Abstract
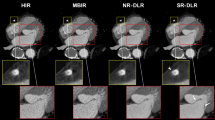
In many clinical scenarios, medical data visualization and interaction are important to physicians for exploring inner anatomical structures and extracting meaningful diagnostic information. Real-time high-quality volume rendering, artifact-free clipping, and rapid scalar value classification are important techniques employed in this process. Unfortunately, in practice, it is still difficult to achieve an optimal balance. In this paper, we present some strategies to address this issue, which are based on the calculation of segment-based post color attenuation and dynamic ray–plane intersection (RPI) respectively. When implemented within our visualization system, the new classification algorithm can deliver real-time performance while avoiding the “color over-accumulation” artifacts suffered by the commonly used acceleration algorithms that employ pre-integrated classification. Our new strategy can achieve an optimized balance between image quality and classification speed. Next, the RPI algorithm is used with opacity adjustment technique to effectively remove the “striping” artifacts on the clipping plane caused by the nonuniform integration length. Furthermore, we present techniques for multiple transfer function (TF) based anatomical feature enhancement and “keyhole” based endoscopic inner structure view. Finally, the algorithms are evaluated subjectively by radiologists and quantitatively compared using image power spectrum analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bethune, C., Stewart, A.J.: Adaptive slice geometry for hardware-assisted volume rendering. J. Graphics Tools 10(1), 55–70 (2005)
Beyer, J., Hadwiger, M., Wolfsberger, S., Bühler, K.: High-quality multimodal volume rendering for preoperative planning of neurosurgical interventions. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 13(6), 1696–1703 (2007)
Blinn, J.F.: Light reflection functions for simulation of clouds and dusty surfaces. Comput. Graph. 16(3), 21–29 (1982)
Bühler, K., Neubauer, A., Hadwiger, M., Wolsfberger, S., Wegenkittl, R.: Interactive 3D techniques for computer-aided diagnosis and surgery simulation tools. In: Hruby, W. (ed.) Digital Revolution in Radiology—Bridging the Future of Health Care, 2nd edn. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (2005)
Cabral, B., Cam, N., Foran, J.: Accelerated volume rendering and tomographic reconstruction using texture mapping hardware. In: VVS ’94: Proceedings of the 1994 Symposium on Volume Visualization, pp. 91–98. ACM, New York (1994)
Elhajjar, J.F., Marchesin, S., Dischler, J.M., Mongenet, C.: Second order pre-integrated volume rendering. In: IEEE Pacific Visualization Symposium, Kyoto, pp. 9–16 (2008, to appear). doi:10.1109/PACIFICVIS.2008.4475453
Engel, K., Hadwiger, M., Kniss, J., Rezk-Salama, C., Weiskopf, D.: Real-Time Volume Graphics. AK Peters, Wellesley (2006)
Engel, K., Kraus, M., Ertl, T.: High-quality pre-integrated volume rendering using hardware-accelerated pixel shading. In: HWWS’01: Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH/EUROGRAPHICS Workshop on Graphics Hardware, pp. 9–16. ACM Press, New York (2001)
Hauser, H., Mroz, L., Bischi, G.I., Gröller, E.: Two-level volume rendering. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 7(3), 242–252 (2001)
Lum, E.B., Wilson, B., Ma, K.-l.: High-quality lighting and efficient pre-integration for volume rendering. In: Proceedings Joint Eurographics-IEEE TVCG Symposium on Visualization 2004 (VisSym’04), pp. 25–34 (2004)
Kniss, J., Premoze, S., Ikits, M., Lefohn, A., Hansen, C., Praun, E.: Gaussian transfer functions for multi-field volume visualization. In: VIS’03: Proceedings of the 14th IEEE Visualization 2003 (VIS’03), p. 65. IEEE Computer Society, Washington (2003)
Knoll, A., Hijazi, Y., Westerteiger, R., Schott, M., Hansen, C., Hagen, H.: Volume raycasting with peak finding and differential sampling. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comp. Graph. 15, 1571–1578 (2009)
Kraus, M.: Direct volume visualization of geometrically unpleasant meshes. Ph.D. thesis, Universität Stuttgart, Germany (2003)
Kraus, M.: Pre-integrated volume rendering for multi-dimensional transfer functions. In: IEEE/EG Symposium on Volume and Point-based Graphics, pp. 97–104 (2008)
Krüger, J., Schneider, J., Westermann, R.: Clearview: An interactive context preserving hot-spot visualization technique. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 12(5), 941–948 (2006)
Kye, H., Shin, B.S., Shin, Y.G.: Interactive classification for pre-integrated volume rendering of high-precision volume data. Graph. Models 70(6), 125–132 (2008)
Lundström, C., Ljung, P., Persson, A., Ynnerman, A.: Uncertainty visualization in medical volume rendering using probabilistic animation. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 13(6), 1648–1655 (2007)
Lundström, C.L., Ljung, P., Ynnerman, A.: Local histograms for design of transfer functions in direct volume rendering. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 12(6), 1570–1579 (2006)
Max, N.L.: Optical models for direct volume rendering. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 1(2), 99–108 (1995)
Moreland, K., Angel, E.: A fast high accuracy volume renderer for unstructured data. In: VolVis, pp. 9–16 (2004)
Muraki, D.J., Bergner, S., Moller, T., Weiskopf, D.: A spectral analysis of function composition and its implications for sampling in direct volume visualization. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 12(5), 1353–1360 (2006)
Pfister, H., Lorensen, B., Bajaj, C., Kindlmann, G., Schroeder, W., Avila, L.S., Martin, K., Machiraju, R., Lee, J.: The transfer function bake-off. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 21(3), 16–22 (2001)
Pinto, F.D.M., Freitas, C.M.D.S.: Volume visualization and exploration through flexible transfer function design. Comput. Graph. 32(5), 540–549 (2008)
Pommert, A., Höhne, K.H.: Evaluation of image quality in medical volume visualization: the state of the art. In: MICCAI (2), pp. 598–605 (2002)
Preim, B., Bartz, D.: Visualization in Medicine: Theory, Algorithms, and Applications. The Morgan Kaufmann Series in Computer Graphics, 1st edn. Morgan Kaufmann, San Mateo (2007)
Rezk-Salama, C.: Volume rendering techniques for general purpose graphics hardware. Ph.D. dissertation, University Erlangen-Nürnberg (2002)
Rezk-Salama, C.: Visual parameters and transfer functions. In: Zudilova-Seinstra, E., Adriaansen, T., Liere, R.V. (eds.) Trends in Interactive Visualization: State-of-the-Art Survey, pp. 99–116. Springer Publishing Company, Inc., Berlin (2008)
Rezk-Salama, C., Keller, M., Kohlmann, P.: High-level user interfaces for transfer function design with semantics. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 12(5), 1021–1028 (2006)
Roettger, S., Ertl, T.: A two-step approach for interactive pre-integrated volume rendering of unstructured grids. In: VVS ’02: Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE Symposium on Volume Visualization and Graphics, pp. 23–28. IEEE Press, Piscataway (2002)
Roettger, S., Guthe, S., Weiskopf, D., Ertl, T., Strasser, W.: Smart hardware-accelerated volume rendering. In: VISSYM ’03: Proceedings of the Symposium on Data Visualisation 2003, pp. 231–238. Eurographics Association, Aire-la-Ville (2003)
Röttger, S., Kraus, M., Ertl, T.: Hardware-accelerated volume and isosurface rendering based on cell-projection. In: IEEE Visualization, pp. 109–116 (2000)
Scharsach, H., Hadwiger, M., Neubauer, A., Wolfsberger, S., Bühler, K.: Perspective isosurface and direct volume rendering for virtual endoscopy applications. In: EuroVis, pp. 315–322 (2006)
Schulze, J.P., Kraus, M., Lang, U., Ertl, T.: Integrating pre-integration into the Shear-Warp algorithm. In: VG’03: Proceedings of the 2003 Eurographics/IEEE TVCG Workshop on Volume Graphics, pp. 109–118. ACM, New York (2003)
Siewerdsen, J., Antonuk, L., el Mohri, Y., Yorkston, J., Huang, W., Cunningham, I.: Signal noise power spectrum, and detective quantum efficiency of indirect-detection flat-panel images for diagnostic radiology. Med. Phys. 25(5), 614–628 (1998)
Stegmaier, S., Strengert, M., Klein, T., Ertl, T.: A simple and flexible volume rendering framework for graphics-hardware based raycasting. In: Proceedings of the International Workshop on Volume Graphics ’05, pp. 187–195 (2005)
Viola, I., Kanitsar, A., Gröller, M.E.: Importance-driven feature enhancement in volume visualization. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 11(4), 408–418 (2005)
Weiskopf, D., Engel, K., Ertl, T.: Interactive clipping techniques for texture-based volume visualization and volume shading. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 9(3), 298–312 (2003)
Westermann, R., Ertl, T.: Efficiently using graphics hardware in volume rendering applications. In: SIGGRAPH’98: Proceedings of the 25th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, pp. 169–177. ACM, New York (1998)
Williams, P.L., Max, N.L., Stein, C.M.: A high accuracy volume renderer for unstructured data. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 4(1), 37–54 (1998)
Wittenbrink, C.M., Malzbender, T., Goss, M.E.: Opacity-weighted color interpolation, for volume sampling. In: VVS’98: Proceedings of the 1998 IEEE Symposium on Volume Visualization, pp. 135–142. ACM, New York (1998)
Wu, Y., Qu, H.: Interactive transfer function design based on editing direct volume rendered images. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 13(5), 1027–1040 (2007)
Xie, K., Sun, G., Yang, J., Zhu, Y.M.: Interactive volume cutting of medical data. Comput. Biol. Med. 37(8), 1155–1159 (2007)
Zhang, Q., Eagleson, R., Peters, T.M.: Graphics hardware based volumetric medical data set visualization and classification. In: Cleary, K.R., Galloway, J. Robert L. (eds.) SPIE Medical Imaging, vol. 6141, 61412T. SPIE, San Diego (2006)
Zhang, Q., Eagleson, R., Peters, T.M.: Rapid voxel classification methodology for interactive 3D medical image visualization. In: Ayache, N., Ourselin, S., Maeder, A.J. (eds.) MICCAI (2). Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 4792, pp. 86–93. Springer, Berlin (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Eagleson, R. & Peters, T.M. Rapid scalar value classification and volume clipping for interactive 3D medical image visualization. Vis Comput 27, 3–19 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-010-0509-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-010-0509-z