Abstract
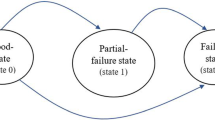
We consider the end-of-life inventory problem for the supplier of a product in its final phase of the service life cycle. This phase starts when the production of the items stops and continues until the warranty of the last sold item expires. At the beginning of this phase the supplier places a final order for spare parts to serve customers coming with defective items. At any time during the final phase the supplier may also decide to switch to an alternative and more cost effective service policy. This alternative policy may be in the form of replacing defective items with substitutable products or offering discounts/rebates on the new generation ones. In this setup, the objective is to find a final order quantity and a time to switch to an alternative policy which will minimize the total expected discounted costs of the supplier. The switching time is a stopping time and is based on the realization of the arrival process of defective items. In this paper, we study this problem under a general cost structure in a continuous-time framework where the arrival of customers is given by a non-homogeneous Poisson process. We show in detail how to compute the value function, and illustrate our approach on numerical examples.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertsekas DP (1995) Dynamic programming and optimal control, vol 1. Athena Scientific, Nashua
Bradley JR, Guerrero HH (2008) Product design for life-time mismatch. Prod Oper Manag 17(5):497–512
Bradley JR, Guerrero HH (2009) Lifetime buy decisions with multiple obsolete parts. Prod Oper Manag 18(1):114–126
Çınlar E (2011) Probability and stochastics. Graduate texts in mathematics. Springer, New York
Davis MHA (1993) Markov Models and Optimization, vol 49. Monographs on Statistics and Applied Probability. Chapman & Hall, London
Fortuin L (1980) The all-time requirement of spare parts for service after sales-theoretical analysis and practical results. Int J Oper Prod Manag 1:59–70
Fortuin L (1981) Reduction of all-time requirements for spare parts. Int J Oper Prod Manag 2(1):29–37
Frenk JBG, Javadi S, Pourakbar M, Sezer SO (2019) An exact static solution approach for the service parts end of life inventory problem. Eur J Oper Res 272(2):496–504
Gugerli US (1986) Optimal stopping of a piecewise-deterministic Markov process. Stochastics 19(4):221–236
Hill RM, Oma M, Smith DK (1999) Stock replenisment policies for a stochastic exponentially-declining demand process. Eur J Oper Res 116(1):347–388
Hong JS, Koo HY, Lee CS, Ahn J (2009) Forecasting service parts demand for a discontinued product. IIE Trans 40(7):640–649
Kim TH, Dekker R, Heij C (2017) Spare part demand forecasting for consumer goods using installed base information. Comput Ind Eng 103:201–215
Moore JR (1971) Forecasting and scheduling for past-model replacement parts. Manag Sci 18:B200–B213
Peskir G, Shiryaev AN (2006) Optimal stopping and free-boundary problems. Lectures in mathematics. ETH Zürich. Springer, Dordrecht
Pourakbar M, Frenk JBG, Dekker R (2012) End-of-life inventory decisions for consumer electronics service parts. Prod Oper Manag 21(5):889–906
Ritchie E, Wilcox P (1977) Renewal theory forecasting for stock control. Eur J Oper Res 1(2):90–93
Sigar T (2007) Inventory control of spare parts in the final phase. Master’s thesis, Erasmus University Rotterdam, Rotterdam
Solomon R, Sandborn P, Pecht M (2000) Electronic part life cycles concepts and obsolescence forecasting. IEEE Trans Compon Packag Technol 23(4):707–717
Teunter RH, Fortuin L (1998) End-of-life service; a case study. Eur J Oper Res 107(1):19–34
Teunter RH, Fortuin L (1999) End-of-life service. Int J Prod Econ 59:487–497
Teunter R H, Klein Haneveld W K (1998) The final order problem. Eur J Oper Res 107:35–44
Teunter R H, Klein Haneveld W K (2002) Inventory control of service parts in the final phase. Eur J Oper Res 137:497–511
van Kooten JPJ, Tan T (2009) The final order problem for repairable spare parts under condemnation. J Oper Res Soc 60(10):1449–1461
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frenk, J.B.G., Javadi, S. & Sezer, S.O. An optimal stopping approach for the end-of-life inventory problem. Math Meth Oper Res 90, 329–363 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00186-019-00680-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00186-019-00680-y