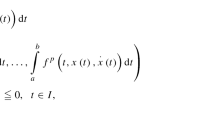Summary.
In nonconvex optimization problems, in particular in nonconvex variational problems, there usually does not exist any classical solution but only generalized solutions which involve Young measures. In this paper, after reviewing briefly the relaxation theory for such problems, an iterative scheme leading to a “sequential linear programming” (=SLP) scheme is introduced, and its convergence is proved by a Banach fixed-point technique. Then an approximation scheme is proposed and analyzed, and calculations of an illustrative 2D “broken-extremal” example are presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, H., Lebech, B., Poulse, H.F.: The structural phase diagram and oxygen equilibrium partial pressure of Y B2Cu3O6+x studied by powder diffraction and gas volumetry. Phys. C 172, 31–42 (1990)
Ball, J.M.: A version of the fundamental theorem for Young measures. Partial differential equations and continuum models of phase transitions. M. Rascle, D. Serre, M. Slemrod (eds.), Lecture Notes in Physics 344, 207–215 (1989)
Ball, J.M., Kirchheim, B., Kristensen, J.: Regularity of quasiconvex envelopes. Calc. Var. Partial Differ. Equ. 11(4), 333–359 (2000)
Bartels, S.: Adaptive approximation of young measure solutions in scalar non-convex variational problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 42 (5), 505–529 (2004)
Bartels, S.: Numerical analysis of some non-convex variational problems. PhD-Thesis. Christian–Albrechts–Universität zu Kiel, Kiel 2001, (Available online at http://e-diss.uni-kiel.de/diss_519/)
Bartels, S., Carstensen, C., Dolzmann, G.: Inhomogenous Dirichlet conditions in a priori and a posteriori finite element error analysis. Numer. Math. (published online) (2004). DOI: 10.1007/s00211-004-0548-3
Brighi, B., Chipot, M.: Approximated convex envelope of a function. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 31, 128–148 (1994)
Carstensen, C.: Numerical analysis of microstructure. Lecture Notes No. 10, Max-Planck-Institute for Mathematics in the Sciences, Leipzig, 2001
Carstensen, C., Bartels, S.: Each averaging technique yields reliable a posteriori error control in FEM on unstructured grids. Part I: Low order conforming, nonconforming, and mixed FEM. Math. Comp. 71(239), 945–969 (2002)
Carstensen, C., Jochimsen, K.: Adaptive finite element methods for micro-structures? Numerical experiments for a 2-well benchmark. Computing 71(2) 175–204 (2003)
Carstensen, C., Plecháč, P.: Numerical solution of the scalar double-well problem allowing microstructure. Math. Comp. 66, 997–1026 (1997)
Carstensen, C., Plecháč, P.: Numerical analysis of compatible phase transitions in elastic solids. SIAM. J. Numer. Anal. 37, 2061–2081 (2000)
Carstensen, C., Roubíček, T.: Numerical approximation of Young measures in nonconvex variational problems. Numer. Math. 84, 395–415 (2000)
Chipot, M.: Numerical analysis of oscillations in conconvex problems. Numer. Math. 59, 747–767 (1991)
Chipot, M.: The use of Young measures for constructing minimizing sequences in the calculus of variations. J. Appl. Anal. 1, 71–81 (1995)
Chipot, M., Collins, C.: Numerical approximations in variational problems with potential wells. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 29, 1002–1019 (1992)
Chipot, M., Collins, C., Kinderlehrer, D.: Numerical analysis of oscillations in multiple well problems. Numer. Math. 70, 259–282 (1995)
DeSimone, A.: Energy minimizers for large ferromagnetic bodies. Arch. Rat. Mech. Anal. 125, 99–143 (1993)
Fletcher, R., Sainz de la Maza, E.: Nonlinear programming and nonsmooth optimization by sequential linear programming. Math. Prog. 43, 235–256 (1989)
Friesecke, G.: A necessary and sufficient conditions for nonattainment and formation of microstructure almost ewerywhere in scalar variational problems. Proc. Royal Soc. Edinburgh 124A, 437–471 (1994)
Goodman, J., Kohn, R.V., Reyna, L.: Numerical study of a relaxed variational problem from optimal design. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 57, 107–127 (1986)
Govindjee, S., Mielke, A., Hall, G.J.: Free-energy of mixing for n-variant martensitic phase transformations using quasi-convex analysis. J. Mech. Physics Solids 50, 1897–1922 (2002)
Griewank, A., Rabier, P.J.: On the smoothness of convex envelopes. Trans. A.M.S. 322(2), 691–709 (1990)
Horgan, C.O.: Anti-plane shear deformation in linear and nonlinear solid mechnaics. SIAM Review 1995, pp. 53–81
Kinderlehrer, D., Pedregal, P.: Gradient Young measures generated by sequences in Sobolev spaces. J. Geom. Anal. 4, 59–90 (1994)
Kohn, R.: The relaxation of a double-well energy. Contin. Mech. Thermodyn. 3, 193–236 (1991)
Kružík, M.: Numerical approach to double-well problem. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 35, 1833–1849 (1998)
Kružík, M.: Maximum principle based algorithm for hysteresis in micromagnetics. Adv. Math. Sci. Appl. 13(2), 461–485 (2003)
Kružík, M., Prohl, A.: Young measures approximation in micromagnetics, Numer. Math. 90, 291–307 (2001)
Luskin, M.: On the computation of crystalline microstructure. Acta Numerica 5, 191–257 (1996)
Mach, J.: Numerical solution of a class of nonconvex variational problems by SQP. Numer. Funct. Anal. Optim. 23, 573–587 (2002)
Mataché, A.-M., Roubíček, T., Schwab, C.: Higher-order convex approximations of Young measures in optimal control. Adv. Comput. Math. Adv. Comput. Math. 19, 158–167 (2003)
Meziat, R.: Analysis of two dimensional non convex variational problems. In: Qi, Teo, and Yang (eds.), Optimization and control with applications. Kluwer
Nicolaides, R.A., Walkington, N.J.: Computation of microstructure utilizing Young measure representations. In: C.A. Rogers, R.A. Rogers, (eds.), Recent Advances in Adaptive and Sensory Materials and their Applications. Technomic Publ. Lancaster, 1992, pp. 131–141
Nicolaides, R.A., Walkington, N.J.: Strong convergence of numerical solutions to degenerate variational problems. Math. Comp. 64, 117–127 (1995)
Osborne, M.R., Womersley, R.S.: Strong uniqueness in sequential linear programming. J. Aust. Math. Soc. B 31, 379–384 (1990)
Pedregal, P.: Numerical approximation of parametrized measures. Numer. Funct. Anal. Opt. 16, 1049–1066 (1995)
Pedregal, P.: On the numerical analysis of non-convex variational problems. Numer. Math. 74, 325–336 (1996)
Pedregal, P.: Parametrized Measures and Variational Principles. Basel, Birkäuser, 1997
Roubíček, T.: Approximation theory for generalized Young measures. Numer. Funct. Anal. Opt. 16, 1233–1253 (1995)
Roubíček, T.: Numerical approximation of relaxed variational problems. J. Convex Anal. 3, 329–347 (1996)
Roubíček, T.: Relaxation in Optimization Theory and Variational Calculus. W. de Gruyter, Berlin, New York, 1997
Roubíček, T., Kružík, M.: Adaptive approximation algorithm for relaxed optimization problems. In: K.-H. Hoffmann, R.H.W. Hoppe, V. Schultz, (eds.), Proc. Conf. Fast solution of discretized optimization problems ISNM 138, Birkhäuser, Basel, 2001 pp. 242–254
Roubíček, T., Šverák, V.: Nonexistence of solutions in nonconvex multidimensional variational problems. J. Convex Anal. 7, 427–436 (2000)
Showalter, R.E.: Monotone Operators in Banach Spaces and Nonlinear Partial Differential Equations. AMS, Providence, 1997
Swart, P.J., Holmes, P.J.: Energy minimization and the fomration of microstructure in dynamic anti-plane shear. Arch. Rat. Mech. Anal. 121, 37–85 (1992)
Verfürth, R.: A Review of A Posteriori Error Estimation and Adaptive Mesh-Refinement Techniques. Wiley-Teubner, 1996
Smyshlyaev, V.P., Willis, J.R.: On the relaxation of a three-well energy. Proc. Royal Soc. London A 455, 779–814 (1999)
Zhang, J., Kim, N.E., Lasdon, L.: An Improved Successive Linear Programming Algorithm. Management Science 31, 1312–1331 (1985)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Mathematics Subject Classification (2000): 49M05, 65K10, 65N30
Acknowledgement S.B. gratefully acknowledges support by the DFG through the priority program 1095 “Analysis, Modeling and Simulation of Multiscale Problems” while T.R.’s research was partly covered by the grants A 107 5005 (GA AV ČR), and MSM 11320007 (MŠMT ČR).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bartels, S., Roubíček, T. Linear-programming approach to nonconvex variational problems. Numer. Math. 99, 251–287 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00211-004-0549-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00211-004-0549-2