Abstract
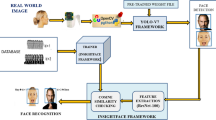
Considering the necessity of sensitive information protection in face image, a cancelable template generation model for multimodal face images is proposed in this paper. Firstly, the visual meaningful face images are transformed into phase-only functions through phase retrieval in gyrator domain. Then random projection and chaotic-based mask are constituted into modulation for achieving revocability and distinguishability. The interim results are mapped to a higher-dimensional space using random Fourier features. Followed by two-stage complex-valued principal component analysis, the convolutional filters are learned efficiently. Together with binary hashing and decimal coding, local histogram features are obtained and forwarded to SVM for training and recognition. Experiments performed on three publicly multimodal datasets demonstrate that the proposed algorithm can obtain higher accuracy, precision, recall and F-score in comparison with some existing algorithms while the templates are non-invertible and easy to revoke.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mai, G., Cao, K., Lan, X., Yuen, P.C.: Secureface: face template protection. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 16, 262–277 (2021)
Morris, J., Newman, S., Palaniappan, K., Fan, J., Lin, D.: “Do you know you are tracked by photos that you didn’t take”: large-scale location-aware multi-party image privacy protection. IEEE Trans. Dep. Secur. Comput. 20(1), 301–312 (2023)
Tang, Y., Shao, Z., Zhao, X., Shang, Y.: Robust multiple color images encryption using discrete Fourier Transforms and chaotic map. Signal Process. Image Commun. 93, 116168 (2021)
Manisha Kumar, N.: Cancelable biometrics: a comprehensive survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 53, 3403–3446 (2020)
Soliman, R.F., El Banby, G.M., Algarni, A.D., Elsheikh, M., Soliman, N.F., Amin, M., Abd El-Samie, F.E.: Double random phase encoding for cancelable face and iris recognition. Appl. Optics 57, 10305–10316 (2018)
Verma, G., Liao, M., Lu, D., He, W., Peng, X.: A novel optical two-factor face authentication scheme. Opt. Lasers Eng. 123, 28–36 (2019)
Abou Elazm, L.A., Ibrahim, S., Egila, M.G., Shawky, H., Elsaid, M.K., El-Shafai, W., Abd El-Samie, F.E.: Cancelable face and fingerprint recognition based on the 3D jigsaw transform and optical encryption. Multim. Tools Appl. 79(19), 14053–14078 (2020)
Alarifi, A., Amoon, M., Aly, M.H., El-Shafai, W.: Optical PTFT asymmetric cryptosystem-based secure and efficient cancelable biometric recognition system. IEEE Access 8, 221246–221268 (2020)
Sardar, A., Umer, S., Pero, C., Nappi, M.: A novel cancelable FaceHashing technique based on non-invertible transformation with encryption and decryption template. IEEE Access 8, 105263–105277 (2020)
Xu, Z., Shao, Z., Shang, Y., Li, B., Ding, H., Liu, T.: Fusing structure and color features for cancelable face recognition. Multim. Tools Appl. 80, 14477–14494 (2021)
Feng, Y.C., Yuen, P.C., Jain, A.K.: A hybrid approach for generating secure and discriminating face template. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 5(1), 103–117 (2010)
Ashiba, H.I.: Proposed framework for cancelable face recognition system. Multim. Tools Appl. 80, 13677–13705 (2021)
Minaee, S., Luo, P., Lin, Z., Bowyer, K.: Going deeper into face detection: A survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.14983 (2021)
He, K., Zhang., X, Ren, S, Sun J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Zhou, D., Feng, S.: M3SPCANet: a simple and effective ConvNets with unsupervised predefined filters for face recognition. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 113, 104936 (2022)
Chen, L., Zhao, G., Zhou, J., Ho, A.T., Cheng, L.M.: Face template protection using deep LDPC codes learning. IET Biomet. 8(3), 190–197 (2019)
Kumar Jindal, A., Chalamala, S., Kumar Jami, S.: Face template protection using deep convolutional neural network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 462–470 (2018)
Lee, H., Low, C. Y., Teoh, A. B. J.: SoftmaxOut transformation-permutation network for facial template protection. In: International Conference on Pattern Recognition, pp. 7558–7565 (2021)
Yang, X., Dong, Y., Pang, T., Su, H., Zhu, J., Chen, Y., Xue, H.: Towards face encryption by generating adversarial identity masks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3897–3907 (2021)
Singh, A., Vashist, C., Gaurav, P., Nigam, A.: A generic framework for deep incremental cancelable template generation. Neurocomputing 467, 83–98 (2022)
Hahn, V.K., Marcel, S.: Towards protecting face embeddings in mobile face verification scenarios. IEEE Trans. Biom. Behav. Identity Sci. 4(1), 117–134 (2022)
Gomez-Barrero, M., Rathgeb, C., Li, G., Ramachandra, R., Galbally, J., Busch, C.: Multi-biometric template protection based on bloom filters. Inf. Fusion 42, 37–50 (2018)
Kaur, H., Khanna, P.: Random distance method for generating unimodal and multimodal cancelable biometric features. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 14(3), 709–719 (2019)
Walia, G.S., Jain, G., Bansal, N., Singh, K.: Adaptive weighted graph approach to generate multimodal cancelable biometric templates. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 15, 1945–1958 (2020)
Asthana, R., Walia, G.S., Gupta, A.: Random area-perimeter method for generation of unimodal and multimodal cancelable biometric templates. Appl. Intell. 51, 7281–7297 (2021)
Shao, Z., Shang, Y., Fu, X., Yuan, H., Shu, H.: Double-image cryptosystem using chaotic map and mixture amplitude-phase retrieval in gyrator domain. Multim. Tools Appl. 77(1), 1285–1298 (2018)
Hua, Z., Zhou, Y.: Exponential chaotic model for generating robust chaos. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 51(6), 3713–3724 (2019)
Qaraei, M., Abbaasi, S., Ghiasi-Shirazi, K.: Randomized non-linear PCA networks. Inf. Sci. 545, 241–253 (2021)
Chang, C.C., Lin, C.J.: LIBSVM: A library for support vector machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2(27), 1–27 (2011)
Xu, Y., Zhong, A.N., Yang, J., Zhang, D.: Bimodal biometrics based on a representation and recognition approach. Opt. Eng. 50(3), 037202 (2011)
Goswami, G., Bharadwaj, S., Vatsa, M., Singh, R.: On RGB-D face recognition using Kinect. In: Sixth International Conference on Biometrics: Theory, Applications and Systems, pp.1–6 (2013)
Wang, S., Liu, Z., Lv, S., Lv, Y., Wu, G., Peng, P., Chen, F., Wang, X.: A natural visible and infrared facial expression database for expression recognition and emotion inference. IEEE Trans. Multim. 12(7), 682–691 (2010)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61601311), Research Fund of Guangxi Key Lab of Multi-source Information Mining & Security (MIMS23-08), Science and Technology Innovation Talent Project of Education Department of Henan Province (No. 23HASTIT030), Science and Technology Planning Project of Jiaxing (2022AY10021) and Scientific Research Project of Education Department of Jilin Province (JJKH20240586KJ). The authors greatly appreciate the anonymous reviewers for their helpful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z.S. and L.L.: Methodology, software, writing—original draft. Z.Z., B.L., and X.L.: Software; Visualization. Y.S. and B.C.: Writing—review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, Z., Li, L., Zhang, Z. et al. Cancelable face recognition using phase retrieval and complex principal component analysis network. Machine Vision and Applications 35, 12 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-023-01496-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-023-01496-x