Abstract
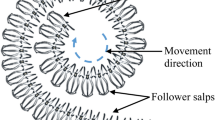
There is a new nature-inspired algorithm called salp swarm algorithm (SSA), due to its simple framework, it has been widely used in many fields. But when handling some complicated optimization problems, especially the multimodal and high-dimensional optimization problems, SSA will probably have difficulties in convergence performance or dropping into the local optimum. To mitigate these problems, this paper presents a chaotic SSA with differential evolution (CDESSA). In the proposed framework, chaotic initialization and differential evolution are introduced to enrich the convergence speed and accuracy of SSA. Chaotic initialization is utilized to produce a better initial population aim at locating a better global optimal. At the same time, differential evolution is used to build up the search capability of each agent and improve the sense of balance of global search and intensification of SSA. These mechanisms collaborate to boost SSA in accelerating convergence activity. Finally, a series of experiments are carried out to test the performance of CDESSA. Firstly, IEEE CEC2014 competition fuctions are adopted to evaluate the ability of CDESSA in working out the real-parameter optimization problems. The proposed CDESSA is adopted to deal with feature selection (FS) problems, then five constrained engineering optimization problems are also adopted to evaluate the property of CDESSA in dealing with real engineering scenarios. Experimental results reveal that the proposed CDESSA method performs significantly better than the original SSA and other compared methods.
Access this article
We’re sorry, something doesn't seem to be working properly.
Please try refreshing the page. If that doesn't work, please contact support so we can address the problem.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen H, Zhang Q, Luo J, Xu Y, Zhang X (2019) An enhanced bacterial foraging optimization and its application for training kernel extreme learning machine. Appl Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105884
Heidari AA, Mirjalili S, Faris H, Aljarah I, Mafarja M, Chen H (2019) Harris hawks optimization: algorithm and applications. Futur Gener Comput Syst 97:849–872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2019.02.028
Yu H, Zhao N, Wang P, Chen H, Li C (2020) Chaos-enhanced synchronized bat optimizer. Appl Math Model 77:1201–1215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2019.09.029
Li S, Chen H, Wang M, Heidari AA, Mirjalili S (2020) Slime mould algorithm: a new method for stochastic optimization. Futur Gener Comput Syst 111:300–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2020.03.055
Wei Y, Lv H, Chen M, Wang M, Heidari AA, Chen H, Li C (2020) Predicting entrepreneurial intention of students: an extreme learning machine with gaussian barebone Harris Hawks optimizer. IEEE Access 8:76841–76855. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2982796
Mirjalili S, Gandomi AH, Mirjalili SZ, Saremi S, Faris H, Mirjalili SM (2017) Salp swarm algorithm: a bio-inspired optimizer for engineering design problems. Adv Eng Softw 114:163–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2017.07.002
Zong WG, Joong HK, Loganathan GV (2001) A new heuristic optimization algorithm: harmony search. SIMULATION 76:60–68. https://doi.org/10.1177/003754970107600201
Kennedy J, Eberhart R (1995) Particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of ICNN'95—international conference on neural networks, vol 1944, pp 1942–1948. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICNN.1995.488968
Rashedi E, Nezamabadi-pour H, Saryazdi S (2009) GSA: a gravitational search algorithm. Inf Sci 179:2232–2248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2009.03.004
Yang X-S (2012) Flower pollination algorithm for global optimization. In: Unconventional computation and natural computation, Berlin, pp 240–249. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-32894-7_27
Coello CAC, Pulido GT, Lechuga MS (2004) Handling multiple objectives with particle swarm optimization. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 8:256–279. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2004.826067
Zhang Q, Li H (2007) MOEA/D: a multiobjective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 11:712–731. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2007.892759
Abbassi A, Abbassi R, Heidari AA, Oliva D, Chen H, Habib A, Jemli M, Wang M (2020) Parameters identification of photovoltaic cell models using enhanced exploratory salp chains-based approach. Energy 198:117333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.117333
Zhang Q, Chen H, Heidari AA, Zhao X, Xu Y, Wang P, Li Y, Li C (2019) Chaos-induced and mutation-driven schemes boosting salp chains-inspired optimizers. IEEE Access 7:31243–31261. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2019.2902306
Gupta S, Deep K, Heidari AA, Moayedi H, Chen H (2021) Harmonized salp chain-built optimization. Eng Comput 37:1049–1079. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-019-00871-5
Faris H, Mirjalili S, Aljarah I, Mafarja M, Heidari AA (2020) Nature-inspired optimizers: theories, literature reviews and applications. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 185–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-12127-3_11
Faris H, Mafarja MM, Heidari AA, Aljarah I, Al-Zoubi AM, Mirjalili S, Fujita H (2018) An efficient binary salp swarm algorithm with crossover scheme for feature selection problems. Knowl Based Syst 154:43–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2018.05.009
Sayed GI, Khoriba G, Haggag MH (2018) A novel chaotic salp swarm algorithm for global optimization and feature selection. Appl Intell 48:3462–3481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-018-1158-6
Tubishat M, Ja’afar S, Alswaitti M, Mirjalili S, Idris N, Ismail MA, Omar MS (2021) Dynamic Salp swarm algorithm for feature selection. Expert Syst Appl 164:113873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113873
El-Fergany AA (2018) Extracting optimal parameters of PEM fuel cells using salp swarm optimizer. Renew Energy 119:641–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.12.051
Zhang J, Wang Z, Luo X (2018) Parameter estimation for soil water retention curve using the salp swarm algorithm. Water 10(6):815. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10060815
Hussien AG, Hassanien AE, Houssein EH (2017) Swarming behaviour of salps algorithm for predicting chemical compound activities. In: 2017 eighth international conference on intelligent computing and information systems (ICICIS), pp 315–320. https://doi.org/10.1109/INTELCIS.2017.8260072
Zhao H, Huang G, Yan N (2018) Forecasting energy-related CO2 emissions employing a novel SSA-LSSVM model: considering structural factors in China. Energies. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11040781
Ateya AA, Muthanna A, Vybornova A, Algarni AD, Abuarqoub A, Koucheryavy Y, Koucheryavy A (2019) Chaotic salp swarm algorithm for SDN multi-controller networks. Eng Sci Technol 22:1001–1012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2018.12.015
Yang B, Zhong L, Zhang X, Shu H, Yu T, Li H, Jiang L, Sun L (2019) Novel bio-inspired memetic salp swarm algorithm and application to MPPT for PV systems considering partial shading condition. J Clean Prod 215:1203–1222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.01.150
Wang J, Gao Y, Chen X (2018) A novel hybrid interval prediction approach based on modified lower upper bound estimation in combination with multi-objective salp swarm algorithm for short-term load forecasting. Energies 11:1–30. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11061561
Abbassi R, Abbassi A, Heidari AA, Mirjalili S (2019) An efficient salp swarm-inspired algorithm for parameters identification of photovoltaic cell models. Energy Convers Manag 179:362–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2018.10.069
Abadi MQH, Rahmati S, Sharifi A, Ahmadi M (2021) HSSAGA: designation and scheduling of nurses for taking care of COVID-19 patients using novel method of hybrid salp swarm algorithm and genetic algorithm. Appl Soft Comput 108:107449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107449
Abd el-sattar S, Kamel S, Ebeed M, Jurado F (2021) An improved version of salp swarm algorithm for solving optimal power flow problem. Soft Comput 25:4027–4052. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-05431-4
Ewees AA, Al-qaness MAA, Abd EM (2021) Enhanced salp swarm algorithm based on firefly algorithm for unrelated parallel machine scheduling with setup times. Appl Math Model 94:285–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2021.01.017
Salgotra R, Singh U, Singh S, Singh G, Mittal N (2021) Self-adaptive salp swarm algorithm for engineering optimization problems. Appl Math Model 89:188–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2020.08.014
Ibrahim RA, Ewees AA, Oliva D, Abd EM, Lu S (2019) Improved salp swarm algorithm based on particle swarm optimization for feature selection. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 10:3155–3169. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-018-1031-9
Rizk-Allah RM, Hassanien AE, Elhoseny M, Gunasekaran M (2019) A new binary salp swarm algorithm: development and application for optimization tasks. Neural Comput Appl 31:1641–1663. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-3613-z
Bairathi D, Gopalani D (2021) An improved salp swarm algorithm for complex multi-modal problems. Soft Comput 25:10441–10465. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-021-05757-7
Braik M, Sheta A, Turabieh H, Alhiary H (2021) A novel lifetime scheme for enhancing the convergence performance of salp swarm algorithm. Soft Comput 25:181–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-05130-0
Nautiyal B, Prakash R, Vimal V, Liang G, Chen H (2021) Improved salp swarm algorithm with mutation schemes for solving global optimization and engineering problems. Eng Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-020-01252-z
Ouaar F, Boudjemaa R (2021) Modified salp swarm algorithm for global optimisation. Neural Comput Appl 33:8709–8734. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-05621-z
Panda N, Majhi SK (2021) Oppositional salp swarm algorithm with mutation operator for global optimization and application in training higher order neural networks. Multimed Tools Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-10304-x
Ren H, Li J, Chen H, Li C (2021) Stability of salp swarm algorithm with random replacement and double adaptive weighting. Appl Math Model 95:503–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2021.02.002
Saafan MM, El-Gendy EM (2021) IWOSSA: an improved whale optimization salp swarm algorithm for solving optimization problems. Expert Syst Appl 176:114901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.114901
Chen W, Zhang J, Lin Y, Chen N, Zhan Z, Chung HS, Li Y, Shi Y (2013) Particle swarm optimization with an aging leader and challengers. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 17:241–258. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2011.2173577
Liang JJ, Qin AK, Suganthan PN, Baskar S (2006) Comprehensive learning particle swarm optimizer for global optimization of multimodal functions. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 10:281–295. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2005.857610
Qin AK, Huang VL, Suganthan PN (2009) Differential evolution algorithm with strategy adaptation for global numerical optimization. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 13:398–417. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2008.927706
Brest J, Greiner S, Boskovic B, Mernik M, Zumer V (2006) Self-adapting control parameters in differential evolution: a comparative study on numerical benchmark problems. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 10:646–657. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2006.872133
Zhu A, Xu C, Li Z, Wu J, Liu Z (2015) Hybridizing grey wolf optimization with differential evolution for global optimization and test scheduling for 3D stacked SoC. J Syst Eng Electron 26:317–328. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEE.2015.00037
Luo J, Chen H, Zhang Q, Xu Y, Huang H, Zhao X (2018) An improved grasshopper optimization algorithm with application to financial stress prediction. Appl Math Model 64:654–668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2018.07.044
Çelik E, Öztürk N, Arya Y (2021) Advancement of the search process of salp swarm algorithm for global optimization problems. Expert Syst Appl 182:115292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115292
Liu Y, Shi Y, Chen H, Heidari AA, Gui W, Wang M, Chen H, Li C (2021) Chaos-assisted multi-population salp swarm algorithms: framework and case studies. Expert Syst Appl 168:114369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.114369
Salgotra R, Singh U, Singh G, Singh S, Gandomi AH (2021) Application of mutation operators to salp swarm algorithm. Expert Syst Appl 169:114368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.114368
Zhang H, Wang Z, Chen W, Heidari AA, Wang M, Zhao X, Liang G, Chen H, Zhang X (2021) Ensemble mutation-driven salp swarm algorithm with restart mechanism: framework and fundamental analysis. Expert Syst Appl 165:113897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113897
Andersen V, Nival P (1986) A model of the population dynamics of salps in coastal waters of the Ligurian Sea. J Plankton Res 8:1091–1110. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/8.6.1091
He Q, Wang L (2007) An effective co-evolutionary particle swarm optimization for constrained engineering design problems. Eng Appl Artif Intell 20:89–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2006.03.003
Mahdavi M, Fesanghary M, Damangir E (2007) An improved harmony search algorithm for solving optimization problems. Appl Math Comput 188:1567–1579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2006.11.033
Gao W-F, Huang L-L, Wang J, Liu S-Y, Qin C-D (2016) Enhanced artificial bee colony algorithm through differential evolution. Appl Soft Comput 48:137–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2015.10.070
Xiang W-L, Li Y-Z, Meng X-L, Zhang C-M, An M-Q (2017) A grey artificial bee colony algorithm. Appl Soft Comput 60:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.06.015
Tian D, Zhao X, Shi Z (2019) Chaotic particle swarm optimization with sigmoid-based acceleration coefficients for numerical function optimization. Swarm Evol Comput 51:100573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2019.100573
Wang X, Wang Z, Weng J, Wen C, Chen H, Wang X (2018) A new effective machine learning framework for sepsis diagnosis. IEEE Access 6:48300–48310. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2867728
Zhang Q, Chen H, Luo J, Xu Y, Wu C, Li C (2018) Chaos enhanced bacterial foraging optimization for global optimization. IEEE Access 6:64905–64919. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2876996
Luo J, Chen H, Heidari AA, Xu Y, Zhang Q, Li C (2019) Multi-strategy boosted mutative whale-inspired optimization approaches. Appl Math Model 73:109–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2019.03.046
Tizhoosh HR (2005) Opposition-based learning: a new scheme for machine intelligence. In: international conference on computational intelligence for modelling, control and automation and international conference on intelligent agents, web technologies and internet commerce (CIMCA-IAWTIC'06), pp 695–701. https://doi.org/10.1109/CIMCA.2005.1631345
Chen H, Wang M, Zhao X (2020) A multi-strategy enhanced sine cosine algorithm for global optimization and constrained practical engineering problems. Appl Math Comput 369:124872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2019.124872
Derrac J, García S, Molina D, Herrera F (2011) A practical tutorial on the use of nonparametric statistical tests as a methodology for comparing evolutionary and swarm intelligence algorithms. Swarm Evol Comput 1:3–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2011.02.002
Jia D, Zheng G, Khurram KM (2011) An effective memetic differential evolution algorithm based on chaotic local search. Inf Sci 181:3175–3187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2011.03.018
Civicioglu P, Besdok E, Gunen MA, Atasever UH (2020) Weighted differential evolution algorithm for numerical function optimization: a comparative study with cuckoo search, artificial bee colony, adaptive differential evolution, and backtracking search optimization algorithms. Neural Comput Appl 32:3923–3937. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-3822-5
Qais MH, Hasanien HM, Alghuwainem S (2019) Enhanced salp swarm algorithm: application to variable speed wind generators. Eng Appl Artif Intell 80:82–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2019.01.011
Frank AA (2010) UCI machine learning repository
Pan W-T (2012) A new fruit fly optimization algorithm: taking the financial distress model as an example. Knowl Based Syst 26:69–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2011.07.001
Mirjalili S (2015) Moth-flame optimization algorithm: a novel nature-inspired heuristic paradigm. Knowl Based Syst 89:228–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2015.07.006
Mirjalili S, Lewis A (2016) The whale optimization algorithm. Adv Eng Softw 95:51–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2016.01.008
Yang, S., Yu, X., Ding, M., He, L., Cao, G., Zhao, L.,... Ren, N. (2021). Simulating a combined lysis-cryptic and biological nitrogen removal system treating domestic wastewater at low C/N ratios using artificial neural network. Water research (Oxford), 189, 116576. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.116576
Che, H., & Wang, J. (2021). A Two-Timescale Duplex Neurodynamic Approach to Mixed-Integer Optimization. IEEE transaction on neural networks and learning systems, 32(1), 36-48. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.2973760
Meng, Q., Lai, X., Yan, Z., Su, C., & Wu, M. (2021). Motion Planning and Adaptive Neural Tracking Control of an Uncertain Two-Link Rigid-Flexible Manipulator With Vibration Amplitude Constraint. IEEE transaction on neural networks and learning systems, PP, 1-15. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3054611
Zhang, M., Chen, Y., & Susilo, W. (2020). PPO-CPQ: A Privacy-Preserving Optimization of Clinical Pathway Query for E-Healthcare Systems. IEEE internet of things journal, 7(10), 10660-10672. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3007518
Belegundu AD, Arora JS (1985) A study of mathematical programming methods for structural optimization. Part II: numerical results. Int J Numer Methods Eng 21:1601–1623. https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.1620210905
Coello Coello CA, Mezura Montes E (2002) Constraint-handling in genetic algorithms through the use of dominance-based tournament selection. Adv Eng Inform 16:193–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-0346(02)00011-3
Arora JS (2017) Introduction to optimum design, 4th edn. Academic Press, Boston, pp 601–680. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-800806-5.00014-7
Krohling RA, Coelho L (2006) Coevolutionary particle swarm optimization using gaussian distribution for solving constrained optimization problems. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B (Cybernetics) 36:1407–1416. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMCB.2006.873185
Zahara E, Kao Y-T (2009) Hybrid Nelder–Mead simplex search and particle swarm optimization for constrained engineering design problems. Expert Syst Appl 36:3880–3886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2008.02.039
Li LJ, Huang ZB, Liu F, Wu QH (2007) A heuristic particle swarm optimizer for optimization of pin connected structures. Comput Struct 85:340–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2006.11.020
Zhang HL, Cai ZN, Ye XJ, Wang MJ, Kuang FJ, Chen HL, Li CY, Li YP (2020) A multi-strategy enhanced salp swarm algorithm for global optimization. Eng Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-020-01099-4
Wang G-G, Guo L, Gandomi AH, Hao G-S, Wang H (2014) Chaotic Krill Herd algorithm. Inf Sci 274:17–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2014.02.123
Coello-Coello CA, Becerra RL (2004) Efficient evolutionary optimization through the use of a cultural algorithm. Eng Optim 36:219–236. https://doi.org/10.1080/03052150410001647966
Eskandar H, Sadollah A, Bahreininejad A, Hamdi M (2012) Water cycle algorithm—a novel metaheuristic optimization method for solving constrained engineering optimization problems. Comput Struct 110–111:151–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2012.07.010
Kannan BK, Kramer SN (1994) An augmented Lagrange multiplier based method for mixed integer discrete continuous optimization and its applications to mechanical design. J Mech Des 116:405–411. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2919393
Sandgren E (1990) Nonlinear integer and discrete programming in mechanical design optimization. J Mech Des 112:223–229. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2912596
Huang F-Z, Wang L, He Q (2007) An effective co-evolutionary differential evolution for constrained optimization. Appl Math Comput 186:340–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2006.07.105
He Q, Wang L (2007) A hybrid particle swarm optimization with a feasibility-based rule for constrained optimization. Appl Math Comput 186:1407–1422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2006.07.134
Coelho L (2010) Gaussian quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization approaches for constrained engineering design problems. Expert Syst Appl 37:1676–1683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2009.06.044
Ray T, Liew KM (2003) Society and civilization: an optimization algorithm based on the simulation of social behavior. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 7:386–396. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2003.814902
Sadollah A, Bahreininejad A, Eskandar H, Hamdi M (2013) Mine blast algorithm: a new population based algorithm for solving constrained engineering optimization problems. Appl Soft Comput 13:2592–2612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2012.11.026
Ray T, Saini P (2001) Engineering design optimization using a swarm with an intelligent information sharing among individuals. Eng Optim 33:735–748. https://doi.org/10.1080/03052150108940941
Zhang M, Luo W, Wang X (2008) Differential evolution with dynamic stochastic selection for constrained optimization. Inf Sci 178:3043–3074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2008.02.014
Liu H, Cai Z, Wang Y (2010) Hybridizing particle swarm optimization with differential evolution for constrained numerical and engineering optimization. Appl Soft Comput 10:629–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2009.08.031
Gandomi AH, Yang X-S, Alavi AH (2013) Cuckoo search algorithm: a metaheuristic approach to solve structural optimization problems. Eng Comput 29:17–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-011-0241-y
Savsani P, Savsani V (2016) Passing vehicle search (PVS): a novel metaheuristic algorithm. Appl Math Model 40:3951–3978. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2015.10.040
Adarsh BR, Raghunathan T, Jayabarathi T, Yang X-S (2016) Economic dispatch using chaotic bat algorithm. Energy 96:666–675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2015.12.096
Rao RV, Savsani VJ, Vakharia DP (2011) Teaching–learning-based optimization: a novel method for constrained mechanical design optimization problems. Comput Aided Des 43:303–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cad.2010.12.015
Chen, S., Zhang, J., Meng, F., & Wang, D. (2021). A Markov Chain Position Prediction Model Based on Multidimensional Correction. Complexity (New York, N.Y.), 2021. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6677132
He, Y., Dai, L., & Zhang, H. (2020). Multi-Branch Deep Residual Learning for Clustering and Beamforming in User-Centric Network. IEEE communications letters, 24(10), 2221-2225. https://doi.org/10.1109/LCOMM.2020.3005947
Wu, X., Zheng, W., Chen, X., Zhao, Y., Yu, T., & Mu, D. (2021). Improving high-impact bug report prediction with combination of interactive machine learning and active learning. Information and Software Technology, 133, 106530.
Wu, Z., Cao, J., Wang, Y., Wang, Y., Zhang, L., & Wu, J. (2018). hPSD: a hybrid PU-learning-based spammer detection model for product reviews. IEEE transactions on cybernetics, 50(4), 1595-1606.
Wang, G. G., Deb, S., & Cui, Z. (2019). Monarch butterfly optimization. Neural computing and applications, 31(7), 1995-2014.
Wang, G. G., Deb, S., & Coelho, L. D. S. (2018). Earthworm optimisation algorithm: a bio-inspired metaheuristic algorithm for global optimisation problems. International journal of bio-inspired computation, 12(1), 1-22.
Wang, G. G., Deb, S., & Coelho, L. D. S. (2015, December). Elephant herding optimization. In 2015 3rd International Symposium on Computational and Business Intelligence (ISCBI) (pp. 1-5). IEEE. doi: 10.1109/ISCBI.2015.8
Wang, G. G. (2018). Moth search algorithm: a bio-inspired metaheuristic algorithm for global optimization problems. Memetic Computing, 10(2), 151-164.
Liu, X. F., Zhan, Z. H., Lin, Y., Chen, W. N., Gong, Y. J., Gu, T. L., ... & Zhang, J. (2018). Historical and heuristic-based adaptive differential evolution. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 49(12), 2623-2635.
Zhao, H., Zhan, Z. H., Lin, Y., Chen, X., Luo, X. N., Zhang, J., ... & Zhang, J. (2019). Local binary pattern-based adaptive differential evolution for multimodal optimization problems. IEEE transactions on cybernetics, 50(7), 3343-3357.
Zhan, Z. H., Wang, Z. J., Jin, H., & Zhang, J. (2019). Adaptive distributed differential evolution. IEEE transactions on cybernetics, 50(11), 4633-4647.
Zhan, Z. H., Liu, X. F., Zhang, H., Yu, Z., Weng, J., Li, Y., ... & Zhang, J. (2016). Cloudde: A heterogeneous differential evolution algorithm and its distributed cloud version. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 28(3), 704-716.
Liu, X. F., Zhan, Z. H., & Zhang, J. (2021) Resource-Aware Distributed Differential Evolution for Training Expensive Neural-Network-Based Controller in Power Electronic Circuit. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems 1-11 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3075205
Chen, Z. G., Zhan, Z. H., Wang, H., & Zhang, J. (2019). Distributed individuals for multiple peaks: A novel differential evolution for multimodal optimization problems. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 24(4), 708-719.
Chen, H., Li, S., Heidari, A. A., Wang, P., Li, J., Yang, Y., ... & Huang, C. (2020). Efficient multi-population outpost fruit fly-driven optimizers: Framework and advances in support vector machines. Expert Systems with Applications, 142, 112999.
Chen, H., Yang, C., Heidari, A. A., & Zhao, X. (2020). An efficient double adaptive random spare reinforced whale optimization algorithm. Expert Systems with Applications, 154, 113018.
Zhang, H., Heidari, A. A., Wang, M., Zhang, L., Chen, H., & Li, C. (2020). Orthogonal Nelder-Mead moth flame method for parameters identification of photovoltaic modules. Energy Conversion and Management, 211, 112764.
Ridha, H. M., Heidari, A. A., Wang, M., & Chen, H. (2020). Boosted mutation-based Harris hawks optimizer for parameters identification of single-diode solar cell models. Energy Conversion and Management, 209, 112660.
Chen, H., Jiao, S., Wang, M., Heidari, A. A., & Zhao, X. (2020). Parameters identification of photovoltaic cells and modules using diversification-enriched Harris hawks optimization with chaotic drifts. Journal of Cleaner Production, 244, 118778.
Chen, H., Heidari, A. A., Chen, H., Wang, M., Pan, Z., & Gandomi, A. H. (2020). Multi-population differential evolution-assisted Harris hawks optimization: Framework and case studies. Future Generation Computer Systems, 111, 175-198.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the college-enterprise cooperation project of the domestic visiting engineer of colleges (FG2020077), Zhejiang, China, General research project of Zhejiang Provincial Education Department (Y201942618), Zhejiang, China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62076185, U1809209), the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (L182015), Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LY21F020030), Wenzhou Science & Technology Bureau (2018ZG016). We acknowledge comments of the reviewers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix A
Appendix A
See Tables 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, and 24.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Liu, T., Ye, X. et al. Differential evolution-assisted salp swarm algorithm with chaotic structure for real-world problems. Engineering with Computers 39, 1735–1769 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-021-01545-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-021-01545-x