Abstract
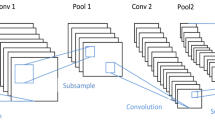
With the recent development and application of human–computer interaction systems, facial expression recognition (FER) has become a popular research area. The recognition of facial expression is a difficult problem for existing machine learning and deep learning models because that the images can vary in brightness, background, pose, etc. Deep learning methods also require the support of big data. It does not perform well when the database is small. Feature extraction is very important for FER, even a simple algorithm can be very effective if the extracted features are sufficient to be separable. However, deep learning methods automatically extract features so that some useless features can interfere with useful features. For these reasons, FER is still a challenging problem in computer vision. In this paper, with the aim of coping with few data and extracting only useful features from image, we propose new face cropping and rotation strategies and simplification of the convolutional neural network (CNN) to make data more abundant and only useful facial features can be extracted. Experiments to evaluate the proposed method were performed on the CK+ and JAFFE databases. High average recognition accuracies of 97.38% and 97.18% were obtained for 7-class experiments on the CK+ and JAFFE databases, respectively. A study of the impact of each proposed data processing method and CNN simplification is also presented. The proposed method is competitive with existing methods in terms of training time, testing time, and recognition accuracy.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dalal, N., Triggs, B.: Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 886–893. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2005.177 (2005)
De la Torre, F., Chu, W.S., Xiong, X., Vicente, F., Ding, X., Cohn, J.F.: Intraface. In: IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, pp 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/FG.2015.7163082 (2015)
Ekman, P., Friesen, W.V.: Facial action coding system: a technique for the measurement of facial movement. In: Consulting Psychologists, Palo Alto (1978)
Glorot, X., Bengio, Y.: Understanding the difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 9, 249–256 (2010)
Gogić, I., Manhart, M., Pandžić, I.S., Ahlberg, J.: Fast facial expression recognition using local binary features and shallow neural networks. Vis. Comput. 1–16 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-018-1585-8
Goh, K.M., Ng, C.H., Lim, L.L., Sheikh, U.: Micro-expression recognition: an updated review of current trends, challenges and solutions. Vis. Comput. 1–24 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-018-1607-6
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 770–778 (2016)
Jarrett, K., Kavukcuoglu, K., Ranzato, M., Lecun, Y.: What is the best multi-stage architecture for object recognition? In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, vol 30, pp 2146–2153 (2009)
Jin, H., Wang, X., Lian, Y., Hua, J.: Emotion information visualization through learning of 3d morphable face model. Vis. Comput. 1–14 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-018-1482-1
Jones, J.P., Palmer, L.A.: An evaluation of the two-dimensional gabor filter model of simple receptive fields in cat striate cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 58(6), 1233–1258 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1987.58.6.1233
King, D.E.: Dlib-ml: a machine learning toolkit. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 10, 1755–1758 (2009)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Pereira, F., Burges, C.J.C., Bottou, L., Weinberger, K.Q. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp 1097–1105. Curran Associates, Inc., Lake Tahoe, Nevada, USA (2012)
Liu, M., Li, S., Shan, S., Chen, X.: Au-inspired deep networks for facial expression feature learning. Neurocomputing 159(C), 126–136 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2015.02.011
Liu, P., Han, S., Meng, Z., Tong, Y.: Facial expression recognition via a boosted deep belief network. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 1805–1812 (2014)
Lopes, A.T., Aguiar, E.D., Souza, A.F.D., Oliveira-Santos, T.: Facial expression recognition with convolutional neural networks: coping with few data and the training sample order. Pattern Recognit. 61, 610–628 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2016.07.026
Lucey, P., Cohn, J.F., Kanade, T., Saragih, J.: The extended cohn-kanade dataset (ck+): a complete dataset for action unit and emotion-specified expression. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops, pp 94–101. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW.2010.5543262 (2010)
Lyons, M.J., Budynek, J., Akamatsu, S.: Automatic classification of single facial images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 21(12), 1357–1362 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1109/34.817413
Lcun, Y., Bottou, L., Bengio, Y., Haffner, P.: Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 86(11), 2278–2324 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1109/5.726791
Matthews, I., Baker, S.: Active appearance models revisited. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 60, 135–164 (2004)
Mayya, V., Pai, R.M., Pai, M.M.M.: Automatic facial expression recognition using dcnn. Proc. Comput. Sci. 93, 453–461 (2016a). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2016.07.233
Mayya, V., Pai, R.M., Pai, M.M.M.: Combining temporal interpolation and dcnn for faster recognition of micro-expressions in video sequences. In: International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics, pp 699–703. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICACCI.2016.7732128 (2016)
Mehrabian, A.: Communication without words. Commun. Theory, 193–200 (2008)
Mohammadi, M.R., Fatemizadeh, E., Mahoor, M.H.: Pca-based dictionary building for accurate facial expression recognition via sparse representation. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 25(5), 1082–1092 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvcir.2014.03.006
Ojala, T., Pietikäinen, M., Harwood, D.: A comparative study of texture measures with classification based on featured distributions. Pattern Recognit. 29(1), 51–59 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-3203(95)00067-4
Owusu, E., Zhan, Y., Mao, Q.R.: An svm-adaboost facial expression recognition system. Appl. Intell. 40(3), 536–545 (2014)
Pu, X., Fan, K., Chen, X., Ji, L., Zhou, Z.: Facial expression recognition from image sequences using twofold random forest classifier. Neurocomputing 168(C), 1173–1180 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2015.05.005
Rashid, M., Abu-Bakar, S., Mokji, M.: Human emotion recognition from videos using spatio-temporal and audio features. Vis. Comput. 29(12), 1269–1275 (2013)
Rivera, A.R., Castillo, J.R., Chae, O.: Local directional number pattern for face analysis: face and expression recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 22(5), 1740–1752 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2012.2235848
Shan, C., Gong, S., Mcowan, P.W.: Facial expression recognition based on local binary patterns: a comprehensive study. Image Vis. Comput. 27(6), 803–816 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imavis.2008.08.005
Srivastava, N., Hinton, G., Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Salakhutdinov, R.: Dropout: a simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 15, 1929–1958 (2014)
Sutskever, I., Martens, J., Dahl, G., Hinton, G.: On the importance of initialization and momentum in deep learning. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp 1139–1147 (2013)
Uddin, M.Z., Hassan, M.M., Almogren, A., Zuair, M., Fortino, G., Torresen, J.: A facial expression recognition system using robust face features from depth videos and deep learning. Comput. Electr. Eng. 63, 114–125 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2017.04.019
Wen, G., Hou, Z., Li, H., Li, D., Jiang, L., Xun, E.: Ensemble of deep neural networks with probability-based fusion for facial expression recognition. Cogn. Comput. 9(5), 597–610 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-017-9472-6
Yang, P., Liu, Q., Metaxas, D.N.: Boosting coded dynamic features for facial action units and facial expression recognition. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2007.383059 (2007)
Yu, Z., Liu, Q., Liu, G.: Deeper cascaded peak-piloted network for weak expression recognition. Vis. Comput. 34(12), 1691–1699 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-017-1443-0
Zeng, N., Zhang, H., Song, B., Liu, W., Li, Y., Dobaie, A.M.: Facial expression recognition via learning deep sparse autoencoders. Neurocomputing 273, 643–649 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2017.08.043
Zhang, K., Huang, Y., Wu, H., Wang, L.: Facial smile detection based on deep learning features. In: 2015 3rd IAPR Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition (ACPR). IEEE, pp 534–538 (2015)
Zhao, G., Pietikinen, M., Member, S.: Dynamic texture recognition using local binary patterns with an application to facial expressions. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 29(6), 915–928 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2007.1110
Zhao, J., Mao, X., Zhang, J.: Learning deep facial expression features from image and optical flow sequences using 3D CNN. Vis. Comput. 34(10), 1461–1475 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-018-1477-y
Funding
This research was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51605464), National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (2014CB049500) and Research on the Major Scientific Instrument of National Natural Science Foundation of China (61727809).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, K., Jin, Y., Akram, M.W. et al. Facial expression recognition with convolutional neural networks via a new face cropping and rotation strategy. Vis Comput 36, 391–404 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-019-01627-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-019-01627-4