Abstract
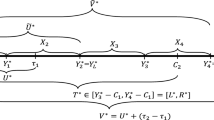
In this article, we consider nonparametric estimation of the cumulative incidence function (CIF) for left-truncated and interval-censored competing risks (LT-ICC) data. To reduce the bias of the pseudo-likelihood estimator (PLE) of CIF in the literature, we proposed two alternative estimators. The first estimator, called the modified PLE (MPLE), is obtained based on the modified NPMLE of F(t). The second estimator, called the modified maximum likelihood estimator (MMLE), is derived using modified likelihood functions for LT-ICC data, where the left endpoints of the intervals for left-censored observations with failure type j are the maximum of left-truncated variables and the estimated left endpoint of the support of the observations. Simulation studies show that the MPLE and MMLE are less biased than the PLE for most of the cases considered and their standard deviations are significantly smaller than that of the PLE.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aalen OO (1976) Nonparametric inference in connection with multiple decrement models. Scand J Stat 3:15–27
Alioum A, Commenges D (1996) A proportional hazards model for arbitrarily censored and truncated data. Biometrics 52:512–524
Chen C-M, Shen P-S, Lin C-C, Wu C-C (2020) Semiparametric mixture cure model analysis with competing risks data: application to vascular access thrombosis data. Stat Med 39:4086–4099
Choi S, Huang X (2014) Maximum likelihood estimation of semiparametric mixture component models for competing risks data. Biometrics 70:588–598
Frydman H (1994) A note on nonparametric estimation of the distribution function from interval-censored and truncated data. J Roy Stat Soc B 56:71–74
Gentleman R, Geyer CJ (1994) Maximum likelihood for interval censored data: consistency and computation. Biometrika 81:618–623
Groeneboom P, Wellner JA (1992) Information bounds and nonparametric maximum likelihood estimation. Birkhäuser, Basel
Hudgens MG, Satten GA, Longini IM Jr (2001) Nonparametric maximum likelihood estimation for competing risks survival data subject to interval censoring and truncation. Biometrics 57:74–80
Hudgens MG (2005) On nonparametric maximum likelihood estimation with interval censoring and truncation. J Roy Stat Soc B 67:573–587
Kalbfleisch JD, Prentice RL (2002) The statistical analysis of failure time data. Wiley, New York
Lin DY, Mao L (2017) Efficient Estimation of semiparametric transformation models for the cumulative incidence of competing risks. J R Stat Soc Ser B (Stat Methodol) 79:573–587
Mahdizadeh M, Strzalkowska-Kominiak E (2017) Resampling based inference for a distribution function using censored ranked set samples. Comput Stat 32:1285–1308
Mahdizadeh M, Zamanzade E (2018) Interval estimation of P(XY) in ranked set sampling. Comput Stat 33:1325–1348
Pan W, Chappell R (1998) A nonparametric estimator of survival functions for arbitrarily truncated and censored data. Lifetime Data Anal 4:187–202
Ren J, Gui W (2021) Inference and optimal censoring scheme for progressively Type-II censored competing risks model for generalized Rayleigh distribution. Comput Stat 36:479–513
Scheike TH, Zhang M-J (2011) Analyzing competing risk data using the R timereg package. J Stat Softw 38(2):1–16
Schick A, Yu Q (2000) Consistency of the GMLE with mixed case interval-censored data. Scand J Stat 27:45–55
Shen P-S (2020) Nonparametric Estimators of survival function under the mixed case interval-censored model with left truncation. Lifetime Data Anal 26:624–637
Song S (2004) Estimation with univariate “mixed case’’ interval censored data. Stat Sin 14:269–282
Turnbull BW (1976) The empirical distribution with arbitrarily grouped, censored and truncated data. J R Stat Soc Ser B 38:290–295
Vanichseni S, Kitayaporn D, Mastro TD, Mock PA, Raktham S, Des Jarlais DC, Sujarita S, Srisuwanvilai LO, Young NL, Wasi C, Subbarao S, Heyward WL, Esparza L, Choopanya K (2001) Continued high HIV-1 incidence in a vaccine trial preparatory cohort of injection drug users in Bangkok, Thailand. AIDS 15:397–405
Yu Q, Schick A, Li L, Wong GYC (1998a) Asymptotic properties of the GMLE in the case 1 interval-censorship model with discrete inspection times. Can J Stat 26:619–627
Yu Q, Schick A, Li L, Wong GYC (1998b) Asymptotic properties of the GMLE with case 2 interval-censored data. Stat Probab Lett 37:223–228
Zhang X, Zhang M-J, Fine J (2011) A proportional hazards regression model for the subdistribution with right-censored and left-truncated competing risks data. Stat Med 30:1933–1951
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank the Associate Editor and two reviewers for their constructive comments and helpful suggestions that greatly improved the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, Ps. Nonparametric estimation for competing risks survival data subject to left truncation and interval censoring. Comput Stat 37, 29–42 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00180-021-01111-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00180-021-01111-5