Abstract.
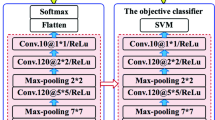
Morphological shared-weight neural networks (MSNN) combine the feature extraction capability of mathematical morphology with the function-mapping capability of neural networks in a single trainable architecture. The MSNN method has been previously demonstrated using a variety of imaging sensors, including TV, forward-looking infrared (FLIR) and synthetic aperture radar (SAR). In this paper, we provide experimental results with laser radar (LADAR). We present three sets of experiments. In the first set of experiments, we use the MSNN to detect different types of targets simultaneously. In the second set, we use the MSNN to detect only a particular type of target. In the third set, we test a novel scenario, referred to as the Sims scenario: we train the MSNN to recognize a particular type of target using very few examples. A detection rate of 86% with a reasonable number of false alarms was achieved in the first set of experiments and a detection rate of close to 100% with very few false alarms was achieved in the second and third sets of experiments. In all the experiments, a novel pre-processing method is used to create a pseudo-intensity images from the original LADAR range images.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khabou, M., Gader, P. & Keller, J. LADAR target detection using morphological shared-weight neural networks. Machine Vision and Applications 11, 300–305 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001380050114
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001380050114