Abstract
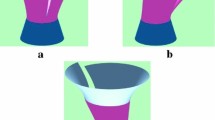
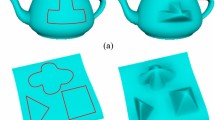
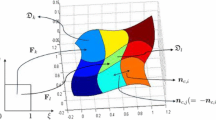
This paper proposes the concept of blending time-dependent varying surfaces, and develops a new method to create a controllable C1 continuous blending surface between primary parametric surfaces whose position and shape change with time. We treat it as a boundary-valued problem defined by the mathematical model of a vectored dynamic fourth-order partial differential equation subjected to time-dependent C1 continuous blending boundary constraints. High performance blending surface generation is achieved through the development of an approximate analytical solution of the mathematical model. We investigate the accuracy and efficiency of the solution, study the effective shape control of the blending surfaces, and apply the obtained solution to tackle surface blending problems. The applications demonstrate that our proposed approach is very effective and efficient in dealing with controllable C1 continuous surface blending between time-dependent varying parametric surfaces.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vida, J., Martin, R.R., Varady, T.: A survey of blending methods that use parametric surfaces. Comput. Aided Des. 26(5), 341–365 (1994)
Rossignac, J.R., Requicha, A.A.G.: Constant-radius blending in solid modeling. CIME, Comput. Mech. Eng. 3(1), 65–73 (1984)
Choi, B.K., Ju, S.Y.: Constant-radius blending in surface modeling. Comput. Aided Des. 21(4), 213–220 (1989)
Sanglikar, M.A., Koparkar, P., Joshi, V.N.: Modelling rolling ball blends for computer aided geometric design. Comput. Aided Geom. Des. 7, 399–414 (1990)
Barnhill, R.E., Farin, G.E., Chen, Q.: Constant-radius blending of parametric surfaces. Computing, Suppl. 8, 1–20 (1993)
Chuang, J.-H., Lin, C.-H., Hwang, W.-C.: Variable-radius blending of parametric surfaces. Vis. Comput. 11, 513–525 (1995)
Farouki, R.A.M., Sverrisson, R.: Approximation of rolling-ball blends for free-form parametric surfaces. Comput. Aided Des. 28(11), 871–878 (1996)
Chuang, J.H., Hwang, W.C.: Variable-radius blending by constrained spine generation. Vis. Comput. 13, 316–329 (1997)
Chuang, J.-H., Lien, P.-L.: One and two-parameter blending for parametric surfaces. J. Inf. Sci. Eng. 14, 461–477 (1998)
Lukács, G.: Differential geometry of G1 variable-radius rolling ball blend surfaces. Comput. Aided Geom. Des. 15, 585–613 (1998)
Kós, G., Martin, R.R., Vrady, T.: Methods to recover constant-radius rolling ball blends in reverse engineering. Comput. Aided Geom. Des. 17, 127–160 (2000)
Bloor, M.I.G., Wilson, M.J.: Generating blend surfaces using partial differential equations. Comput. Aided Des. 21(3), 165–171 (1989)
Cheng, S.Y., Bloor, M.I.G., Saia, A., Wilson, M.J.: Blending between quadric surfaces using partial differential equations. In: Ravani, B. (ed.) Advances in Design Automation, Vol. 1, Computer and Computational Design, pp. 257–263. New York, ASME (1990)
Bloor, M.I.G., Wilson, M.J.: Representing PDE surfaces in terms of B-splines. Comput. Aided Des. 22(6), 324–331 (1990)
Bloor, M.I.G., Wilson, M.J.: Using partial differential equations to generate free-form surfaces. Comput. Aided Des. 22(4), 202–212 (1990)
Bloor, M.I.G., Wilson, M.J.: Spectral approximations to PDE surfaces. Comput. Aided Des. 28(2), 145–152 (1996)
Bloor, M.I.G., Wilson, M.J.: Generating blend surfaces using a perturbation method. Math. Comput. Model. 31(1), 1–13 (2000)
Brown, J.M., Bloor, M.I.G., Bloor, M.S., Wilson, M.J.: The accuracy of B-spline finite element approximations to PDE surfaces. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 158(3–4), 221–234 (1998)
Li, Z.C.: Boundary penalty finite element methods for blending surfaces. I. Basic theory. J. Comput. Math. 16, 457–480 (1998)
Li, Z.C.: Boundary penalty finite element methods for blending surfaces. II. Biharmonic equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 110, 155–176 (1999)
Li, Z.C., Chang, C.-S.: Boundary penalty finite element methods for blending surfaces. III. Superconvergence and stability and examples. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 110, 241–270 (1999)
You, L.H., Zhang, J.J., Comninos, P.: Blending surface generation using a fast and accurate analytical solution of a fourth order PDE with three shape control parameters. Vis. Comput. 20, 199–214 (2004)
You, L.H., Comninos, P., Zhang, J.J.: PDE blending surfaces with C2 continuity. Comput. Graph. 28(6), 895–906 (2004)
Ugail, H., Bloor, M.I.G., Wilson, M.J.: Techniques for interactive design using the PDE method. ACM Trans. Graph. 18(2), 195–212 (1999)
Zhang, J.J., You, L.H.: Fast surface modeling using a 6th order PDE. Comput. Graph. Forum 23(3), 311–320 (2004)
Gonzalez, C.G., Athanasopoulos, M., Ugail, H.: Cyclic animation using partial differential equations. Vis. Comput. 26(5), 325–338 (2010)
Sheng, Y., Sourin, S., Gonzalez, C.G., Ugail, H.: A PDE method for patchwise approximation of large polygon meshes. Vis. Comput. 26(6–8), 975–984 (2010)
You, L.H., Chang, J., Yang, X., Zhang, J.J.: Solid modeling based on sixth order partial differential equations. Comput. Aided Des. 43(6), 720–729 (2011)
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by the grant of UK Royal Society International Joint Projects/NSFC 2010.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
You, L.H., Ugail, H. & Zhang, J.J. Controllable C1 continuous blending of time-dependent parametric surfaces. Vis Comput 28, 573–583 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-012-0693-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-012-0693-0