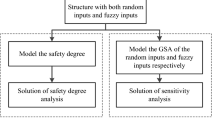
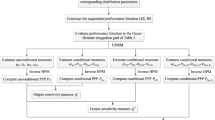
Abstract
The failure probability-based global sensitivity is proposed to evaluate the influence of input variables on the failure probability. But for the problem that the distribution parameters of variables are uncertain due to the lack of data or acknowledgement, if the original failure probability-based global sensitivity is employed to evaluate the influences of different uncertainty sources directly, the computational cost will be prohibitive. To address this issue, this work proposes the novel predictive failure probability (PFP) based on global sensitivity. By separating the overall uncertainty of variables into inherent uncertainty and distribution parameter uncertainty, the PFP can be evaluated by a single loop with equivalent transformation. Then, the PFP based global sensitivities with respect to (w.r.t) the overall uncertainty, inherent uncertainty and distribution parameter uncertainty are proposed, respectively, and their relationships are discussed, which can be used to measure the influences of different uncertainty sources. To compute those global sensitivities efficiently, the Monte Carlo method and Kriging-based method are employed for comparison. Several examples including two numerical examples and three engineering practices are investigated to validate the reasonability and efficiency of the proposed method.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fort JC, Klein T, Rachdi N (2016) New sensitivity analysis subordinated to contrast. Commun Stat Theory Methods 45(15):4349–4364
Andrea S (2002) Sensitivity analysis for importance assessment. Risk Anal 22:579–590
Dellino G, Meloni C (2015) Uncertainty management in simulation-optimization of complex systems: algorithms and applications. Oper Res 59:101–122
Wei P, Lu Z, Song S (2015) Variable importance analysis: a comprehensive review. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 142:399–432
Saltelli A, Tarantola S, Campolongo F et al (2004) Sensitivity analysis in practice: a guide to assessing scientific models. J R Stat Soc Ser A 101:398–399
Helton JC, Johnson JD, Sallaberry CJ et al (2006) Survey of sampling-based methods for uncertainty and sensitivity analysis. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 91:1175–1209
Storlie CB, Swiler LP, Helton JC et al (2009) Implementation and evaluation of nonparametric regression procedures for sensitivity analysis of computationally demanding models. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 94:1735–1763
Song S, Wang L (2021) A novel global sensitivity measure based on probability weighted moments. Symmetry 13(1):90
Kala Z (2021) Global sensitivity analysis of quantiles: new importance measure based on superquantiles and subquantiles. Symmetry 13(2):263
Molkenthin C, Scherbaum F, Griewank A et al (2017) Derivative-based global sensitivity analysis: upper bounding of sensitivities in seismic-hazard assessment using automatic differentiation. Bull Seismol Soc Amer 107(2):984–1004
Li L, Lu Z, Chen C (2016) Moment-independent importance measure of correlated input variable and its state dependent parameter solution. Aerosp Sci Technol 48:281–290
Morris MD (2012) Factorial sampling plans for preliminary computational experiments. Technometrics 33(2):161–174
Xiao S, Lu Z, Xu L (2016) A new effective screening design for structural sensitivity analysis of failure probability with the epistemic uncertainty. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 156:1–14
Saltelli A, Marivoet J (1990) Non-parametric statistics in sensitivity analysis for model output: a comparison of selected techniques. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 28(2):229–253
Borgonovo E (2007) A new uncertainty importance measure. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 92(6):771–784
Borgonovo E, Tarantola S, Plischke E et al (2014) Transformations and invariance in the sensitivity analysis of computer experiments. J R Stat Soc Ser B 76:925–947
Castaings W, Borgonovo E, Morris MD et al (2012) Sampling strategies in density-based sensitivity analysis. Environ Modell Softw 38:13–26
Gamboa F, Klein T, Lagnoux A (2018) Sensitivity analysis based on cramer-von mises distance. SIAM/ASA J Uncertain Quantif 6(2):522–548
Liu Q, Homma T (2012) A new importance measure for sensitivity analysis. Taylor & Francis Group 47(1):53–61
Lemaître P, Sergienko E, Arnaud A et al (2015) Density modification-based reliability sensitivity analysis. J Stat Comput Simul 85:1200–1223
Wei P, Lu Z, Wu D et al (2013) Moment-independent regional sensitivity analysis: application to an environmental model. Environ Modell Softw 47:55–63
Greegar G, Manohar CS (2015) Global response sensitivity analysis using probability distance measures and generalization of Sobol’s analysis. Probabilistic Eng Mech 41:21–33
Stefanak J, Kala Z, Mica L et al (2018) Global sensitivity analysis for transformation of Hoek-Brown failure criterion for rock mass. J Civ Eng Manag 24(3–5):390–398
Mahmoudi E, Holter R, Georgieva R, Konig M, Schanz T (2019) On the global sensitivity analysis methods in geotechnical engineering: a comparative study on a rock salt energy storage. Int J Civ Eng 17:131–143
Pitchai P, Jha NK, Nair RG, Guruprasad PJ (2021) A coupled framework of variational asymptotic method based homogenization technique and Monte Carlo approach for the uncertainty and sensitivity analysis of unidirectional composites. Compos Struct 263:113656
Ma YZ, Li HS, Zhao ZZ (2021) Reliability sensitivity analysis of thermal protection system. Struct Multidiscip Optim. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-021-02909-z
Yang Z, Unsong P, Zhao H (2020) Reliability sensitivity analysis of stochastic resonance failure of vehicle drum brake. ICECTT. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICECTT50890.2020.00011
Kala Z (2020) Sensitivity analysis in probabilistic structural design: a comparison of selected techniques. Sustainability 12(11):4788
Cui LJ, Lu ZZ, Zhao XP (2010) Moment-independent importance measure of basic random variable and its probability density evolution solution. Sci China Technol Sci 53:1138–1145
Li L, Lu Z, Jun F et al (2012) Moment-independent importance measure of basic variable and its state dependent parameter solution. Struct Saf 38:40–47
Xiao S, Lu Z (2017) Structural reliability sensitivity analysis based on classification of model output. Aerosp Sci Technol 71:52–61
Wei P, Lu Z, Yuan X (2013) Monte Carlo simulation for moment-independent sensitivity analysis. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 110:60–67
Wei P, Lu Z, Hao W et al (2012) Efficient sampling methods for global reliability sensitivity analysis. Comput Phys Commun 183(8):1728–1743
Merz B, Thieken AH (2005) Separating natural and epistemic uncertainty in flood frequency analysis. J Hydrol 309:114–132
Helton JC (2004) Alternative representations of epistemic uncertainty. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 85:1–10
Eldred MS, Swiler LP, Tang G (2011) Mixed aleatory-epistemic uncertainty quantification with stochastic expansions and optimization-based interval estimation. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 96:1092–1113
Helton JC, Oberkampf WL (2004) Alternative representations of epistemic uncertainty. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 85:1–10
Sun S, Fu G, Djordjevic S et al (2012) Separating aleatory and epistemic uncertainties: probabilistic sewer flooding evaluation using probability box. J Hydrol 420:360–372
Urbina A, Mahadevan S, Paez TL (2011) Quantification of margins and uncertainties of complex systems in the presence of aleatoric and epistemic uncertainty. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 96:1114–1125
Wang P, Lu ZZ, Xiao SN (2017) A generalized separation for the variance contributions of input variables and their distribution parameters. Appl Math Model 47:381–399
Morio J (2011) Influence of input PDF parameters of a model on a failure probability estimation. Simul Model Pract Theory 19(10):2244–2255
Krzykacz-Hausmann B (2006) An approximate sensitivity analysis of results from complex computer models in the presence of epistemic and aleatory uncertainties. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 91:1210–1218
Hofer E, Kloos M, Krzykacz-Hausmann B et al (2002) An approximate epistemic uncertainty analysis approach in the presence of epistemic and aleatory uncertainties. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 77:229–238
Wang P, Lu Z, Tang Z (2013) An application of the kriging method in global sensitivity analysis with parameter uncertainty. Appl Math Model 37:6543–6555
Wang P, Lu ZZ, Tang ZC (2013) Importance measure analysis with epistemic uncertainty and its moving least squares solution. Comput Math Appl 66(4):460–471
Sankararaman S, Mahadevan S (2011) Model validation under epistemic uncertainty. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 96:1232–1241
Sankararaman S, Mahadevan S (2013) Separating the contributions of variability and parameter uncertainty in probability distributions. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 112:187–199
Chabridon V, Balesdent M, Bourinet J-M et al (2017) Evaluation of failure probability under parameter epistemic uncertainty: application to aerospace system reliability assessment. Aerosp Sci Technol 69:526–537
Chabridon V, Balesdent M, Perrin G, Morio J, Bourinet J-M, Gayton N (2018) Reliability-based sensitivity estimators of rare event probability in the presence of distribution parameter uncertainty. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 178:164–178
Chabridon V, Balesdent M, Perrin G et al (2021) Global reliability-oriented sensitivity analysis under distribution parameter uncertainty. Wiley, Hoboken
Li G, Rabitz H (2012) General formulation of HDMR component functions with independent and correlated variables. J Math Chem 50(1):99–130
Echard B, Gayton N, Lemaire M (2011) AK-MCS: an active learning reliability method combining kriging and Monte Carlo simulation. Struct Saf 33:145–154
Echard B, Gayton N, Lemaire M et al (2013) A combined Importance sampling and kriging reliability method for small failure probabilities with time-demanding numerical models. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 111:232–240
Bichon BJ, Eldred MS, Swiler LP et al (2012) Efficient global reliability analysis for nonlinear implicit performance functions. AIAA J 46:2459–2468
Dumas A, Echard B, Gayton N et al (2013) AK-ILS: an active learning method based on kriging for the inspection of large surfaces. Precis Eng 37:1–9
Ishigami T, Homma T (1990) An importance quantification technique in uncertainty analysis for computer models, international symposium on uncertainty modeling & analysis. IEEE Xplore. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISUMA.1990.151285
Lv Z, Lu Z, Wang P (2015) A new learning function for kriging and its applications to solve reliability problems in engineering. Comput Math Appl 70:1182–1197
Xiao NC, Zhan HY, Kai Y (2020) A new reliability method for small failure probability problems by combining the adaptive importance sampling and surrogate models. Comput Math Appl Mech Eng 372:113336
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51975473) and the Aviation Science Foundation for the Aviation Key Laboratory of Science and Technology on Life-support Technology (Grant No. 201929053001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, P., Li, C., Liu, F. et al. Global sensitivity analysis of failure probability of structures with uncertainties of random variable and their distribution parameters. Engineering with Computers 38 (Suppl 5), 4367–4385 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-021-01484-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-021-01484-7