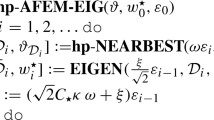Abstract
We design and analyze an adaptive hp-finite element method (\({\mathbf {hp}}\)-AFEM) in dimensions \(n=1,2\). The algorithm consists of iterating two routines: \({\mathbf {hp}}\)-NEARBEST finds a near-best hp-approximation of the current discrete solution and data to a desired accuracy, and REDUCE improves the discrete solution to a finer but comparable accuracy. The former hinges on a recent algorithm by Binev for adaptive hp-approximation, and acts as a coarsening step. We prove convergence and instance optimality.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ainsworth, M., Senior, B.: An adaptive refinement strategy for \(hp\)-finite element computations. Appl. Numer. Math. 26(1–2), 165–178 (1998)
Babuška, I., Craig, A., Mandel, J., Pitkäranta, J.: Efficient preconditioning for the \(p\)-version finite element method in two dimensions. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 28(3), 624–661 (1991)
Bank, R., Parsania, A., Sauter, S.: Saturation estimates for hp-finite element methods. Comput. Vis. Sci. 16(5), 195–217 (2013)
Binev, P.: Instance optimality for hp-type approximation. Oberwolfach Rep. 39, 14–16 (2013)
Binev, P.: Tree approximation for \(hp\)-adaptivity (in preparation)
Binev, P., Dahmen, W., DeVore, R.: Adaptive finite element methods with convergence rates. Numer. Math. 97(2), 219–268 (2004)
Binev, P., DeVore, R.: Fast computation in adaptive tree approximation. Numer. Math. 97(2), 193–217 (2004)
Braess, D., Pillwein, V., Schöberl, J.: Equilibrated residual error estimates are \(p\)-robust. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 198(13–14), 1189–1197 (2009)
Brix, K., Campos Pinto, M., Canuto, C., Dahmen, W.: Multilevel preconditioning of discontinuous Galerkin spectral element methods. Part I: geometrically conforming meshes. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 35(4), 1487–1532 (2015)
Bürg, M., Dörfler, W.: Convergence of an adaptive \(hp\) finite element strategy in higher space-dimensions. Appl. Numer. Math. 61(11), 1132–1146 (2011)
Canuto, C., Nochetto, R.H., Verani, M.: Adaptive Fourier–Galerkin methods. Math. Comput. 83, 1645–1687 (2014)
Canuto, C., Nochetto, R.H., Verani, M.: Contraction and optimality properties of adaptive Legendre–Galerkin methods: the 1-dimensional case. Comput. Math. Appl. 67(4), 752–770 (2014)
Canuto, C., Simoncini, V., Verani, M.: Contraction and optimality properties of an adaptive Legendre–Galerkin method: the multi-dimensional case. J. Sci. Comput. 63(3), 769–798 (2015)
Canuto, C., Hussaini, M.Y., Quarteroni, A., Zang, T.A.: Spectral Methods. Fundamentals in Single Domains. Scientific Computation. Springer, Berlin (2006)
Canuto, C., Verani, M.: On the numerical analysis of adaptive spectral/\(hp\) methods for elliptic problems. In: Analysis and Numerics of Partial Differential Equations. Springer INdAM Series, vol. 4, pp. 165–192. Springer, Milan (2013)
Cascon, J.M., Kreuzer, Ch., Nochetto, R.H., Siebert, K.G.: Quasi-optimal convergence rate for an adaptive finite element method. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 46(5), 2524–2550 (2008)
Carstensen, C., Feischl, M., Page, M., Praetorius, D.: Axioms of adaptivity. Comput. Math. Appl. 67(6), 1195–1253 (2014)
Dahmen, W., Scherer, K.: Best approximation by piecewise polynomials with variable knots and degrees. J. Approx. Theory 26(1), 1–13 (1979)
Demkowicz, L., Oden, J.T., Rachowicz, W., Hardy, O.: Toward a universal \(h\)-\(p\) adaptive finite element strategy. I. Constrained approximation and data structure. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 77(1–2), 79–112 (1989)
Demkowicz, L., Rachowicz, W., Devloo, Ph.: A fully automatic \(hp\)-adaptivity. J. Sci. Comput. 17(1–4), 127–155 (2002)
DeVore, R., Scherer, K.: Variable knot, variable degree spline approximation to \(x^\beta \). In: Quantitative Approximation (Proceedings of the International Symposium. Bonn, 1979), pp. 121–131. Academic Press, New York (1980)
Dörfler, W.: A convergent adaptive algorithm for Poisson’s equation. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 33(3), 1106–1124 (1996)
Dörfler, W., Heuveline, V.: Convergence of an adaptive \(hp\) finite element strategy in one space dimension. Appl. Numer. Math. 57(10), 1108–1124 (2007)
Eibner, T., Melenk, J.M.: An adaptive strategy for \(hp\)-FEM based on testing for analyticity. Comput. Mech. 39(5), 575–595 (2007)
Ern, A., Vohralík, M.: Polynomial-degree-robust a posteriori estimates in a unified setting for conforming, nonconforming, discontinuous Galerkin, and mixed discretizations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 53(2), 1058–1081 (2015)
Gui, W., Babuška, I.: The \(h,\;p\) and \(h\)-\(p\) versions of the finite element method in \(1\) dimension. II. The error analysis of the \(h\)- and \(h\)-\(p\) versions. Numer. Math. 49(6), 613–657 (1986)
Gui, W., Babuška, I.: The \(h,\;p\) and \(h\)-\(p\) versions of the finite element method in \(1\) dimension. III. The adaptive \(h\)-\(p\) version. Numer. Math. 49(6), 659–683 (1986)
Guo, B., Babuška, I.: The \(hp\)-version of the finite element method i: the basic approximation results. Comput. Mech. 1, 21–41 (1986)
Guo, B., Babuška, I.: The \(hp\)-version of the finite element method ii: general results and applications. Comput. Mech. 1, 203–226 (1986)
Guo, B., Babuška, I.: Regularity of the solutions for elliptic problems on nonsmooth domains in \( R^3\). II. Regularity in neighbourhoods of edges. Proc. R. Soc. Edinb. Sect. A 127(3), 517–545 (1997)
Houston, P., Senior, B., Süli, E.: \(hp\)-discontinuous Galerkin finite element methods for hyperbolic problems: error analysis and adaptivity. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 40(1–2), 153–169 (2002) [ICFD Conference on Numerical Methods for Fluid Dynamics (Oxford, 2001)]
Houston, P., Süli, E.: A note on the design of \(hp\)-adaptive finite element methods for elliptic partial differential equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 194(2–5), 229–243 (2005)
Mavriplis, C.: Adaptive mesh strategies for the spectral element method. Comput. Methods. Appl. Mech. Eng. 116, 77–86 (1994)
Melenk, J.M., Wohlmuth, B.I.: On residual-based a posteriori error estimation in \(hp\)-FEM. Adv. Comput. Math. 15(1–4), 311–331 (2002)
Morin, P., Nochetto, R.H., Siebert, K.G.: Data oscillation and convergence of adaptive FEM. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 38(2), 466–488 (2000) (electronic)
Nochetto, R.H., Siebert, K.G., Veeser, A.: Theory of adaptive finite element methods: an introduction. In: Multiscale, Nonlinear and Adaptive Approximation, pp. 409–542. Springer, Berlin (2009)
Oden, J.T., Demkowicz, L., Rachowicz, W., Westermann, T.A.: Toward a universal \(h\)-\(p\) adaptive finite element strategy. II. A posteriori error estimation. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 77(1–2), 113–180 (1989)
Oden, J.T., Patra, A., Feng, Y.: An \(hp\) Adaptive Strategy, vol. 157, pp. 23–46. ASME Publication, New York (1992)
Rachowicz, W., Oden, J.T., Demkowicz, L.: Toward a universal \(h\)-\(p\) adaptive finite element strategy. III. Design of \(h\)-\(p\) meshes. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 77(1–2), 181–212 (1989)
Schwab, Ch.: \(p\)- and \(hp\)-Finite Element Methods. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1998)
Scott, L.R., Zhang, S.: Finite element interpolation of nonsmooth functions satisfying boundary conditions. Math. Comput. 54(190), 483–493 (1990)
Schmidt, A., Siebert, K.G.: A posteriori estimators for the \(h\)-\(p\) version of the finite element method in 1D. Appl. Numer. Math. 35(1), 43–66 (2000)
Schötzau, D., Schwab, C., Wihler, T.: \(hp\)-dgfem for elliptic problems in polyhedra i: stability and quasi-optimality on geometric meshes. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 51(3), 1610–1633 (2013)
Schötzau, D., Schwab, C., Wihler, T.: \(hp\)-dgfem for elliptic problems in polyhedra ii: exponential convergence. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 51(4), 2005–2035 (2013)
Stevenson, R.: Optimality of a standard adaptive finite element method. Found. Comput. Math. 7(2), 245–269 (2007)
Veeser, A.: Approximating gradients with continuous piecewise polynomial functions. Found. Comput. Math. (2015). doi:10.1007/s10208-015-9262-z
Acknowledgments
C. Canuto and M. Verani are partially supported by GNCS-INdAM and the Italian research Grant Prin 2012 2012HBLYE4 “Metodologie innovative nella modellistica differenziale numerica”. R. H. Nochetto is partially supported by NSF Grants DMS-1109325 and DMS-1411808. We would like to thank the referees for their insightful comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Canuto, C., Nochetto, R.H., Stevenson, R. et al. Convergence and optimality of \({\mathbf {hp}}\)-AFEM . Numer. Math. 135, 1073–1119 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00211-016-0826-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00211-016-0826-x