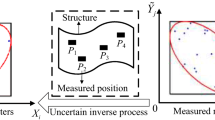
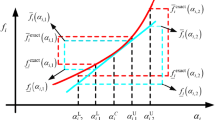
Abstract
This paper investigates a kind of inverse problem for assessing the uncertainties of identified parameters with uncertainties in structural parameters and limited experimental data. The uncertainty is described by the interval model in which only the bounds of uncertain parameters are required. Directly solving this kind of inverse problem involves a double-loop problem where the outer-loop is interval analysis and the inner-loop is deterministic optimization, which requires a large number of calculations. To efficiently evaluate the effect of interval parameters on the identified parameters, a novel method based on the dimension-reduction method and adaptive collocation strategy is proposed. First, the interval inverse problem is transformed into an inverse-propagation problem, and the dimension-reduction interval method is adopted to transform the interval inverse-propagation problem into several one-dimensional interval inverse-propagation problems. Then, an adaptive collocation strategy is proposed to efficiently estimate the lower and upper bounds of identified parameters. Therefore, the double-loop problem can be transformed into several deterministic inverse problems, and the efficiency of solving the uncertain inverse problem is dramatically improved. Two numerical examples and an engineering application are applied to demonstrate the feasibility and efficiency of the proposed method.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Engl HW, Ramlau R (2000) Regularization of inverse problems. Kluwer Academic Publishers
Tarantola A (2005) Inverse problem theory and methods for model parameter estimation, vol xii. Society for Industrial & Applied Mathematics, Philadelphia, p 342
Beck A, Teboulle M (2009) A fast iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems. SIAM J Imag Sci 2(1):183–202
Beck JL, Au SK (2002) Bayesian updating of structural models and reliability using markov chain monte carlo simulation. J Eng Mech 128(4):380–391
Sohn H, Law KH (2015) Bayesian probabilistic damage detection of a reinforced-concrete bridge column. Earthq Eng Struct Dynam 29(8):1131–1152
Liu J, Hu Y, Xu C, Jiang C, Han X (2016) Probability assessments of identified parameters for stochastic structures using point estimation method. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 156:51–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2016.07.021
Fonseca JR, Friswell MI, Mottershead JE, Lees AW (2005) Uncertainty identification by the maximum likelihood method. J Sound Vib 288(3):587–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2005.07.006
Liu H, Tang L, Lin P (2017) Maximum likelihood estimation of model uncertainty in predicting soil nail loads using default and modified FHWA simplified methods. Math Probl Eng 2017:14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7901918
Tang L, Lin P (2018) Estimation of ultimate bond strength for soil nails in clayey soils using maximum likelihood method AU - Liu, Huifen. In: Georisk: Assessment and Management of Risk for Engineered Systems and Geohazards 12 (3):190–202. doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/17499518.2017.1422525
Janda T, Šejnoha M, Šejnoha J (2018) Applying Bayesian approach to predict deformations during tunnel construction. Int J Numer Anal Meth Geomech 42(15):1765–1784. https://doi.org/10.1002/nag.2810
Ma C, Li X, Notarnicola C, Wang S, Wang W (2017) Uncertainty quantification of soil moisture estimations based on a bayesian probabilistic inversion. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 55(6):3194–3207. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2017.2664078
Wang J, Zabaras N (2004) A Bayesian inference approach to the inverse heat conduction problem. Int J Heat Mass Transf 47(17):3927–3941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2004.02.028
Cividini A, Maier G, Nappi A (1983) Parameter estimation of a static geotechnical model using a Bayes’ approach. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstracts 20(5):215–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(83)90002-5
Zhang W, Han X, Liu J, Tan ZH (2011) A combined sensitive matrix method and maximum likelihood method for uncertainty inverse problems. Comput Mater Continua 26(3):201–225
Yang M, Zhang D, Han X (2020) Enriched single-loop approach for reliability-based design optimization of complex nonlinear problems. Eng Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-020-01198-2
Yang M, Zhang D, Han X (2020) New efficient and robust method for structural reliability analysis and its application in reliability-based design optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 366:113018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2020.113018
Xiao N-C, Zhan H, Yuan K (2020) A new reliability method for small failure probability problems by combining the adaptive importance sampling and surrogate models. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 372:113336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2020.113336
Xiao N-C, Zuo MJ, Zhou C (2018) A new adaptive sequential sampling method to construct surrogate models for efficient reliability analysis. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 169:330–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2017.09.008
Zhang D, Zhang N, Ye N, Fang J, Han X (2020) Hybrid learning algorithm of radial basis function networks for reliability analysis. IEEE Trans Reliabi. https://doi.org/10.1109/TR.2020.3001232
Wu J, Zhang D, Jiang C, Han X, Li Q (2021) On reliability analysis method through rotational sparse grid nodes. Mech Syst Signal Process 147:107106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2020.107106
Yang M, Zhang D, Cheng C, Han X (2021) Reliability-based design optimization for RV reducer with experimental constraint. Struct Multidiscip Optim. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-020-02781-3
Moore RE (1966) Interval analysis. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Klir GJ, Yuan B (1995) Fuzzy sets and fuzzy logic: theory and applications. Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Ben-Haim Y (1995) A non-probabilistic measure of reliability of linear systems based on expansion of convex models. Struct Saf 17(2):91–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-4730(95)00004-N
Lü H, Yu D (2014) Brake squeal reduction of vehicle disc brake system with interval parameters by uncertain optimization. J Sound Vib 333(26):7313–7325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2014.08.027
Xia B, Lü H, Yu D, Jiang C (2015) Reliability-based design optimization of structural systems under hybrid probabilistic and interval model. Comput Struct 160:126–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2015.08.009
Moore R (1979) Method and application of interval analysis, vol 2. Siam
Rao SS, Berke L (1997) Analysis of uncertain structural systems using interval analysis. AIAA J 35(4):727–735. https://doi.org/10.2514/2.164
Queipo NV, Haftka RT, Wei S, Goel T, Vaidyanathan R, Tucker PK (2005) Surrogate-based analysis and optimization. Prog Aerosp Sci 41(1):1–28
Forrester AIJ, Sóbester A, Keane AJ (2008) Engineering design via surrogate modelling: a practical guide. Wiley, Chichester
Moore RE, Moore RE (1979) Methods and apolications of interval analysis. Society for Industrial & Applied Mathematics, Philadelphia
Jaulin L, Kieffer M, Didrit O (2001) Applied interval analysis. Springer, Berlin, p 5
Mottershead JE, Friswell MI (1993) Model updating in structural dynamics: a survey. J Sound Vib 167(2):347–375
Hemez FM, Doebling SW (2001) Review and Assessment of Model Updating for Non-Linear Transient Dynamics. Mech Syst Signal Process 15(1):45–74
Teughels A, Maeck J, De Roeck G (2002) Damage assessment by FE model updating using damage functions. Comput Struct 80(25):1869–1879. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-7949(02)00217-1
Fang SE, Zhang QH, Ren WX (2015) An interval model updating strategy using interval response surface models. Mech Syst Signal Process 60–61:909–927
Deng Z, Guo Z, Zhang X (2017) Interval model updating using perturbation method and radial basis function neural networks. Mech Syst Signal Process 84:699–716
Jiang C, Liu GR, Han X (2008) A novel method for uncertainty inverse problems and application to material characterization of composites. Exp Mech 48(4):539–548
Liu J, Han X, Jiang C, Ning HM, Bai YC (2011) Dynamic load identification for uncertain structures based on interval analysis and regularization method. Int J Comput Methods 08(4):667–683
Feng X, Zhuo K, Wu J, Godara V, Zhang Y (2016) A new interval inverse analysis method and its application in vehicle suspension design. SAE Int J Mater Manf 9(2):315–320. https://doi.org/10.4271/2016-01-0277
Liu J, Cai H, Jiang C, Han X, Zhang Z (2018) An interval inverse method based on high dimensional model representation and affine arithmetic. Appl Math Model 63:732–743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2018.07.009
Golub G, Hansen P, O’Leary D (1999) Tikhonov Regularization and Total Least Squares. SIAM J Matrix Anal Appl 21(1):185–194. https://doi.org/10.1137/S0895479897326432
Engl HW, Hanke M, Neubauer A (1996) Regularization of inverse problems, vol 375. Springer Science & Business Media
Rahman S, Xu H (2010) A univariate dimension-reduction method for multi-dimensional integration in stochastic mechanics. Probab Eng Mech 65(13):2292–2292
Ma X, Zabaras N (2010) An adaptive high-dimensional stochastic model representation technique for the solution of stochastic partial differential equations. J Comput Phys 229(10):3884–3915
Li G, Zhang K (2011) A combined reliability analysis approach with dimension reduction method and maximum entropy method. Struct Multidiscip Optim 43(1):121–134
Huang X, Zhang Y (2013) Reliability–sensitivity analysis using dimension reduction methods and saddlepoint approximations. Int J Numer Meth Eng 93(8):857–886. https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.4412
Lee G, Yook S, Kang K, Choi DH (2012) Reliability-based design optimization using an enhanced dimension reduction method with variable sampling points. Int J Precis Eng Manuf 13(9):1609–1618
Ren X, Yadav V, Rahman S (2016) Reliability-based design optimization by adaptive-sparse polynomial dimensional decomposition. Springer-Verlag New York, Inc.
Chen SH, Ma L, Meng GW, Guo R (2009) An efficient method for evaluating the natural frequencies of structures with uncertain-but-bounded parameters. Comput Struct 87(9):582–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2009.02.009
Xu M, Du J, Wang C, Li Y (2017) A dimension-wise analysis method for the structural-acoustic system with interval parameters. J Sound Vib 394:418–433
Tang JC, Fu CM (2017) A dimension-reduction interval analysis method for uncertain problems. CMES-Comput Model Eng Sci 113(3):239–259
Bucher CG (1988) Adaptive sampling—an iterative fast Monte Carlo procedure. Struct Saf 5(2):119–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-4730(88)90020-3
Mori Y, Ellingwood BR (1993) Time-dependent system reliability analysis by adaptive importance sampling. Struct Saf 12(1):59–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-4730(93)90018-V
Bollapragada R, Byrd R, Nocedal J (2018) Adaptive Sampling Strategies for Stochastic Optimization. SIAM J Optim 28(4):3312–3343. https://doi.org/10.1137/17m1154679
Au SK, Beck JL (1999) A new adaptive importance sampling scheme for reliability calculations. Struct Saf 21(2):135–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-4730(99)00014-4
Goldberg DE (1990) Genetic algorithms in search. Optim Mach Learn xiii(7):2104–2116
Kumar V (2002) Introduction to parallel computing. Addison-Wesley Longman Publishing Co., Inc.
Phillips JC, Braun R, Wang W, Gumbart J, Tajkhorshid E, Villa E, Chipot C, Skeel RD, Kalé L, Schulten K (2005) Scalable molecular dynamics with NAMD. J Comput Chem 26(16):1781–1802. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.20289
Coelho PG, Cardoso JB, Fernandes PR, Rodrigues HC (2011) Parallel computing techniques applied to the simultaneous design of structure and material. Adv Eng Softw 42(5):219–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2010.10.003
Gao W, Kemao Q (2012) Parallel computing in experimental mechanics and optical measurement: A review. Opt Lasers Eng 50(4):608–617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2011.06.020
Rubinstein RY (2008) Simulation and the Monte Carlo Method. Wiley
Wu T-J, Sepulveda A (1998) The weighted average information criterion for order selection in time series and regression models. Statist Probab Lett 39(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-7152(98)00003-0
Wu T-J, Chen P, Yan Y (2013) The weighted average information criterion for multivariate regression model selection. Signal Process 93(1):49–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2012.06.017
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51905257); the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (Grant No: 2020JJ6075); the Outstanding Youth Foundation of Hunan Education Department (Grant No: 18B301); the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (Grant No. A2019202171), the Changsha Municipal Natural Science Foundation (Grant No: kq2014050) and the Open Fund of State Key Laboratory of Advanced Design and Manufacturing for Vehicle Body (Grant No. 31915004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, J., Cao, L., Mi, C. et al. Interval assessments of identified parameters for uncertain structures. Engineering with Computers 38 (Suppl 4), 2905–2917 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-021-01432-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-021-01432-5