Abstract
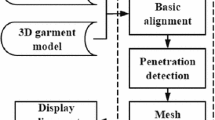
To facilitate the input and improve the practicality of the existing virtual fitting systems, we propose a fully automatic 3D virtual fitting system to fit garment onto human models with various shapes and poses using a 2D full-body image and a 3D garment model. The proposed method constructs the 3D human model from the input 2D full-body image of the user by adopting the SMPLify method. To automatically position garment models onto human models with arbitrary postures, we present a 3D mesh segmentation method based on the discrete Reeb graph to accurately segment the different parts of a garment model, and a skeleton driving method based on mean curvature flow, which automatically adjusts the posture of the garment model according to the skeleton structural difference between the human model and the garment model. In addition, for the purpose of obtaining a more natural dress effect, we further adopt interpenetration removal and physical simulation for the deformed garment model. Compared to existing automatic 3D virtual fitting systems, the experimental results, we obtained based on the Leeds Sports Pose dataset, reveal that the proposed virtual fitting system is stable and effective.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, Z., Jin, X., Barsky, B., Liu, J.: 3D clothing fitting based on the geometric feature matching. In: 2009 11th IEEE International Conference on Computer-Aided Design and Computer Graphics, pp. 74-80. IEEE (2009)
Li, J., Ye, J., Wang, Y., Bai, L., Lu, G.: Fitting 3D garment models onto individual human models. Comput. Graph. 34(6), 742–755 (2010)
Brouet, R., Sheffer, A., Boissieux, L., Cani, M. P.: Design preserving garment transfer. ACM Trans. Graph. 31(4) (2012)
Pons-Moll, G., Pujades, S., Hu, S., Black, M.J.: ClothCap: seamless 4D clothing capture and retargeting. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 36(4), 73 (2017)
Li, J., Lu, G.: Customizing 3D garments based on volumetric deformation. Comput. Ind. 62(7), 693–707 (2011)
Lee, Y., Ma, J., Choi, S.: Automatic pose-independent 3D garment fitting. Comput. Graph. 37(7), 911–922 (2013)
Narita, F., Saito, S., Kato, T., Fukusato, T., Morishima, S.: Pose-independent garment transfer. In: SIGGRAPH Asia 2014 Posters, p. 12 (2014)
Narita, F., Saito, S., Kato, T., Fukusato, T., Morishima, S.: Texture preserving garment transfer. In: ACM SIGGRAPH 2015 Posters, p 91 (2015)
Jiang, L., Ye, J., Sun, L., Li, J.: Transferring and fitting fixed-sized garments onto bodies of various dimensions and postures. Comput.-Aided Des. 106, 30–42 (2019)
Tisserand, Y., Cuel, L., Magnenat-Thalmann, N.: Automatic 3D garment positioning based on surface metric. Comput. Anim. Virtual Worlds 28, e1770 (2017)
Wu, N., Deng, Z., Huang, Y., Liu, C., Zhang, D., Jin, X.: A fast garment fitting algorithm using skeleton-based error metric. Comput. Anim. Virtual Worlds 29(3–4), e1811 (2018)
Guan, P., Reiss, L., Hirshberg, D.A., Weiss, A., Black, M.J.: DRAPE: dressing any person. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 31(4), 1–10 (2012)
Wang, C.C.: Parameterization and parametric design of mannequins. Comput.-Aided Des. 37(1), 83–98 (2005)
Baek, S.Y., Lee, K.: Parametric human body shape modeling framework for human-centered product design. Comput.-Aided Des. 44(1), 56–67 (2012)
Xu, W., Chatterjee, A., Zollhöfer, M., Rhodin, H., Mehta, D., Seidel, H.P., Theobalt, C.: Monoperfcap: Human performance capture from monocular video. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 37(2), 27 (2018)
Alldieck, T., Kassubeck, M., Wandt, B., Rosenhahn, B., Magnor, M.: Optical flow-based 3d human motion estimation from monocular video. In: German Conference on Pattern Recognition, pp. 347–360. Springer (2017)
Grest, D., Herzog, D., Koch, R.: Human model fitting from monocular posture images. In: Proceedings of the VMV, pp. 665–1344 (2005)
Balan, A. O., Sigal, L., Black, M. J., Davis, J. E., Haussecker, H. W.: Detailed human shape and pose from images. In: 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1–8. IEEE (2007)
Jain, A., Thormählen, T., Seidel, H.P., Theobalt, C.: Moviereshape: tracking and reshaping of humans in videos. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 29(6), 148 (2010)
von Marcard, T., Rosenhahn, B., Black, M.J., Pons-Moll, G.: Sparse inertial poser: automatic 3d human pose estimation from sparse imus. Comput. Graph. Forum. 36, 349–360 (2017)
Weiss, A., Hirshberg, D., Black, M. J.: Home 3D body scans from noisy image and range data. In: 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1951–1958. IEEE (2011)
Sigal, L., Balan, A., Black, M. J.: Combined discriminative and generative articulated pose and non-rigid shape estimation. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 1337–1344 (2008)
Guan, P., Weiss, A., Balan, A. O., Black, M. J.: Estimating human shape and pose from a single image. In: 2009 International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1381–1388. IEEE (2009)
Anguelov, D., Srinivasan, P., Koller, D., Thrun, S., Rodgers, J., Davis, J.: SCAPE: shape completion and animation of people. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 24(3), 408–416 (2005)
Bogo, F., Kanazawa, A., Lassner, C., Gehler, P., Romero, J., Black, M. J.: Keep it SMPL: Automatic estimation of 3D human pose and shape from a single image. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 561–578 (2016)
Loper, M., Mahmood, N., Romero, J., Pons-Moll, G., Black, M.J.: SMPL: a skinned multi-person linear model. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 34(6), 248 (2015)
Lassner, C., Romero, J., Kiefel, M., Bogo, F., Black, M. J., Gehler, P. V.: Unite the people: closing the loop between 3d and 2d human representations. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6050–6059 (2017)
Tan, V., Budvytis, I., Cipolla, R.: Indirect deep structured learning for 3d human body shape and pose prediction. BMVC 3, 6 (2017)
Pavlakos, G., Zhu, L., Zhou, X., Daniilidis, K.: Learning to estimate 3D human pose and shape from a single color image. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 459–468 (2018)
Varol, G., Ceylan, D., Russell, B., Yang, J., Yumer, E., Laptev, I., Schmid, C.: Bodynet: Volumetric inference of 3d human body shapes. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 20–36 (2018)
Kanazawa, A., Black, M. J., Jacobs, D. W., Malik, J.: End-to-end recovery of human shape and pose. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7122–7131 (2018)
Omran, M., Lassner, C., Pons-Moll, G., Gehler, P., Schiele, B.: Neural body fitting: unifying deep learning and model based human pose and shape estimation. In: International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), pp. 484–494 (2018)
Kolotouros, N., Pavlakos, G., Daniilidis, K.: Convolutional Mesh regression for single-image human shape reconstruction. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4501–4510 (2019)
Kolotouros, N., Pavlakos, G., Black, M. J., Daniilidis, K.: Learning to Reconstruct 3D Human Pose and shape via model-fitting in the loop. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2252–2261 (2019)
Rong, Y., Liu, Z., Li, C., Cao, K., Loy, C. C.: Delving deep into hybrid annotations for 3D Human recovery in the wild. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 5340–5348 (2019)
Fuhrmann, A., Groß, C., Luckas, V., Weber, A.: Interaction-free dressing of virtual humans. Comput. Graph. 27(1), 71–82 (2003)
Volino, P., Cordier, F., Magnenat-Thalmann, N.: From early virtual garment simulation to interactive fashion design. Comput.-Aided Des. 37(6), 593–608 (2005)
Metaaphanon, N., Kanongchaiyos, P.: Real-time cloth simulation for garment CAD. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques in Australasia and South East Asia, pp. 83–89 (2005)
Clegg, A., Tan, J., Turk, G., Liu, C.K.: Animating human dressing. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 34(4), 116 (2015)
Clegg, A., Yu, W., Tan, J., Liu, C. K., Turk, G.: Learning to dress: synthesizing human dressing motion via deep reinforcement learning. In: SIGGRAPH Asia 2018, pp. 179 (2018)
Cai, H., Shi, G., Gao, C., Wang, D.: Automatic 3D garment fitting based on skeleton driving. In: Pacific rim conference on multimedia, pp. 267–277 (2018)
Pishchulin, L., Insafutdinov, E., Tang, S., Andres, B., Andriluka, M., Gehler, P. V., Schiele, B.: Deepcut: Joint subset partition and labeling for multi person pose estimation. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 4929–4937 (2016)
Werghi, N., Xiao, Y., Siebert, J.P.: A functional-based segmentation of human body scans in arbitrary postures. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B (Cybern.) 36(1), 153–165 (2006)
Tagliasacchi, A., Alhashim, I., Olson, M., Zhang, H.: Mean curvature skeletons. Comput. Graph. Forum 31(5), 1735–1744 (2012)
Cornea, N.D., Silver, D., Min, P.: Curve-skeleton properties, applications, and algorithms. IEEE Trans. Visual. Comput. Graph. 13, 530–548 (2007)
Au, O.K.C., Tai, C.L., Chu, H.K., Cohen-Or, D., Lee, T.Y.: Skeleton extraction by mesh contraction. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 27(3), 44 (2008)
Wang, Y.S., Lee, T.Y.: Curve-skeleton extraction using iterative least squares optimization. IEEE Trans. Visual. Comput. Graph. 14(4), 926–936 (2008)
Dey, T.K., Sun, J.: Defining and computing curve-skeletons with medial geodesic function. Symp. Geom. Process. 6, 143–152 (2006)
Eberly, D.: Triangulation by ear clipping. Geom. Tools. 2002–2005 (2008)
Johnson, S., Everingham, M.: Clustered Pose and nonlinear appearance models for Human Pose estimation. BMVC 2, 5 (2010)
Sorkine, O., Cohen-Or, D., Lipman, Y., Alexa, M., Rössl, C., Seidel, H. P.: Laplacian surface editing. In: 2004 Eurographics/ACM SIGGRAPH Symposium on Geometry Processing, pp. 175–184 (2004)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (Grant No. 2019A1515011075), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61972433, 61872394) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (19lgjc11).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, G., Gao, C., Wang, D. et al. Automatic 3D virtual fitting system based on skeleton driving. Vis Comput 37, 1075–1088 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-020-01853-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-020-01853-1