Abstract
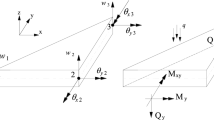
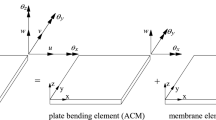
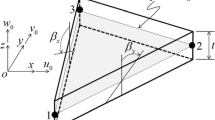
This paper presents a new four-node quadrilateral flat shell element, named QFSUQ, for analysis of shell structures. The element is formed by assemblage of a new membrane element and a plate-bending element. The membrane component is an unsymmetric quadrilateral element with drilling degrees of freedom. The trial functions of the membrane element are determined using the element stress fields formulated based on the analytical solutions of the Airy stress function in global Cartesian coordinate system. The corresponding test functions are obtained through the four-node isoparametric-based displacement fields which are enhanced by drilling rotations. The bending component is based on the Hellinger–Reissner variational principle for analysis of Reissner–Mindlin plates. To validate the performance of the proposed element several numerical benchmark problems are employed and the obtained results are compared with other shell elements. The results prove that the QFSUQ element preserves the advantages of the parent element formulation namely explicit stiffness matrix, free of membrane locking, shear locking and singularity problems and is also appropriate in analysis of shell structures with complex geometry, loading and boundary conditions.























Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Nguyen-Hoang S, Phung-Van P, Natarajan S, Kim HG (2016) A combined scheme of edge-based and node-based smoothed finite element methods for Reissner–Mindlin flat shells. Eng Comput 32:267–284
Rezaiee-Pajand M, Arabi E, Masoodi AR (2018) A triangular shell element for geometrically nonlinear analysis. Acta Mech 229:323–342
Tornabene F, Viola E (2013) Static analysis of functionally graded doubly-curved shells and panels of revolution. Meccanica 48:901–930
Hernández E, Spa C, Surriba S (2018) A non-standard finite element method for dynamical behavior of cylindrical classical shell model. Meccanica 53:1037–1048
Cheung YK, Zhang YX, Chen WJ (2000) A refined nonconforming plane quadrilateral element. Comput Struct 78:699–709
Cen S, Chen XM, Fu XR (2007) Quadrilateral membrane element family formulated by the quadrilateral area coordinate method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 196:4337–4353
Chen J, Li CJ, Chen WJ (2010) A family of spline finite elements. Comput Struct 88:718–727
Zhang L, Bathe KJ (2017) Overlapping finite elements for a new paradigm of solution. Comput Struct 187:64–76
Rajendran S, Liew KM (2003) A novel unsymmetric 8-node plane element immune to mesh distortion under a quadratic displacement field. Int J Numer Meth Eng 58:1713–1748
Liew KM, Rajendran S, Wang J (2006) A quadratic plane triangular element immune to quadratic mesh distortions under quadratic displacement fields. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 195:1207–1223
Ooi ET, Rajendran S, Yeo JH (2008) Remedies to rotational frame dependence and interpolation failure of US-QUAD8 element. Commun Numer Methods Eng 24:1203–1217
Cen S, Zhou GH, Fu XR (2012) A shape-free 8-node plane element unsymmetric analytical trial function method. Int J Numer Meth Eng 91:158–185
Zhou PL, Cen S, Huang JB, Li CF, Zhang Q (2017) An unsymmetric 8-node hexahedral element with high distortion tolerance. Int J Numer Meth Eng 109:1130–1158
Xie Q, Sze KY, Zhou YX (2016) Modified and Trefftz unsymmetric finite element models. Int J Mech Mater Des 12:53–70
Shang Y, Ouyang W (2018) 4-Node unsymmetric quadrilateral membrane element with drilling DOFs insensitive to severe mesh-distortion. Int J Numer Meth Eng 113:1589–1606
Shi G, Liu Y, Wang X (2015) Accurate, efficient, and robust Q4-like membrane elements formulated in Cartesian coordinates using the quasi-conforming element technique. Math Probl Eng 2015:198390
Wang C, Zhang X, Hu P (2016) New formulation of quasi-conforming method: a simple membrane element for analysis of planar problems. Eur J Mech A/Solids 60:122–133
Allman DJ (1984) A compatible triangular element including vertex rotations for plane elasticity analysis. Comput Struct 19:1–8
Cook RD (1986) On the Allman triangle and a related quadrilateral element. Comput Struct 22:1065–1067
Groenwold AA, Xiao QZ, Theron NJ (2004) Accurate solution of traction free boundaries using hybrid stress membrane elements with drilling degrees of freedom. Comput Struct 82:2071–2081
Çalık Karaköse ÜH, Askes H (2010) Static and dynamic convergence studies of a four-noded membrane finite element with rotational degrees of freedom based on displacement superposition. Int J Numer Methods Biomed Eng 26:1263–1275
Zouari W, Hammadi F, Ayad R (2016) Quadrilateral membrane finite elements with rotational DOFs for the analysis of geometrically linear and nonlinear plane problems. Comput Struct 173:139–149
Batoz JL, Hammadi F, Zheng C, Zhong W (2000) On the linear analysis of plates and shells using a new-16 degrees of freedom flat shell element. Comput Struct 78:11–20
Batoz JL, Zheng CL, Hammadi F (2001) Formulation and evaluation of new triangular, quadrilateral, pentagonal and hexagonal discrete Kirchhoff plate/shell elements. Int J Numer Meth Eng 52:615–630
Zengjie G, Wanji C (2003) Refined triangular discrete Mindlin flat shell elements. Comput Mech 33:52–60
Pimpinelli G (2004) An assumed strain quadrilateral element with drilling degrees of freedom. Finite Elem Anal Des 41:267–283
Sabourin F, Carbonniere J, Brunet M (2009) A new quadrilateral shell element using 16 degrees of freedom. Eng Comput 26:500–540
Wang Z, Sun Q (2014) Corotational nonlinear analyses of laminated shell structures using a 4-node quadrilateral flat shell element with drilling stiffness. Acta Mech Sin 30:418–429
Hamadi D, Ayoub A, Abdelhafid O (2015) A new flat shell finite element for the linear analysis of thin shell structures. Eur J Comput Mech 24:232–255
Sangtarash H, Arab HG, Sohrabi MR, Ghasemi MR (2019) Formulation and evaluation of a new four-node quadrilateral element for analysis of the shell structures. Eng Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-019-00763-8
Shang Y, Cen S, Li CF (2016) A 4-node quadrilateral flat shell element formulated by the shape-free HDF plate and HSF membrane elements. Eng Comput 33:713–741
Huang M, Zhao Z, Shen C (2010) An effective planar triangular element with drilling rotation. Finite Elem Anal Des 46:1031–1036
Cen S, Fu XR, Zhou MJ (2011) 8-and 12-node plane hybrid stress-function elements immune to severely distorted mesh containing elements with concave shapes. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 200:2321–2336
Tang LM, Liu YX (1985) Quasi-conforming element techniques for penalty finite element methods. Finite Elem Anal Des 1:25–33
Wang C, Zhang X, Hu P (2016) A 4-node quasi-conforming quadrilateral element for couple stress theory immune to distorted mesh. Comput Struct 175:52–64
Wang C, Wang X, Zhang X, Hu P (2017) Assumed stress quasi-conforming technique for static and free vibration analysis of Reissner–Mindlin plates. Int J Numer Meth Eng 112:303–337
Cook RD, Malkus DS, Plesha ME, Witt RJ (1974) Concepts and applications of finite element analysis, vol 4. Wiley, New York
Taylor RL (1987) Finite element analysis of linear shell problems. In: Whiteman JR (ed) Proceedings of the mathematics in finite elements and applications, pp 191–203
Ooi ET, Rajendran S, Yeo JH (2004) A 20-node hexahedron element with enhanced distortion tolerance. Int J Numer Meth Eng 60:2501–2530
Dvorkin EN, Bathe KJ (1984) A continuum mechanics based four-node shell element for general non-linear analysis. Eng Comput 1:77–88
Ko Y, Lee PS, Bathe KJ (2017) A new 4-node MITC element for analysis of two-dimensional solids and its formulation in a shell element. Comput Struct 192:34–49
ABAQUS (2012) Abaqus 6.12 Theory Manual. Dassault Systèmes Simulia Corp., Providence, Rhode Island
Klinkel S, Gruttmann F, Wagner W (2006) A robust non-linear solid shell element based on a mixed variational formulation. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 195:179–201
Rezaiee-Pajand M, Yaghoobi M (2018) An efficient flat shell element. Meccanica 53:1015–1035
Ibrahimbegović A, Frey F (1994) Stress resultant geometrically non-linear shell theory with drilling rotations. Part III: Linearized kinematic. Int J Numer Meth Eng 37:3659–3683
Belytschko T, Leviathan I (1994) Physical stabilization of the 4-node shell element with one point quadrature. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 113:321–350
Alves de Sousa RJ, Cardoso RP, Fontes Valente RA, Yoon JW, Grácio JJ, Natal Jorge RM (2005) A new one-point quadrature enhanced assumed strain (EAS) solid-shell element with multiple integration points along thickness: Part I—geometrically linear applications. Int J Numer Meth Eng 62:952–977
Hu P, Xia Y, Tang L (2011) A four-node Reissner–Mindlin shell with assumed displacement quasi-conforming method. Comput Model Eng Sci 73:103–135
Norachan P, Suthasupradit S, Kim KD (2012) A co-rotational 8-node degenerated thin-walled element with assumed natural strain and enhanced assumed strain. Finite Elem Anal Des 50:70–85
Alves de Sousa RJ, Natal Jorge RM, Fontes Valente RA, César de Sá JMA (2003) A new volumetric and shear locking-free 3D enhanced strain element. Eng Comput 20:896–925
Abed-Meraim F, Combescure A (2007) A physically stabilized and locking-free formulation of the (SHB8PS) solid-shell element. Eur J Comput Mech/Revue Européenne de Mécanique Numérique 16:1037–1072
Nguyen-Thanh N, Rabczuk T, Nguyen-Xuan H, Bordas SP (2008) A smoothed finite element method for shell analysis. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 198:165–177
Moreira RAS, Rodrigues JD (2011) A non-conforming plate facet-shell finite element with drilling stiffness. Finite Elem Anal Des 47:973–981
Wang C, Hu P, Xia Y (2012) A 4-node quasi-conforming Reissner–Mindlin shell element by using Timoshenko's beam function. Finite Elem Anal Des 61:12–22
Timoshenko SP, Woinowsky-Krieger S (1959) Theory of plates and shells. McGraw-hill, New York
Timoshenko S, Goodier JN (1979) Theory of elasticity, 3rd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Flügge W (1973) Stresses in shells. Springer-Verlag, New York
Macneal RH, Harder RL (1985) A proposed standard set of problems to test finite element accuracy. Finite Elem Anal Des 1:3–20
Simo JC, Fox DD, Rifai MS (1989) On a stress resultant geometrically exact shell model. Part II: the linear theory; computational aspects. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 73:53–92
Knight NF (1997) Raasch challenge for shell elements. AIAA J 35:375–381
Belytschko T, Stolarski H, Liu WK, Carpenter N, Ong JS (1985) Stress projection for membrane and shear locking in shell finite elements. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 51:221–258
Lee PS, Bathe KJ (2002) On the asymptotic behavior of shell structures and the evaluation in finite element solutions. Comput Struct 80:235–255
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sangtarash, H., Arab, H.G., Sohrabi, M.R. et al. A high-performance four-node flat shell element with drilling degrees of freedom. Engineering with Computers 37, 2837–2852 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-020-00974-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-020-00974-4