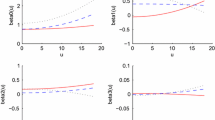
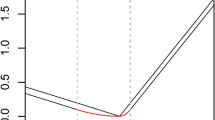
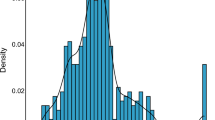
Abstract
In this paper we propose a new nonparametric regression method called composite support vector quantile regression (CSVQR) that combines the formulations of support vector regression and composite quantile regression. First the CSVQR using the quadratic programming (QP) is proposed and then the CSVQR utilizing the iteratively reweighted least squares (IRWLS) procedure is proposed to overcome weakness of the QP based method in terms of computation time. The IRWLS procedure based method enables us to derive a generalized cross validation (GCV) function that is easier and faster than the conventional cross validation function. The GCV function facilitates choosing the hyperparameters that affect the performance of the CSVQR and saving computation time. Numerical experiment results are presented to illustrate the performance of the proposed method

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cole T, Green P (1992) Smoothing reference centile curves: the LMS method and penalized likelihood. Stat Med 11:1305–1319
Craven P, Wahba G (1979) Smothing noisy data with spline functions. Numer Math 31:377–403
Cristianini N, Shawe-Taylor J (2000) An introduction to support vector machines. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Fan J, Gijbels I (1992) Variable bandwidth and local linear regression smoothers. Ann Stat 20:2008–2036
Gunn S (1998) Support vector machines for classification and regression. University of Southampton, ISIS Technical Report
Härdle W (1990) Applied nonparametric regression. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Heagerty P, Pepe M (1999) Semiparametric estimation of regression quantiles with application to standardizing weight for height and age in U.S. children. J R Stat Soc Ser C 48:533–551
Hendricks W, Koenker R (1992) Hierarchical spline models for conditional quantiles and the demand for electricity. J Am Stat Assoc 93:58–68
Jiang R, Zhou Z, Qian W, Shao W (2012) Single-index composite quantile regression. J Korean Stat Soc 41:323–332
Kai B, Li R, Zou H (2010) Local composite quantile regression smoothing: an efficient and safe alternative to local polynomial regression. J R Stat Soc Ser B 72:49–69
Kai B, Li R, Zou H (2011) New efficient estimation and variable selection methods for semiparametric varying-coefficient partially linear models. Ann Stat 39:305–332
Koenker R, Bassett G (1978) Regression quantiles. Econometrica 46:33–50
Kimeldorf G, Wahba G (1971) Some results on Tchebycheffian spline functions. J Math Anal Appl 33:82–95
Koenker R, Geling R (2001) Reappraising medfly longevity: a quantile regression survival analysis. J Am Stat Assoc 96:458–468
Koenker R, Hallock KF (2001) Quantile regression. J Econ Perspect 15:143–156
Kuhn H, Tucker A (1951) Nonlinear programming. In: Proceedings of 2nd Berkeley symposium. University of California Press, Berkeley, pp 481–492
Li Y, Kiu Y, Zhu J (2007) Quantile regression in reproducing kernel Hilbert space. J Am Stat Assoc 103:255–268
Mercer J (1909) Functions of positive and negative type and their connection with theory of integral equations. Philos Trans R Soc A, 415–446
Powell JL (1984) Least absolute deviations estimation for the censored regression model. J Econ 25:303–325
Shim J, Hwang C (2009) Support vector censored quantile regression under random censoring. Comput Stat Data Anal 53:912–919
Smola A, Schölkopf B (1998) On a kernel-based method for pattern recognition, regression, approximation and operator inversion. Algorithmica 22:211–231
Suyekns JAK (2000) Least squares support vector machine for classification and nonlinear modelling. Neural Network World, Special Issue on PASE 2000(10):29–48
Takeuchi I, Le QV, Sears TD, Smola AJ (2006) Nonparametric quantile estimation. J Mach Learn Res 7:1231–1264
Vapnik VN (1995) The nature of statistical learning theory. Springer, New York
Vapnik VN (1998) Statistical learning theory. Springer, New York
Wang L (ed) (2005) Support vector machines: theory and application. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York
Wei Y, He X (2006) Conditional growth charts (with discussions). Ann Stat 34:2069–2097
Ye A, Hyndman RJ, Le Z (2006) Local linear multivariate regression with variable bandwidth in the presence of heteroscedasticity. Working paper of Department of Econometrics and Business Statistics, Monash University, Australia
Ying Z, Jung SH, Wei LJ (1995) Survival analysis with median regression models. J Am Stat Assoc 90:178–184
Yuan M (2006) GACV for quantile smoothing splines. Conput Stat Data Anal 5:813–829
Yu K, Lu Z, Stander J (2003) Quantile regression: applications and current research area. The Statistician 52:331–350
Zou H, Yuan M (2008) Composite quantile regression and the oracle model selection theory. Ann Stat 36:1108–1126
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea Grant funded by the Korean Government (NRF-2012S1A3A2033330). This research was also supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea(NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2012000646) and (2011-0009705).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shim, J., Hwang, C. & Seok, K. Composite support vector quantile regression estimation. Comput Stat 29, 1651–1665 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00180-014-0511-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00180-014-0511-4