Abstract
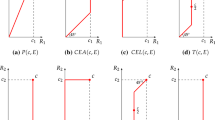
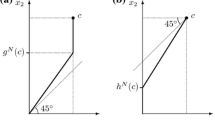
A division rule for claims problems, also known as bankruptcy or rationing problems, based on the pseudo-average solution is studied (for 2-person problems). This solution was introduced in Moulin (Jpn Econ Rev 46:303–332, 1995) for discrete cost allocation problems. Using the asymptotic approach, we obtain a division rule for claims problems. We characterize the division rule axiomatically and show that it coincides with the rule associated to the equal area bargaining solution (this is not true for n = 3). Moreover, following Moulin and Shenker (J Econ Theor 64:178–201, 1994), we show that its associated solution for continuous homogeneous goods is precisely the continuous pseudo-average solution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albizuri MJ, Santos JC, Zarzuelo JM (2002) On the serial cost sharing rule. Int J Game Theor 31: 437–446
Aumann RJ, Maschler M (1985) Game-theoretic analysis of a bankruptcy problem from the Talmud. J Econ Theor 36: 195–213
Aumann RJ, Shapley LS (1974) Values of non-atomic games. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Calvo E (1989) Solución de alternativas no dominadas iguales en el problema del regateo. Ph.D. thesis Department of Applied Economics IV, University of the Basque Country
Calvo E, Santos JC (2000) A value for multichoice games. Math Soc Sci 40: 341–354
Dagan N, Volij O (1993) The bankruptcy problem: a cooperative bargaining approach. Math Soc Sci 26: 287–297
Derks J, Peters H (1993) A Shapley value for games with restricted coalitions. Int J Game Theor 21: 351–360
Hougaard JL (2009) An introduction to allocation rules. Springer, Heidelberg
Hsiao C, Raghavan TES (1992) Monotonicity and dummy free property for multi-choice cooperative games. Int J Game Theor 21: 301–312
Klijn F, Slikker M, Zarzuelo J (1999) Characterizations of a multichoice value. Int J Game Theor 28: 521–532
Koster M (2009) Cost Sharing. In: Meyers R (eds) Encyclopedia of complexity and systems science. Springer, New York, pp 1660–1689
Larrea C, Santos C (2006) Cost allocation schemes: an asymptotic approach. Games Econ Behav 57: 63–72
Larrea C, Santos JC (2007) A characterization of the pseudo-average cost method. Math Soc Sci 53: 140–149
Moulin H (1995) On additive methods to share joint costs. Jpn Econ Rev 46: 303–332
Moulin H (2002) Axiomatic cost and surplus-sharing. In: Arrow KJ, Sen AK, Suzumura K (eds) Handbook of social choice and welfare, vol 1. Elsevier, North Holland, pp 289–357
Moulin H, Shenker S (1992) Serial cost sharing. Econometrica 60: 1009–1037
Moulin H, Shenker S (1994) Average cost pricing versus serial cost sharing: an axiomatic comparison. J Econ Theor 64: 178–201
Moulin H, Sprumont Y (2007) Fair allocation of production externalities: recent results. Rev d’Econ Pol 117: 7–36
Myerson R (1980) Conference structures and fair allocation rules. Int J Game Theor 9: 169–182
Peters H, Tijs SH (1985) Risk sensitivity and related properties for bargaining solutions. In: Roth AE (eds) Game-theoretic models of bargaining. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 215–231
Shapley LS (1953) A value for n-person games. In: Kuhn HW, Tucker AW (eds) Contributions to theory of games II. Ann. Math. Stud., vol 28. Princeton University Press, Princeton, pp 307–317
Tauman Y (1988) The Aumann–Shapley prices: a survey. In: Roth A (eds) The shapley value. Cambridge University Press, New York, pp 279–304
Thomson W (2003) Axiomatic and game-theoretic analysis of bankruptcy and taxation problems: a survey. Math Soc Sci 45: 249–297
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ortells, T., Santos, J.C. The pseudo-average rule: bankruptcy, cost allocation and bargaining. Math Meth Oper Res 73, 55–73 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00186-010-0333-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00186-010-0333-2