Abstract
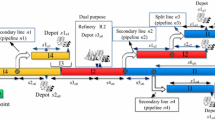
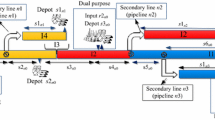
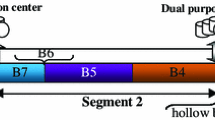
In this paper, a mathematical model to petroleum derivatives transportation scheduling is developed. The problem discussed in this paper is concerned with the scheduling of one-source tree-structured pipeline connected to several output terminals. A tree-structured pipeline is composed of a mainline conveying high-volume of petroleum products over long ways and secondary lines transporting smaller volumes over shorter distances. In such a pipeline, batches of petroleum products are pumped back-to-back at the origin of the mainline, without any separation device between them. This paper introduces a continuous mathematical representation, mixed integer linear programming, for the operational planning of tree-structured pipeline systems. Previous contributions on tree-structured pipeline planning deal with the sequence deliveries at receiving terminals, i.e., at any time only a unique terminal receives material from the pipeline. On the contrary, the proposed approach permits a receiving terminal on the mainline to simultaneously receive products when one of the secondary lines is taking material from the mainline. The problem’s aim is to find the optimal sequences of product injection and dispatching operations that satisfy product demands at minimum total cost, accounting for pumping and backordered demand costs during the specified planning horizon. The approach has been validated by solving three case studies of growing complexity.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cafaro DC, Cerdá J (2004) Optimal scheduling of multiproduct pipeline systems using a non-discrete MILP formulation. Comput Chem Eng 28:2053–2068
Cafaro DC, Cerdá J (2008) Efficient tool for the scheduling of multiproduct pipelines and terminal operations. Ind Eng Chem Res 47:9941–9956
Cafaro DC, Cerdá J (2008) Dynamic scheduling of multiproduct pipelines with multiple delivery due dates. Comput Chem Eng 32:728–753
Cafaro DC, Cerdá J (2011) A rigorous mathematical formulation for the scheduling of tree-structure pipeline networks. Ind Eng Chem Res 50:5064–5085
Cafaro VG, Cafaro DC, Mendéz CA, Cerdá J (2012) Detailed scheduling of single-source pipelines with simultaneous deliveries to multiple offtake stations. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:6145–6165
Hane CA, Ratliff HD (1995) Sequencing inputs to multi-commodity pipelines. Ann Oper Res 57:73–101
Mirhassani SA, Ghorbanalizadeh M (2008) The multi-product pipeline scheduling system. Comput Math Appl 56:891–897
Mirhassani SA, Fani Jahromi H (2011) Scheduling multi-product tree-structure pipelines. Comput Chem Eng 35:165–176
Mostafaei H, Ghaffari-Hadigheh A (2014) A general modeling framework for the long-term scheduling of multiproduct pipelines with delivery constraints. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:7029–7042
Rejowski R, Pinto JM (2003) Scheduling of a multiproduct pipeline system. Comput Chem Eng 27:1229–1246
Rejowski R, Pinto JM (2004) Efficient MILP formulations and valid cuts for multiproduct pipeline scheduling. Comput Chem Eng 28:1511–1528
Rejowski R, Pinto JM (2008) A novel continuous time representation for the scheduling of pipeline systems with pumping yield rate constraints. Comput Chem Eng 32:1042–1066
Relvas S, Matos HM, Barbosa-Po’voa AFD, Fialho J, Pinheiro AS (2006) Pipeline scheduling and inventory management of a multiproduct distribution oil system. Ind Eng Chem Res 45:7841–7855
Relvas S, Matos HM, Barbosa-Po’voa AFD (2009) Heuristic batch sequencing on a multiproduct oil distribution system. Comput Chem Eng 33:712–730
Sasikumar M, Prakash PR, Patil SM (1997) PIPES: a heuristic search model for pipeline schedule generation. Knowl Based Syst 10:169–175
Shah N (1996) Mathematical programming techniques for crude oil scheduling. Comput Chem Eng 20:1227–1232
Trench CJ (2001) How pipelines make the oil market work -their networks, operation and regulation. Allegro Energy Group, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mostafaei, H., Alipouri, Y. & Zadahmad, M. A mathematical model for scheduling of real-world tree-structured multi-product pipeline system. Math Meth Oper Res 81, 53–81 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00186-014-0486-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00186-014-0486-5