N.: Stacked autoencoder-based deep learning for remote-sensing image classification: a case study of african land-cover mapping. Int. J. Remote Sens. 37(23), 5632–5646 (2016)
Pi, Y., Nath, N.D., Behzadan, A.H.: Convolutional neural networks for object detection in aerial imagery for disaster response and recovery. Adv. Eng. Inform. 43, 101009 (2020)
Baker, S., Kanade, T.: Limits on super-resolution and how to break them. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 24(9), 1167–1183 (2002)
Tai, Y.-W., Liu, S., Brown, M.S., Lin, S.: Super resolution using edge prior and single image detail synthesis. In: 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2400–2407. IEEE (2010)
Gupta, R., Sharma, A., Kumar, A.: Super-resolution using gans for medical imaging. Procedia Comput. Sci. 173, 28–35 (2020)
Cai, W., et al.: Remote sensing image recognition based on multi-attention residual fusion networks. ASP Trans. Pattern Recognit. Intell. Syst. 1(1), 1–8 (2021)
Meng, W., Tia, M.: Unmanned aerial vehicle classification and detection based on deep transfer learning. In: 2020 International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Human-Computer Interaction (ICHCI), pp. 280–285. IEEE (2020)
Sandler, M., Howard, A., Zhu, M., Zhmoginov, A., Chen, L.-C.: Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4510–4520 (2018)
Ahmad, F., Farooq, A., Ghani, M.U.: Deep ensemble model for classification of novel coronavirus in chest x-ray images. In: Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience 2021 (2021)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Identity mappings in deep residual networks. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 630–645. Springer (2016)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Rezende, E., Ruppert, G., Carvalho, T., Ramos, F., De Geus, P.: Malicious software classification using transfer learning of resnet-50 deep neural network. In: 2017 16th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), pp. 1011–1014. IEEE (2017)
Evans, B.: Population-based ensemble learning with tree structures for classification (2019)
Ding, X., Li, Y., Yang, J., Li, H., Liu, L., Liu, Y., Zhang, C.: An adaptive capsule network for hyperspectral remote sensing classification. Remote Sens. 13(13), 2445 (2021)
Kruthika, K., Maheshappa, H., Initiative, A.D.N., et al.: Cbir system using capsule networks and 3d cnn for alzheimer’s disease diagnosis. Inf. Med. Unlocked 14, 59–68 (2019)
Kandel, I., Castelli, M., Popoviˇc, A.: Comparing stacking ensemble techniques to improve musculoskeletal fracture image classification. J. Imaging 7(6), 100 (2021)
Abro, A.A., Tasci, E., Aybars, U.: A stacking-based ensemble learning method for outlier detection. Balkan J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 8(2), 181–185 (2020)
Niloy, F.F., Siddik Nayem, A.B., Sarker, A., Paul, O., Ashraful Amin, M., Ali, A.A., Zaber, M.I., Mahbubur Rahman, A.K.M.: A novel disaster image data-set and characteristics analysis using attention model. In: 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), pp. 6116–6122. IEEE (2021)
Munawar, H.S., Ullah, F., Qayyum, S., Heravi, A.: Application of deep learning on uav-based aerial images for flood detection. Smart Cities 4(3), 1220–1242 (2021)
Chowdhury, T., Murphy, R., Rahnemoonfar, M.: Rescuenet: a high resolution UAV semantic segmentation benchmark dataset for natural disaster damage assessment. arXiv:2202.12361 (2022)
Zou, Z., Gan, H., Huang, Q., Cai, T., Cao, K.: Disaster image classification by fusing multimodal social media data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inf. 10(10), 636 (2021)
Dinani, S.T., Caragea, D.: Disaster image classification using capsule networks. In: 2021 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 1–8. IEEE (2021)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bhadra, P., Balabantaray, A. & Pasayat, A.K. MFEMANet: an effective disaster image classification approach for practical risk assessment. Machine Vision and Applications 34, 76 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-023-01430-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-023-01430-1