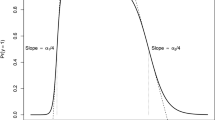
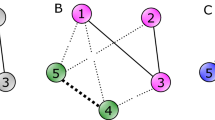
blocs
and legislative measures are partitioned into types so that, as nearly as possible, votes by each bloc for each type of measure are either all YEAs or all NAYs. A probability model is given for the partitions into blocs and types, and for the pattern of YEAs and NAYs given the partitions. The Alternating Randomized Combination algorithm is presented for searching for high probability partition pairs. The probability of each bloc and type in the final optimal partition pair is estimated by Markov Chain Monte Carlo. The final partition identifies 18 blocs of Senators, and 14 types of legislative measures. The blocs and types are delineated in a table reporting all decisive votes in the 103rd Congress. The blocs are characterized by the types of measures in which they vote against the majority party.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hartigan, J. Bloc Voting in the United States Senate. J. of Classification 17, 29–49 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003570000003
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003570000003