Abstract
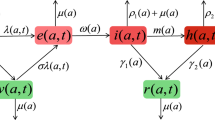
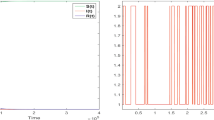
In this paper, we propose a stochastic SIR epidemic model with vertical transmission and varying total population size. Firstly, we prove the existence and uniqueness of the global positive solution for the stochastic model. Secondly, we establish three thresholds \(\lambda _{1},\) \(\lambda _{2} \) and \(\lambda _{3}\) of the model. The disease will die out when \(\lambda _{1}<0 \) and \(\lambda _{2}<0,\) or \(\lambda _{1}>0\) and \(\lambda _{3}<0\), but the disease will persist when \(\lambda _{1}<0\) and \(\lambda _{2}>0,\) or \( \lambda _{1}>0\) and \(\lambda _{3}>0\) and the law of the solution converge to a unique invariant measure. Moreover, we find that when \(\lambda _{1}<0\) some stochastic perturbations can increase the threshold \(\lambda _{2}\), while others can decrease the threshold \(\lambda _{2}\). That is, some stochastic perturbations enhance the spread of the disease, but others are just the opposite. On the other hand, when \(\lambda _{1}>0\), some stochastic perturbations increase or decrease the threshold \(\lambda _{3}\) with different parameter sets. Finally, we give some numerical examples to illustrate obtained results.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Li, M.Y., Smith, H.L., Wang, L.: Global dynamics of an SEIR epidemic model with vertical transmission. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 62(1), 58–69 (2001)
Lu, Z., Chi, X., Chen, L.: The effect of constant and pulse vaccination on SIR epidemic model with horizontal and vertical transmission. Math. Comput. Model. 36(9–10), 1039–1057 (2002)
Keeling, M.J., Woolhouse, M.E.J., Shaw, D.J., Louise, M., Chase-Topping, M., Haydon, D.T., Cornell, S.J., Kappey, J., Wilesmith, J., Grenfell, B.T.: Dynamics of the 2001 UK foot and mouth epidemic: stochastic dispersal in a heterogeneous landscape. Science 294(5543), 813–817 (2001)
May, R.M.: Stability and Complexity in Model Ecosystems. Princeton University, Princeton (2001)
Imhof, L., Walcher, S.: Exclusion and persistence in deterministic and stochastic chemostat models. J. Differ. Equ. 217(1), 26–53 (2005)
Dennis, B.: Allee effects in stochastic populations. Oikos 96(3), 389–401 (2002)
Zhu, C., Yin, G.: On competitive Lotka-Volterra model in random environments. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 357(1), 154–170 (2009)
Mao, X., Marion, G., Renshaw, E.: Environmental brownian noise suppresses explosions in population dynamics. Stoch. Process. Appl. 97(1), 95–110 (2002)
Dieu, N.T.: Asymptotic properties of a stochastic SIR epidemic model with Beddington-Deangelis incidence rate. J. Dyn. Diff. Equ. 30(1), 93–106 (2018)
Zhang, X.B., Liu, R.J.: The stationary distribution of a stochastic SIQS epidemic model with varying total population size. Appl. Math. Lett. 116, 106974 (2021)
Zhang, Y., Li, Y., Zhang, Q., Li, A.: Behavior of a stochastic SIR epidemic model with saturated incidence and vaccination rules. Phys. A 501, 178–187 (2018)
Gray, A., Greenhalgh, D., Hu, L., Mao, X., Pan, J.: A stochastic differential equation SIS epidemic model. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 71(3), 876–902 (2011)
Cai, Y., Kang, Y., Banerjee, M., Wang, W.: A stochastic SIRS epidemic model with infectious force under intervention strategies. J. Diff. Equ. 259(12), 7463–7502 (2015)
Zhang, X., Chang, S., Shi, Q., Huo, H.: Qualitative study of a stochastic SIS epidemic model with vertical transmission. Phys. A 505, 805–817 (2018)
Miao, A., Zhang, T., Zhang, J., Wang, C.: Dynamics of a stochastic SIR model with both horizontal and vertical transmission. J. Appl. Anal. Comput. 8(4), 1108–1121 (2018)
Ji, C., Jiang, D.: Threshold behaviour of a stochastic SIR model. Appl. Math. Model. 38(21–22), 5067–5079 (2014)
Dieu, N.T., Nguyen, D.H., Du, N.H., Yin, G.: Classification of asymptotic behavior in a stochastic SIR model. SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst. 15(2), 1062–1084 (2016)
Nguyen, D.H., Yin, G., Zhu, C.: Long-term analysis of a stochastic SIRS model with general incidence rates. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 80(2), 814–838 (2020)
Du, N.H., Nhu, N.N.: Permanence and extincton for the stochastic SIR epidemic model. J. Diff. Equ. 269(11), 9619–9652 (2020)
Du, N.H., Dieu, N.T., Ky, T.Q., Sam, V.H.: Long-time behavior of a stochastic SIQR model with Markov switching. Acta Math. Vietnam. 45(4), 903–915 (2020)
Mao, X.: Stochastic Differential Equations and Applications. Elsevier, New York (2007)
Gardiner, C.W.: Handbook of Stochastic Methods: For Physics, Chemistry and the Natural Sciences. Series in Synergetics. Springer, Berlin (2004)
Kallenberg, O.: Foundations of Modern Probability. Springer, New York (2002)
Zhang, X.B., Zhang, X.H.: The threshold of a deterministic and a stochastic SIQS epidemic model with varying total population size. Appl. Math. Model. 91, 749–767 (2021)
Hening, A., Nguyen, D.H.: Coexistence and extinction for stochastic Kolmogorov systems. Ann. Appl. Probab. 28(3), 1893–1942 (2018)
Evans, S.N., Hening, A., Schreiber, S.J.: Protected polymorphisms and evolutionary stability of patch-selection strategies in stochastic environments. J. Math. Biol. 71(2), 325–359 (2015)
Kliemann, W.: Recurrence and invariant measures for degenerate diffusions. Ann. Probab. 15(2), 690–707 (1987)
Jarner, S.F., Roberts, G.O.: Polynomial convergence rates of Markov chains. Ann. Appl. Probab. 12(1), 224–247 (2002)
Khasminskii, R.: Stochastic stability of differential equations, Sijthoff & Noordhoff, (1980)
Higham, D.J.: An algorithmic introduction to numerical simulation of stochastic differential equations. SIAM Rev. 43, 525–546 (2001)
Zhang, X.B., Shi, Q., Ma, S.H., Huo, H.F., Li, D.: Dynamic behavior of a stochastic SIQS epidemic model with levy jumps. Nonlinear Dyn. 93(3), 1481–1493 (2018)
Li, S., Guo, S.: Persistence and extinction of a stochastic SIS epidemic model with regime switching and levy jumps. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst. B 187, 308–336 (2021)
Yang, Q., Zhang, X., Jiang, D.: Asymptotic behavior of a stochastic SIR model with general incidence rate and nonlinear levy jumps. Nonlinear Dyn. 107, 2975–2993 (2022)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Nature Science Foundation of China (12361041, 12361029, 12161051), Science and Technology Plan Foundation of Gansu Province of China (No. 21JR7RA216, 21JR7RA209), the Development Program for HongLiu Outstanding Young Teachers in Lanzhou University of Technology (Q201308) and the HongLiu first-class disciplines Development Program of Lanzhou University of Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Anthony Bloch.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, XB., Zheng, L. Complex Dynamics of a Stochastic SIR Epidemic Model with Vertical Transmission and Varying Total Population Size. J Nonlinear Sci 33, 108 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00332-023-09960-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00332-023-09960-8