Abstract
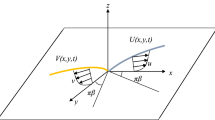
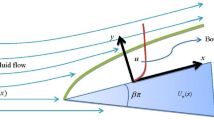
This paper is devoted to mathematical analysis of three-dimensional boundary-layer flow and heat transfer over a wedge. The boundary layer is formed due to the flow of a viscous and incompressible fluid and grows downstream along the walls of the wedge. This is appropriately approximated by a power of distances along both lateral directions. This analysis introduces a shear-to-strain-rate parameter \(\gamma\) in the study which plays an essential role in three-dimensional boundary-layer study. A set of boundary-layer equations along with the conservation of energy has been transformed into a coupled nonlinear ordinary differential equations. Two methods are employed. The fluid–wedge interaction problem is solved in the circumstances where the equations are linearized and obtained the solutions in terms of confluent hypergeometric functions, and otherwise, the full-nonlinear problem numerically using the Keller-box method. In the former case, the results of eigenfunction analysis that is based on asymptotic study of the problem qualitatively support the latter numerical results. In either methods, the existence of solutions and range of parameter domain depending on various physical quantities is successfully analyzed. The two different approaches give good agreement with each other in predicting the velocity and temperature profiles in three-dimensional boundary layer. However, both approaches show that a solution to the problem exist only \(-\,1< \gamma < \infty\). Since the Reynolds number is asymptotically large, the flow clearly divides into two regions showing the effects of viscosity and thermal conductivity. The velocity and thermal profiles are found to be benign. Flow always attached to the wedge surfaces and, thus, related thicknesses are becoming thinner. Extensive comparisons of the various results are made and a possible explanation on the results is discussed in some detail.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Constant
- \(C_\mathrm{p}\) :
-
Specific heat at constant pressure
- \(\text{ erf }\) :
-
Error function
- \(\text{ erfc }\) :
-
Complementary error function
- f, g, \(\theta\) :
-
Dimensionless velocities and temperature
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity of the fluid
- m :
-
Pressure gradient
- N :
-
Exponent wall temperature
- p :
-
Pressure
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number
- \(q_\mathrm{w}\) :
-
Heat flux
- T :
-
Temperature of the fluid
- \(T_\mathrm{w}\), \(T_\infty\) :
-
Wall temperature and temperature of the mainstream flow
- u, v, w :
-
Velocity components in (x, y, z) directions
- U, V :
-
Mainstream flows in x- and y-directions
- \(U_\infty\), \(V_\infty\) :
-
Strain and shear rates of mainstream flows
- \(U_\mathrm{w}\), \(V_\mathrm{w}\) :
-
Wedge surface velocities
- \(U_0\), \(V_0\) :
-
Strain and shear rates of the wedge velocities
- \(\mathscr {F}(\eta)\), \(\mathscr {G}(\eta )\), \(\mathscr {L}(\eta)\) :
-
Asymptotic velocities and temperature
- \(\gamma\) :
-
Shear-to strain-rate parameter or three-dimensionality parameter
- \(\beta\) :
-
Pressure gradient
- \(\rho\), \(\mu\) :
-
Density and dynamic viscosity
- \(\nu\) :
-
Kinematic viscosity
- \(\alpha = \frac{k}{\rho C_\mathrm{p}}\) :
-
Thermal diffusivity
- \(\delta\), \(\delta _\mathrm{t}\) :
-
Thickness of momentum and thermal boundary layer
- \(\psi _1\), \(\psi _2\) :
-
Stream functions
- \(\eta\) :
-
Similarity variable
- \(\lambda _1\), \(\lambda _2\) :
-
wedge velocities in x and y directions
- \(\tau\) :
-
Wall shear stress
- \(\varGamma\) :
-
Gamma function
References
Blasius H (1908) Grenzschichten in Flussigkeiten mit lieiner Reibung. Zentralblatt Math Phys 56:1–37
Sakiadis BC (1961) Boundary layer behaviour on continuous flat surface. AICHE J 7:221–225
Crane LJ (1970) Flow past a stretching plate. Zeitschrift fur Angewandte Mathematik und Physik 21(4):645–647
Klemp JB, Acrivos AA (1976) A moving-wall boundary layer with reverse flow. J Fluid Mech 76:363–381
Riley N, Weidman PD (1989) Multiple solutions of the Falkner–Skan equation for flow past a stretching boundary. SIAM J Appl Math 49(5):1350–1358
Fang T (2008) Boundary layer flow over a shrinking sheet with power-law velocity. Int J Heat Mass Transf 51:5838–5843
Hirschel EH, Cousteix J, Koradulla W (2014) Three-dimensional attached viscous flow. Springer, Berlin
Davey A (1961) Boundary layer flow at a saddle point of attachment. J Fluid Mech 10:593–610
Davey A, Schofield D (1967) Three-dimensional flow near a two-dimensional stagnation point. J Fluid Mech 28:149–151
Wiedman PD (2012) Non-axisymmetric Homann stagnation -point flows. J Fluid Mech 702:460–469
Kudenatti RB, Kirsur SR (2017) Numerical and asymptotic study of non-axisymmetric magnetohydrodynamic boundary layer stagnation point flows. Math Methods Appl Sci 40:5841–5850
Kudenatti RB, Gogate SP, Bujurke NM (2018) Asymptotic and numerical solutions of three-dimensional boundary-layer flow past a moving wedge. Math Methods Appl Sci 4761:1–13
Ali ME (1995) On thermal boundary layer on a power-law stretched surface with suction or injection. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 16:280–290
Yih KA (1998) The effect of uniform suction/blowing on heat transfer of magnetohydrodynamic Hiemenz flow through porous media. Acta Mechanica 130:147–158
Cortell R (2007) Viscous flow and heat transfer over a nonlinearly stretching sheet. Appl Math Comput 184:864–873
Fitt AD (2012) Generalized exact solutions for boundary layer flow and heat transfer over permeable stretching sheets. Appl Math Comput 219:1468–1473
Shahzad A, Ali R, Khan M (2012) On the exact solution for axisymmetric flow and heat transfer over a nonlinear radially stretching sheet. Chin Phys Lett 29(8):084705
Khan M, Hashim (2015) Boundary layer flow and heat transfer to Carreau fluid over a nonlinear stretching sheet. AIP Adv 5:107203
Ahmed J, Begum A, Shahzad A, Ali R (2016) MHD axisymmetric flow of power-law fluid over an unsteady stretching sheet with convective boundary conditions. Results Phys 6:973–981
Wang CY (1984) Three-dimensional flow due to stretching flat surface. Phys Fluids 27:1915–1917
Bachok N, Ishak A, Pop I (2010) Unsteady three-dimensional boundary layer flow due to a permeable shrinking sheet. Appl Math Mech 31:1421–1428
Khan JA, Mustafa M, Hayat T, Alsaedi A (2014) On three-dimensional flow and heat transfer over a non-linearly stretching sheet:analytical and numerical solutions. PLoS One 9(9):e107287
Hayat T, Imtiaz M, Alsaedi A, Kutbi MA (2015) MHD three-dimensional flow of nanofluid with velocity slip and nonlinear thermal radiation. J Magn Magn Mater 396:31–37
Borrelli A, Giantesio G, Patria MC, Rosca NC, Rosca AV, Pop I (2017) Buoyancy effects on the 3D MHD stagnation-point flow of a Newtonian fluid. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 43:1–13
Farooq A, Ali R, Benim AC (2018) Soret and Dufour effects on three dimensional Oldroyd-B fluid. Phys A Stat Mech Appl 503:345–354
Ahmad K, Nazar R (2011) Magnetohydrodynamic three-dimensional flow and heat transfer over a stretching surface in a viscoelastic fluid. J Sci Technol 3(1):33–46
Xu H, Liao S, Pop I (2008) Series solutions of unsteady free convection flow in the stagnation-point region of a three dimensional body. Int J Therm Sci 47:600–608
Tzirtzilakis EE, Kafoussias NG (2010) Three-dimensional magnetic fluid boundary-layer flow over a linearly stretching sheet. ASME J Heat Transf 132:011702-1-8
Duck PW, Dry SL (2001) On a class of unsteady, nonparallel, three-dimensional disturbances to boundary-layer flows. J Fluid Mech 441:31–65
Keller HB (1970) Numerical methods in boundary layer theory. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 10:417–428
Sachdev PL, Kudenatti RB, Bujurke NM (2008) Exact analytical solution of a boundary value problem for the Falkner–Skan equation. Stud Appl Math 120:1–16
Kudenatti RB, Kirsur SR, Achala LN, Bujurke NM (2013) MHD boundary layer flow over a non-linear stretching boundary with suction and injection. Int J Nonlinear Mech 50:58–67
Abramowitz M, Stegun I (1970) Handbook of mathematical functions with formulas, graphs and mathematical tables, 9th edn. Dover Publications, New York
Andrews L (1998) Special functions of mathematics for engineers, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Corbett P, Bottaro A (2000) Optimal perturbations for boundary layers subject to stream-wise pressure gradient. Phys Fluids 12:120
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for the educative comments that led to present form.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix: An algorithm of the Keller-box method
Appendix: An algorithm of the Keller-box method

Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kudenatti, R.B., Jyothi, B. Computational and asymptotic methods for three-dimensional boundary-layer flow and heat transfer over a wedge. Engineering with Computers 36, 1467–1483 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-019-00776-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-019-00776-3