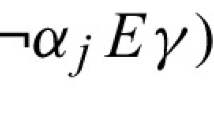Abstract
Vectorization of a class of structures is a natural notion in finite model theory. Roughly speaking, vectorizations allow tuples to be treated similarly to elements of structures. The importance of vectorizations is highlighted by the fact that if the complexity class PTIME corresponds to a logic with reasonable syntax, then it corresponds to a logic generated via vectorizations by a single generalized quantifier (Dawar in J Log Comput 5(2):213–226, 1995). It is somewhat surprising, then, that there have been few systematic studies of the expressive power of vectorizations of various quantifiers. In the present paper, we consider the simplest case: the cardinality quantifiers C S . We show that, in general, the expressive power of the vectorized quantifier logic \({{\rm FO}(\{{\mathsf C}_S^{(n)}\, | \, n \in \mathbb{Z}_+\})}\) is much greater than the expressive power of the non-vectorized logic FO(C S ).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dawar A.: Generalized quantifiers and logical reducibilities. J. Log. Comput. 5(2), 213–226 (1995)
Ebbinghaus, H.D.: Extended logics: the general framework. In: Model-Theoretic Logics, Perspect. Math. Logic, pp. 25–76. Springer, New York (1985)
Graham R.L., Rothschild B.L., Spencer J.H.: Ramsey Theory. 2nd edn. Wiley-Interscience Series in Discrete Mathematics and Optimization. Wiley, New York (1990) (A Wiley-Interscience Publication)
Gurevich, Y.: Toward logic tailored for computational complexity. In: Computation and Proof Theory (Aachen, 1983), Lecture Notes in Math., vol. 1104, pp. 175–216. Springer, Berlin (1984). doi:10.1007/BFb0099486. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BFb0099486
Gurevich, Y.: Logic and the challenge of computer science. In: Trends in Theoretical Computer Science (Udine, 1984), Principles Comput. Sci. Ser., vol. 12, pp. 1–57. Computer Sci. Press, Rockville, MD (1988)
Hella L.: Definability hierarchies of generalized quantifiers. Ann. Pure Appl. Log. 43(3), 235–271 (1989)
Hella L., Krynicki M.: Remarks on the Cartesian closure. Z. Math. Logik Grundlag. Math. 37(6), 539–545 (1991)
Hella, L., Luosto, K.: Finite generation problem and n-ary quantifiers. In: Krynicki, M., Mostowski, M., Szczerba, L.W. (eds.) Quantifiers: Logics, Models and Computation, vol. I, pp. 63–104. Kluwer (1995)
Hella L., Nurmonen J.: Vectorization hierarchies of some graph quantifiers. Arch. Math. Log. 39(3), 183–207 (2000)
Kaila R.: On probabilistic elimination of generalized quantifiers. Random Struct. Algorithms 19(1), 1–36 (2001)
Kolaitis, P.G.: Implicit definability on finite structures and unambiguous computations. In: Fifth Annual IEEE Symposium on Logic in Computer Science (Philadelphia, PA, 1990), pp. 168–180. IEEE Comput. Soc. Press, Los Alamitos, CA (1990)
Kolaitis P.G., Väänänen J.A.: Generalized quantifiers and pebble games on finite structures. Ann. Pure Appl. Log. 74(1), 23–75 (1995)
Krynicki M.: Notion of interpretation and nonelementary languages. Z. Math. Logik Grundlag. Math. 34(6), 541–552 (1988)
Lindström P.: First order predicate logic with generalized quantifiers. Theoria 32, 186–195 (1966)
Lothaire M.: Combinatorics on Words, Encyclopedia of Mathematics and its Applications, vol. 17. Addison-Wesley, Reading, Mass (1983)
Lothaire M.: Algebraic Combinatorics on Words, Encyclopedia of Mathematics and its Applications, vol. 90. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2002)
Luosto K.: Hierarchies of monadic generalized quantifiers. J. Symb. Log. 65(3), 1241–1263 (2000)
Makowsky J.A., Shelah S., Stavi J.: Δ-logics and generalized quantifiers. Ann. Math. Log. 10(2), 155–192 (1976)
Nešetřil J., Väänänen J.A.: Combinatorics and quantifiers. Comment. Math. Univ. Carolin. 37(3), 433–443 (1996)
Väänänen, J.: A hierarchy theorem for Lindström quantifiers. In: Furberg, T.W.M., Åberg, C. (eds.) Logic and Abstraction, vol. Acta Philosophica Gothoburgesia 1, pp. 317–323 (1986)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luosto, K. On vectorizations of unary generalized quantifiers. Arch. Math. Logic 51, 241–255 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00153-011-0262-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00153-011-0262-7