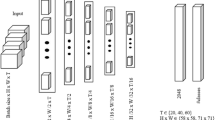
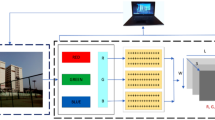
Abstract
Activities of daily living (ADLs) are the activities which humans perform every day of their lives. Walking, sleeping, eating, drinking and sleeping are examples for ADLs. Compared to RGB videos, depth video-based activity recognition is less intrusive and eliminates many privacy concerns, which are crucial for applications such as life-logging and ambient assisted living systems. Existing methods rely on handcrafted features for depth video classification and ignore the importance of audio stream. In this paper, we propose an ADL recognition system that relies on both audio and depth modalities. We propose to adopt popular convolutional neural network (CNN) architectures used for RGB video analysis to classify depth videos. The adaption poses two challenges: (1) depth data are much nosier and (2) our depth dataset is much smaller compared RGB video datasets. To tackle those challenges, we extract silhouettes from depth data prior to model training and alter deep networks to be shallower. As per our knowledge, we used CNN to segment silhouettes from depth images and fused depth data with audio data to recognize ADLs for the first time. We further extended the proposed techniques to build a real-time ADL recognition system.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arshad, S., Feng, C., Liu, Y., Hu, Y., Yu, R., Zhou, S., Li, H.: Wi-chase: a wifi based human activity recognition system for sensorless environments. In: 2017 IEEE 18th International Symposium on A World of Wireless, Mobile and Multimedia Networks (WoWMoM), pp. 1–6 (2017)
Baccouche, M., Mamalet, F., Wolf, C., Garcia, C., Baskurt, A.: Sequential deep learning for human action recognition. In: Salah, A.A., Lepri, B. (eds.) Human Behavior Understanding, pp. 29–39. Springer, Berlin (2011)
Badrinarayanan, V., Kendall, A., Cipolla, R.: Segnet: a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39(12), 2481–2495 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2644615
Biswas, K.K., Basu, S.K.: Gesture recognition using microsoft kinect\(\textregistered \). In: The 5th International Conference on Automation, Robotics and Applications, pp. 100–103 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICARA.2011.6144864
Chen, J., Kam, A.H., Zhang, J., Liu, N., Shue, L.: Bathroom activity monitoring based on sound. In: Gellersen, H.W., Want, R., Schmidt, A. (eds.) Pervasive Computing, pp. 47–61. Springer, Berlin (2005)
Cheng, J., Sundholm, M., Zhou, B., Hirsch, M., Lukowicz, P.: Smart-surface: large scale textile pressure sensors arrays for activity recognition. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 30, 97–112 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmcj.2016.01.007
Chollet, F., et al.: Keras. (2015). https://keras.io
Cristani, M., Bicego, M., Murino, V.: Audio-visual event recognition in surveillance video sequences. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 9(2), 257–267 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2006.886263
Das, S., Thonnat, M., Bremond, F.F.: Looking deeper into time for activities of daily living recognition. In: WACV 2020-IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision. Snowmass village, Colorado, United States (2020). https://hal.inria.fr/hal-02368366
Das Dawn, D., Shaikh, S.H.: A comprehensive survey of human action recognition with spatio-temporal interest point (stip) detector. Vis. Comput. 32, 289–306 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-015-1066-2
Donahue, J., Hendricks, L.A., Rohrbach, M., Venugopalan, S., Guadarrama, S., Saenko, K., Darrell, T.: Long-term recurrent convolutional networks for visual recognition and description. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39(4), 677–691 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2599174
Gasparrini, S., Cippitelli, E., Spinsante, S., Gambi, E.: A depth-based fall detection system using a Kinect\(\textregistered \) sensor. Sensors (Switzerland) 14(2), 2756–2775 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3390/s140202756
Grushin, A., Monner, D.D., Reggia, J.A., Mishra, A.: Robust human action recognition via long short-term memory. In: The 2013 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 1–8 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/IJCNN.2013.6706797
Hou, J.C., Wang, S.S., Lai, Y.H., Tsao, Y., Chang, H.W., Wang, H.m.: Audio-visual speech enhancement using multimodal deep convolutional neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computational Intelligence 2 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TETCI.2017.2784878
Ji, S., Xu, W., Yang, M., Yu, K.: 3d convolutional neural networks for human action recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 35(1), 221–231 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2012.59
Jiang, X., Zhong, F., Peng, Q., Qin, X.: Online robust action recognition based on a hierarchical model. Vis. Comput. 30, 1021–1033 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-014-0923-8
Kamal, S., Jalal, A., Kim, D.: Depth images-based human detection, tracking and activity recognition using spatiotemporal features and modified hmm. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 11(6), 1857–1862 (2016). https://doi.org/10.5370/jeet.2016.11.6.1857
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 60(6), 84–90 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1145/3065386
Ma, H., Li, W., Zhang, X., Gao, S., Lu, S.: Attnsense: Multi-level attention mechanism for multimodal human activity recognition. pp. 3109–3115. International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence Organization (2019). https://doi.org/10.24963/ijcai.2019/431
Mainetti, L., Manco, L., Patrono, L., Secco, A., Sergi, I., Vergallo, R.: An ambient assisted living system for elderly assistance applications. In: 2016 IEEE 27th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), pp. 1–6 (2016)
Microsoft Corporation: Kinect - Windows app development. https://developer.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/kinect
Movo Photo Corporation: MOVO USB computer Lavalier microphone (20’ft cord). https://www.movophoto.com/products/movo-m1-usb-lavalier-lapel-condenser-computer-microphone
Muda, L., Begam, M., Elamvazuthi, I.: Voice recognition algorithms using mel frequency cepstral coefficient (mfcc) and dynamic time warping (dtw) techniques. J. Comput. 2, 34–41 (2010). https://doi.org/10.5120/20312-2362
Naronglerdrit, P., Mporas, I., Sotudeh, R.: Monitoring of indoors human activities using mobile phone audio recordings. In: Proceedings-2017 IEEE 13th International Colloquium on Signal Processing and its Applications, CSPA 2017 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/CSPA.2017.8064918
Ni, B., Wang, G., Moulin, P.: RGBD-HuDaAct: a color-depth video database for human daily activity recognition BT - consumer depth cameras for computer vision. 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops pp. 1147–1153 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCVW.2011.6130379
Ordóñez, F.J., Roggen, D.: Deep convolutional and lstm recurrent neural networks for multimodal wearable activity recognition. Sensors 16, 115 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3390/s16010115
Oreifej, O., Liu, Z.: Hon4d: histogram of oriented 4d normals for activity recognition from depth sequences. In: 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 716–723 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2013.98
Pieropan, A., Salvi, G., Pauwels, K., Kjellström, H.: Audio–visual classification and detection of human manipulation actions. In: 2014 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 3045–3052 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2014.6942983
PrimeSense: prime sensortm nite 1.3 algorithms notes-version 1.0 (2010)
Ronao, C., Cho, S.B.: Human activity recognition with smartphone sensors using deep learning neural networks. Expert Syst. Appl. 59, 235–244 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2016.04.032
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. (2015). ArXiv arXiv:abs/1505.04597
Sainburg, T.: noisereduce \(\cdot \) PyPI. https://pypi.org/project/noisereduce/
Salamon, J., Bello, J.P.: Deep convolutional neural networks and data augmentation for environmental sound classification. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 24(3), 279–283 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/LSP.2017.2657381
Siantikos, G., Giannakopoulos, T., Konstantopoulos, S.: A low-cost approach for detecting activities of daily living using audio information: a use case on bathroom activity monitoring. In: International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health (2016)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos. (2014) ArXiv arXiv:abs/1406.2199
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. ICLR pp. 1–14 (2014). arXiv:1409.1556
Stork, J.A., Spinello, L., Silva, J., Arras, K.O.: Audio-based human activity recognition using non-markovian ensemble voting. In: 2012 IEEE RO-MAN: The 21st IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication, pp. 509–514 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/ROMAN.2012.6343802
Tran, D., Bourdev, L., Fergus, R., Torresani, L., Paluri, M.: Learning spatiotemporal features with 3d convolutional networks. In: 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 4489–4497 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.510
Tran, P.V.: A fully convolutional neural network for cardiac segmentation in short-axis mri. (2016) CoRR arXiv:abs/1604.00494
Trinh, L.A., Thang, N.D., Tran, H.H., Hung, T.C.: Human extraction from a sequence of depth images using segmentation and foreground detection. Proceedings of the 5th Symposium on Information and Communication Technology-SoICT 14, (2014). https://doi.org/10.1145/2676585.2676624
Wang, P., Li, W., Gao, Z., Zhang, J., Tang, C., Ogunbona, P.O.: Action recognition from depth maps using deep convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Hum. Mach. Syst. 46(4), 498–509 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/THMS.2015.2504550
Wang, W., Liu, A.X., Shahzad, M., Ling, K., Lu, S.: Device-free human activity recognition using commercial wifi devices. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 35(5), 1118–1131 (2017)
Wu, Q., Wang, Z., Deng, F., Chi, Z., Feng, D.D.: Realistic human action recognition with multimodal feature selection and fusion. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 43(4), 875–885 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMCA.2012.2226575
Wu, Z., Jiang, Y.G., Wang, X., Ye, H., Xue, X.: Multi-stream multi-class fusion of deep networks for video classification. In: Proceedings of the 24th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, MM ’16, pp. 791–800. ACM, New York, NY, USA (2016). https://doi.org/10.1145/2964284.2964328
Wu, Z., Wang, X., Jiang, Y.G., Ye, H., Xue, X.: Modeling spatial-temporal clues in a hybrid deep learning framework for video classification. In: Proceedings of the 23rd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, MM ’15, pp. 461–470. ACM, New York, NY, USA (2015). https://doi.org/10.1145/2733373.2806222
Xia, L., Aggarwal, J.K.: Spatio-temporal depth cuboid similarity feature for activity recognition using depth camera. Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition pp. 2834–2841 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2013.365
Yang, X., Tian, Y.: Super normal vector for activity recognition using depth sequences. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR ’14, pp. 804–811. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, DC, USA (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2014.108
Yang, X., Zhang, C., Tian, Y.: Recognizing actions using depth motion maps-based histograms of oriented gradients. In: Proceedings of the 20th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, MM ’12, pp. 1057–1060. ACM, New York, NY, USA (2012). https://doi.org/10.1145/2393347.2396382
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madhuranga, D., Madushan, R., Siriwardane, C. et al. Real-time multimodal ADL recognition using convolution neural networks. Vis Comput 37, 1263–1276 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-020-01864-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-020-01864-y