Abstract
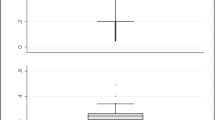
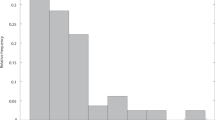
We develop a robust methodology which estimates the consequences of DRG cost weight volatility on hospital performance. The methodology is first developed using the hospital baserate as quantitative measure of hospital performance, then analyzed theoretically in the more general framework of cost-benefit analysis, and finally applied to two groups of hospitals. The first data set consists of a homogeneous group of 21 maximum-care hospitals in Germany and incorporates approximately 936,000 inpatient cases in 2003. The second data set consists of a heterogeneous group of 97 German hospitals and incorporates approximately 896,000 inpatient cases in 2003. The main finding is that the robust cost-benefit methodology developed in this study leads to results that are consistent with the theoretical background, since the hospital baserate spread in the more homogeneous group of hospitals is clearly lower than in the more heterogeneous group of hospitals. Our methodology illustrates the robustness of a hospital’s performance with respect to DRG cost weight changes and, therefore, represents a helpful tool in discussions about hospital budgets, strategic alliances, mergers, etc.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen P, Petersen NC (1993) A procedure for ranking efficient units in data envelopment analysis. Manage Sci 39(10):1261–1264
Asper EM, Hassan M (1993) The impact of PPS legislation on the systematic risk of hospitals. J Econ Financ 17(3):121–135
Baker JJ (2002) Medicare payment system for hospital inpatients: diagnosis related groups. J Health Care Financ 28(3):1–13
Boardman A, Greenberg D, Vining A, Weimer D (2001) Cost-benefit analysis: concepts and practice, 2nd edn. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Cooper WW, Seiford LM, Tone K (2000) Data envelopment analysis. Kluwer, Norwell
Dada M, White WD (1999) Evaluating financial risk in the medicare prospective payment system. Manage Sci 45(3):316–329
Darr K (1999a) Risk management and quality improvement: together at last—part 1. Hosp Top 77(1):27–31
Darr K (1999b) Risk management and quality improvement: together at last—Part 2. Hosp Top 77(2):29–35
Dreze J, Stern N (1987) Theory of cost-benefit analysis. In: Auerbach AJ, Feldstein M (eds) Handbook of public economics, vol 2. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp. 909–989
Eastaugh SR (1999) Managing risk in a risky world. J Health Care Financ 25(3):10–16
Fetter RB, Freeman JL (1986) Diagnosis related groups: product line management within hospitals. Acad Manage Rev 11(1):41–54
Fetter RB, Shin Y, Freeman JL, Averill RF, Thompson JD (1980) Case mix definition by diagnosis related groups. Med Care 18(2):1–53
Gapenski LC, Langland-Orban B (1998) The financial risk of hospitals inherent in DRG, per diem, and capitation reimbursement. J Healthcare Manage 43(4):323–338
Jackson T (2001) Using computerised patient-level costing data for setting DRG-weights: the Victorian (Australia) cost weight studies. Health Policy 56(2):149–163
Kuntz L, Scholtes S (2000) Measuring the robustness of empirical efficiency valuations. Manage Sci 46(6):807–823
Lungen M, Lapsley I (2003) The reform of hospital financing in Germany: an international solution? J Health Organ Manage 17(5):360–372
Mishan EJ (1976) Cost-benefit analysis. Praeger, New York
National Health Ministers’ Benchmarking Working Group (1999) Third National Report on Health Sector Performance Indicators. Department of Health and Aged Care, Canberra
O’Donovan M (1997) Risk Management and the medical profession. J Manage Develop 16(2–3):125–133
Olesen OB, Petersen NC (2002) The use of data envelopment analysis with probabilitic assurance regions for measuring hospital efficiency. J Productivity Anal 17(1–2):83–109
Phelan PD, Tate R, Webster F, Marshall RP (1998) DRG cost weights—getting it right. Med J Aust 169(suppl.):36–38
Roeder N, Rochell B, Hindle D (2002) Per case payment in Germany: all in a mess. Aust Health Rev 25(6):223–238
Scheel H, Scholtes S (2003) Continuity of DEA efficiency measures. Oper Res 51(1):149–159
Shleifer A (1985) A theory of yardstick competition. RAND J Econ 16(3):319–327
Sloan FA, Morrisey MA, Valvona J (1988) Effects of the medicare prospective payment system on hospital cost containment. Milbank Q 66(2):191–220
Thompson RG, Singleton FD, Thrall RM, Smith BA (1986) Comparative site evaluation for locating a high-energy physics lab in texas. Interfaces 16(6):35–49
Thompson RG, Langmeier LN, Lee CT, Lee E, Thrall RM (1990) The role of multiplier bounds in efficiency analysis with application to Kansas farming. J Econom 46(1–2):93–108
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuntz, L., Scholtes, S. & Vera, A. DRG cost weight volatility and hospital performance. OR Spectrum 30, 331–354 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00291-006-0063-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00291-006-0063-2