Abstract
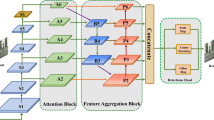
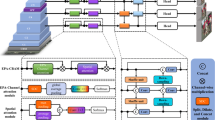
In recent years, despite the significant performance improvement for pedestrian detection algorithms in crowded scenes, an imbalance between detection accuracy and speed still exists. To address this issue, we propose an adjacent features complementary network for crowded pedestrian detection based on one-stage anchor-free detector, which is called AFC-Net. Firstly, deep dilated convolution (DDC) is invoked in the backbone to expand receptive fields, so that the feature map can remain its original size with feature spatial sensitivity enhanced. Secondly, hierarchical feature extraction (HFE) is designed to extract feature information pertinently according to the feature properties from different layers. Specifically, multi-scale feature extractor and channel attention mechanism are employed to extract contextual information among features on high-level features. Spatial attention mechanism is applied to filter background information on low-level features. Finally, adjacent feature integration (AFI) is proposed to aggregate the correlative features of adjacent layers so as to make expressive ability of features more comprehensive, thus improving the pedestrian detection results. In the challenging CityPersons dataset and CrowdHuman dataset, the crowded scene pedestrian detection network with complementary adjacent features has achieved great results in pedestrian detection. The result achieved from the experiment shows that the proposed algorithm can still maintain the comparability and stability of detection accuracy, while the network parameters are greatly reduced and the speed is effectively improved.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bi, L., Feng, D.D., Fulham, M., Kim, J.: Multi-label classification of multi-modality skin lesion via hyper-connected convolutional neural network. Pattern Recogn. 107, 107502 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107502
Ke, X., Lin, X., Qin, L.: Lightweight convolutional neural network-based pedestrian detection and re-identification in multiple scenarios. Mach. Vis. Appl. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-021-01169-7
Murthy, C.B., Hashmi, M.F., Keskar, A.: Efficientlitedet: a real-time pedestrian and vehicle detection algorithm. Mach. Vis. Appl. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-022-01293-y
Jung, H.-K., Choi, G.-S.: Improved yolov5: efficient object detection using drone images under various conditions. Appl. Sci. (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/app12147255
Lowe, D.G.: Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 60, 91–110 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94
Dalal, N., Triggs, B.: Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In: IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), volume 1. IEEE, vol. 2005, pp. 886–893 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2005.177
Fu, K., Zhao, Q., Gu, I.Y.-H., Yang, J.: Deepside: a general deep framework for salient object detection. Neurocomputing 356, 69–82 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2019.04.062
Lin, C., Lu, J., Wang, G., Zhou, J.: Graininess-aware deep feature learning for pedestrian detection. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) Computer Vision—ECCV 2018, pp. 745–761. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01240-3_45
Xie, J., Pang, Y., Cholakkal, H., Anwer, R., Khan, F., Shao, L.: PSC-NET: learning part spatial co-occurrence for occluded pedestrian detection. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 64, 1–13 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-020-2969-8
Liu, W., Liao, S., Ren, W., Hu, W., Yu, Y.: High-level semantic feature detection: a new perspective for pedestrian detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5187–5196 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00533
Zhuang, C., Li, Z., Zhu, X., Lei, Z., Li, S.Z.: SADet: learning an efficient and accurate pedestrian detector. In: 2021 IEEE International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB), IEEE, pp. 1–8 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/IJCB52358.2021.9484371
Hou, Q., Cheng, M.-M., Hu, X., Borji, A., Tu, Z., Torr, P.H.: Deeply supervised salient object detection with short connections. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3203–3212 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2815688
Wang, J., Yu, J., He, Z.: DECA: a novel multi-scale efficient channel attention module for object detection in real-life fire images. Appl. Intell. 52, 1362–1375 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02496-y
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., Sun, J.: Faster r-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031
Qin, Z., Li, Z., Zhang, Z., Bao, Y., Yu, G., Peng, Y., Sun, J.: Thundernet: towards real-time generic object detection on mobile devices. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 6718–6727 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00682
Wang, Z., Wu, Z., Lu, J., Zhou, J.: BiDet: an efficient binarized object detector. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2049–2058 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00212
Cui, Y., Yang, L., Liu, D.: Dynamic proposals for efficient object detection (2022). arXiv:2207.05252
Huang, L., Yang, Y., Deng, Y., Yu, Y.: Densebox: unifying landmark localization with end to end object detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:1509.04874 (2015). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1509.04874
Duan, K., Bai, S., Xie, L., Qi, H., Huang, Q., Tian, Q.: Centernet: keypoint triplets for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 6569–6578 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00667
Liu, Z., Zheng, T., Xu, G., Yang, Z., Liu, H., Cai, D.: Training-time-friendly network for real-time object detection. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 11685–11692 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v34i07.6838
Su, H., He, Y., Jiang, R., Zhang, J., Zou, W., Fan, B.: DSLA: dynamic smooth label assignment for efficient anchor-free object detection. Pattern Recogn. 131, 108868 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2022.108868
Liu, S., Huang, D., Wang, Y.: Adaptive NMS: refining pedestrian detection in a crowd. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6459–6468 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00662
Wang, J., Zhao, C., Huo, Z., Qiao, Y., Sima, H.: High quality proposal features generation for crowded pedestrian detection. Pattern Recogn. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2022.108605
Zhou, K., Chen, L., Cao, X.: Improving multispectral pedestrian detection by addressing modality imbalance problems. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 787–803. Springer (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58523-5_46
Lin, T.-Y., Goyal, P., Girshick, R., He, K., Dollár, P.: Focal loss for dense object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2980–2988 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.324
Lin, T.-Y., Dollár, P., Girshick, R., He, K., Hariharan, B., Belongie, S.: Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2117–2125 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.106
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90
Ma, J., Wan, H., Wang, J., Xia, H., Bai, C.: An improved scheme of deep dilated feature extraction on pedestrian detection. SIViP 15, 231–239 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-020-01742-z
Zhang, S., Benenson, R., Schiele, B.: Citypersons: a diverse dataset for pedestrian detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3213–3221 (2017). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1702.05693
Shao, S., Zhao, Z., Li, B., Xiao, T., Yu, G., Zhang, X., Sun, J.: Crowdhuman: a benchmark for detecting human in a crowd. arXiv preprint arXiv:1805.00123 (2018). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1805.00123
Liu, W., Liao, S., Hu, W., Liang, X., Chen, X.: Learning efficient single-stage pedestrian detectors by asymptotic localization fitting. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 618–634 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01264-9_38
Ma, J., Wan, H., Wang, J., Xia, H., Bai, C.: An improved one-stage pedestrian detection method based on multi-scale attention feature extraction. J. Real-Time Image Proc. 18, 1965–1978 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsp.2021.103311
Li, Q., Qiang, H., Li, J.: Conditional random fields as message passing mechanism in anchor-free network for multi-scale pedestrian detection. Inf. Sci. 550, 1–12 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsp.2021.103311
Zhang, S., Wen, L., Bian, X., Lei, Z., Li, S. Z.: Occlusion-aware r-CNN: detecting pedestrians in a crowd. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 637–653 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01219-9_39
Lu, R., Ma, H., Wang, Y.: Semantic head enhanced pedestrian detection in a crowd. Neurocomputing 400, 343–351 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2020.03.037
Wang, X., Xiao, T., Jiang, Y., Shao, S., Sun, J., Shen, C.: Repulsion loss: detecting pedestrians in a crowd. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7774–7783 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00811
Zhang, S., Yang, X., Liu, Y., Xu, C.: Asymmetric multi-stage CNNs for small-scale pedestrian detection. Neurocomputing 409, 12–26 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2020.05.019
Zhang, Y., Yi, P., Zhou, D., Yang, X., Yang, D., Zhang, Q., Wei, X.: CSANet: channel and spatial mixed attention CNN for pedestrian detection. IEEE Access 8, 76243–76252 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2986476
Song, T., Sun, L., Xie, D., Sun, H., Pu, S.: Small-scale pedestrian detection based on topological line localization and temporal feature aggregation. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 536–551 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_33
Wang, Z., Wang, J., Yang, Y.: Resisting the distracting-factors in pedestrian detection. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2020). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2005.07344
Tian, Z., Shen, C., Chen, H., He, T.: FCOS: fully convolutional one-stage object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 9627–9636 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00972
Rukhovich, D., Sofiiuk, K., Galeev, D., Barinova, O., Konushin, A.: IterDet: iterative scheme for object detection in crowded environments. In: Joint IAPR International Workshops on Statistical Techniques in Pattern Recognition (SPR) and Structural and Syntactic Pattern Recognition (SSPR), pp. 344–354. Springer (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-73973-7_33
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Fundamental Research Funds for the Universities of Henan Province (NSFRF220414) and Excellent Young Teachers Program of Henan Polytechnic University (No. 2019XQG-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Zhao, C., Liu, Z. et al. AFC-Net: adjacent feature complementary for crowded pedestrian detection. Machine Vision and Applications 34, 85 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-023-01439-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-023-01439-6