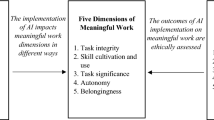
Abstract
Much of the current work on AI ethics has lost its connection to the real-world impact by making AI ethics operable. There exist significant limitations of hyper-focusing on the identification of abstract ethical principles, lacking effective collaboration among stakeholders, and lacking the communication of ethical principles to real-world applications. This position paper presents challenges in making AI ethics operable and highlights key obstacles to AI ethics impact. A preliminary practice example is provided to initiate practical implementations of AI ethics. We aim to inspire discussions on making AI ethics operable and focus on its impact on real-world applications.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data statements
This paper has no associated data.
References
AlgorithmWatch (2020) AI ethics guidelines global inventory. https://algorithmwatch.org/en/project/ai-ethics-guidelines-global-inventory/. Accessed 18 Oct 2020
Alvarez-Melis D, Jaakkola TS (2018) Towards robust interpretability with self-explaining neural networks. arXiv:1806.07538 [cs, stat]
Amrollahi M, Hadayeghparast S, Karimipour H et al (2020) Enhancing network security via machine learning: opportunities and challenges. In: Choo K-KR, Dehghantanha A (eds) Handbook of big data privacy. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 165–189
Anastasopoulos LJ, Whitford AB (2019) Machine learning for public administration research, with application to organizational reputation. J Public Adm Res Theory 29:491–510. https://doi.org/10.1093/jopart/muy060
Awoyemi JO, Adetunmbi AO, Oluwadare SA (2017) Credit card fraud detection using machine learning techniques: a comparative analysis. In: 2017 international conference on computing networking and informatics (ICCNI), pp 1–9
Batmaz Z, Yurekli A, Bilge A, Kaleli C (2019) A review on deep learning for recommender systems: challenges and remedies. Artif Intell Rev 52:1–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-018-9654-y
Bird E, Fox-Skelly J, Jenner N, et al (2020) The ethics of artificial intelligence: issues and initiatives. European Parliamentary Research Service
Blackman R (2022) Why you need an AI ethics committee. Harvard Bus Rev. July-August 2022
Bojarski M, Del Testa D, Dworakowski D et al (2016) End to end learning for self-driving cars. arXiv preprint. arXiv:1604.07316
Bossmann J (2016) Top 9 ethical issues in artificial intelligence. In: World economic forum. https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2016/10/top-10-ethical-issues-in-artificial-intelligence/. Accessed 9 Sept 2019
Capgemini (2019) Why addressing ethical questions in AI will benefit organizations. In: Capgemini worldwide. https://www.capgemini.com/research/why-addressing-ethical-questions-in-ai-will-benefit-organizations. Accessed 10 Oct 2021
Corinium (2019) Ethics of AI. https://cdn2.hubspot.net/hubfs/2631050/CDAO%20New%20Zealand/Corinium_Ethics-of-AI_brochure_NZ.pdf. Accessed 8 Aug 2019
Dawson D, Schleiger E, Horton J, et al (2019) Artificial intelligence—Australia’s ethics framework. In: Data61, CSIRO, Australia
Deane M (2018) AI and the future of privacy. In: Towards data science. https://towardsdatascience.com/ai-and-the-future-of-privacy-3d5f6552a7c4. Accessed 16 May 2019
Dewey J, Tufts JH (2019) Ethics. Good Press, Glasgow
Floridi L, Cowls J (2019) A unified framework of five principles for AI in society. Harvard Data Sci Rev. https://doi.org/10.1162/99608f92.8cd550d1
Foreman E (2014) An agent-centered account of rightness: the importance of a good attitude. Ethical Theory Moral Pract 17:941–954
Gao X, Tian Y, Qi Z (2020) RPD-GAN: learning to draw realistic paintings with generative adversarial network. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:8706–8720. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2020.3018856
Gupta A, Lanteigne C, Heath V et al (2020) The state of AI ethics report (June 2020). arXiv:2006.14662 [cs]
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 770–778
Hursthouse R, Pettigrove G (2018) Virtue ethics. In: Zalta EN (ed) The stanford encyclopedia of philosophy, winter 2018 Edition, Available online: https://plato.stanford.edu/archives/win2018/entries/ethics-virtue/ (This is an online encyclopedia published by Stanford. There is no publisher name and location specificlly. If we need to provide, it could be "Center for the Study of Language and Information, Stanford Univeristy", (this is from the webpage))
IEEE (2019) The IEEE Global Initiative on Ethics of Autonomous and Intelligent Systems. In: IEEE Standards Association. https://standards.ieee.org/industry-connections/ec/autonomous-systems.html
IEEE (2018) IEEE launches ethics certification program for autonomous and intelligent systems. In: IEEE Standards Association. https://standards.ieee.org/news/2018/ieee-launches-ecpais.html. Accessed 18 Sept 2019
Jobin A, Ienca M, Vayena E (2019) The global landscape of AI ethics guidelines. Nat Mach Intell 1:389–399
Korinek A (2020) Integrating ethical values and economic value to steer progress in artificial intelligence. In: Dubber MD, Pasquale F, Das S (eds) The Oxford handbook of ethics of AI. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Lo Piano S (2020) Ethical principles in machine learning and artificial intelligence: cases from the field and possible ways forward. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 7:1–7
Monroe D (2017) Deep learning takes on translation. Commun ACM 60:12–14. https://doi.org/10.1145/3077229
Mooney SJ, Pejaver V (2018) Big data in public health: terminology, machine learning, and privacy. Annu Rev Public Health 39:95–112. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-publhealth-040617-014208
Morley J, Floridi L, Kinsey L, Elhalal A (2019) From what to how. An overview of AI ethics tools, methods and research to translate principles into practices. arXiv:1905.06876 [cs]
Morley J, Kinsey L, Elhalal A et al (2021) Operationalising AI ethics: barriers, enablers and next steps. AI Soc. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00146-021-01308-8
Nguyen TT, Nguyen CM, Nguyen DT et al (2020) Deep learning for deepfakes creation and detection: a survey. arXiv:1909.11573 [cs, eess]
NSW Government (2020) Mandatory ethical principles for the use of AI. In: Artificial intelligence (AI) ethics policy. https://www.digital.nsw.gov.au/policy/artificial-intelligence-ai/artificial-intelligence-ai-ethics-policy/mandatory-ethical. Accessed 20 Oct 2020
Rolnick D, Donti PL, Kaack LH et al (2019) Tackling climate change with machine learning. arXiv:1906.05433 [cs, stat]
Rovatsos M (2019) From AI ethics to ethical AI. IJCAI 2019 tutorial, Macau, China
Samuel AL (1960) Some moral and technical consequences of automation—a refutation. Science 132:741–742. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.132.3429.741
Shen H, Deng WH, Chattopadhyay A, et al (2021) Value cards: an educational toolkit for teaching social impacts of machine learning through deliberation. In: Proceedings of the 2021 ACM conference on fairness, accountability, and transparency. Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, pp 850–861
Taddeo M, Floridi L (2018) How AI can be a force for good. Science 361:751–752. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aat5991
The IEEE Global Initiative on Ethics of Autonomous and Intelligent Systems (2019) Ethically aligned design: a vision for prioritizing human well-being with autonomous and intelligent systems. IEEE
Tolosana R, Vera-Rodriguez R, Fierrez J et al (2020) DeepFakes and beyond: a survey of face manipulation and fake detection. arXiv:2001.00179 [cs]
UKRI (2010) Principles of robotics. In: Engineering and physical sciences research council. https://epsrc.ukri.org/research/ourportfolio/themes/engineering/activities/principlesofrobotics/. Accessed 4 Nov 2020
Wiener N (1960) Some moral and technical consequences of automation. Science 131:1355–1358. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.131.3410.1355
Zhao S, Gao Y, Jiang X et al (2014) Exploring principles-of-art features for image emotion recognition. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM international conference on multimedia. Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, pp 47–56
Zhou J, Chen F (2019) AI in the public interest. In: Bertram C, Gibson A, Nugent A (eds) Closer to the machine: technical, social, and legal aspects of AI. Office of the Victorian Information Commissioner, Melbourne, Australia
Zhou J, Chen F (eds) (2018) Human and machine learning: visible, explainable, trustworthy and transparent. Springer, Berlin
Zhou J, Chen F, Berry A, et al (2020) A survey on ethical principles of AI and implementations. In: Proceedings of 2020 IEEE symposium series on computational intelligence (IEEE SSCI), Canberra, Australia
Zhou J, Chen F, Berry A (2021) AI ethics: from principles to practice. https://open.uts.edu.au/uts-open/study-area/Technology/ethical-ai-from-principles-to-practice/. Accessed 15 Aug 2021
Zhou J, Li Z, Zhi W et al (2017) Using convolutional neural networks and transfer learning for bone age classification. In: 2017 international conference on digital image computing: techniques and applications, DICTA 2017, Sydney, Australia, November 29–December 1, 2017. IEEE
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors state that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Chen, F. AI ethics: from principles to practice. AI & Soc 38, 2693–2703 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00146-022-01602-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00146-022-01602-z