Abstract
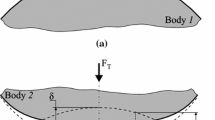
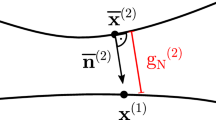
In this paper, an adaptive approach is presented to deal with isogeometric analysis of contact problems. Suggestion of an isogeometric adaptive refinement strategy for contact problems is the subject of this paper. Refinements are performed near the boundaries of the contact zone with insertion of new knots in the parametric domain. The performance and efficiency of the method are demonstrated via four examples, i.e., the Hertz problem and three hyperelastic contact problems. The obtained results are compared with solutions of very fine computational models. The proposed approach shows good convergence not only for the contact pressure but also for the contact zone limits. Another advantage of the method is eliminating the need for a priori guess of the contact zone limits.





















Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Franke D, Düster A, Nübel V, Rank E (2010) A comparison of the h-, p-, hp-, and rp-version of the FEM for the solution of the 2D Hertzian contact problem. Comput Mech 45(5):513–522
Kagan P, Fischer A, Bar-Yoseph PZ (1998) New B-spline finite element approach for geometrical design and mechanical analysis. Int J Numer Methods Eng 41(3):435–458
Gardner L, Gardner G, Dag I (1995) AB-spline finite element method for the regularized long wave equation. Commun Numer Methods Eng 11(1):59–68
Braibant V, Fleury C (1984) Shape optimal design using B-splines. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 44(3):247–267
Hughes TJ, Cottrell JA, Bazilevs Y (2005) Isogeometric analysis: CAD, finite elements, NURBS, exact geometry and mesh refinement. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 194(39–41):4135–4195
Borden MJ, Scott MA, Evans JA, Hughes TJ (2011) Isogeometric finite element data structures based on Bézier extraction of NURBS. Int J Numer Meth Eng 87(1–5):15–47
Nguyen VP, Anitescu C, Bordas SP, Rabczuk T (2015) Isogeometric analysis: an overview and computer implementation aspects. Math Comput Simul 117:89–116
Temizer I, Wriggers P, Hughes T (2011) Contact treatment in isogeometric analysis with NURBS. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 200(9–12):1100–1112
Lu J (2011) Isogeometric contact analysis: geometric basis and formulation for frictionless contact. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 200(5–8):726–741
De Lorenzis L, Temizer I, Wriggers P, Zavarise G (2011) A large deformation frictional contact formulation using NURBS-based isogeometric analysis. Int J Numer Meth Eng 87(13):1278–1300
Dimitri R, De Lorenzis L, Scott M, Wriggers P, Taylor R, Zavarise G (2014) Isogeometric large deformation frictionless contact using T-splines. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 269:394–414
Belgacem FB, Hild P, Laborde P (1998) The mortar finite element method for contact problems. Math Comput Model 28(4):263–272
Kim JY, Youn SK (2012) Isogeometric contact analysis using mortar method. Int J Numer Methods Eng 89(12):1559–1581
De Lorenzis L, Wriggers P, Zavarise G (2017) A mortar formulation for 3D large deformation contact using NURBS-based isogeometric analysis and the augmented Lagrangian method. Comput Mech 49(1):1011–1031
Zimmermann C, Sauer RA (2012) Adaptive local surface refinement based on LR NURBS and its application to contact. Comput Mech 60(1):1–20
Ciarlet PG (1988) Mathematical elasticity, I: three-dimensional elasticity. Vol. 20 of Stud. Math. Appl. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Mooney M (1940) A theory of large elastic deformation. J Appl Phys 11(9):582–592
Rivlin R (1948) Large elastic deformations of isotropic materials IV. Further developments of the general theory. Philos Trans R Soc Lond A. 241(835):379–397
Kim N-H (2014) Introduction to nonlinear finite element analysis. Springer, Berlin
Hassani B, Hinton E (2012) Homogenization and structural topology optimization: theory, practice and software. Springer, Berlin
Wriggers P (2003) Computational contact mechanics. Comput Mech 32(1):141
Matzen ME, Cichosz T, Bischoff M (2013) A point to segment contact formulation for isogeometric, NURBS based finite elements. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 255:27–39
Piegl L, Tiller W (2012) The NURBS book. Springer, Berlin
Cottrell JA, Hughes TJ, Bazilevs Y (2009) Isogeometric analysis: toward integration of CAD and FEA. Wiley, Hoboken
De Lorenzis L, Wriggers P, Hughes TJ (2014) Isogeometric contact: a review. GAMM-Mitteilungen 37(1):85–123
Lu J, Zheng C (2014) Dynamic cloth simulation by isogeometric analysis. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 268:475–493
Hughes TJ, Reali A, Sangalli G (2010) Efficient quadrature for NURBS-based isogeometric analysis. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 199(5–8):301–313
Cottrell J, Hughes T, Reali A (2007) Studies of refinement and continuity in isogeometric structural analysis. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 196(41–44):4160–4183
Babuvška I, Rheinboldt WC (1978) Error estimates for adaptive finite element computations. SIAM J Numer Anal 15(4):736–754
Zienkiewicz OC, Zhu JZ (1987) A simple error estimator and adaptive procedure for practical engineerng analysis. Int J Numer Methods Eng 24(2):337–357
Lee N-S, Bathe K-J (1994) Error indicators and adaptive remeshing in large deformation finite element analysis. Finite Elem Anal Des 16(2):99–139
Wriggers P, Scherf O (1998) Adaptive finite element techniques for frictional contact problems involving large elastic strains. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 151(3–4):593–603
Johnson C, Hansbo P (1992) Adaptive finite element methods in computational mechanics. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 101(1–3):143–181
Carstensen C, Scherf O, Wriggers P (1999) Adaptive finite elements for elastic bodies in contact. SIAM J Sci Comput 20(5):1605–1626
Szabó B, Szabo BA, Babuška I (1991) Finite element analysis. Wiley, Hoboken
Johnson KL, Johnson KL (1987) Contact mechanics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Shigley J, Mischke C, Budynas R (2004) Shigley's mechanical engineering design, 7th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Da Veiga LB, Buffa A, Rivas J, Sangalli G (2011) Some estimates for h–p–k-refinement in isogeometric analysis. Numer Math 118(2):271–305
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bidkhori, E., Hassani, B. A parametric knot adaptation approach to isogeometric analysis of contact problems. Engineering with Computers 38, 609–630 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-020-01073-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-020-01073-0