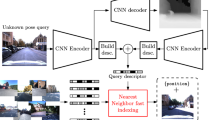
Abstract
Important location information of a query image can be obtained directly through indoor 3D points. However, the 3D model-based indoor positioning is still an open issue to be addressed, especially in large-scale dynamic environments. We design and realize the positioning system for large indoor scenes called the EfiLoc. First, we develop a lightweight network model, which can quickly extract discriminative global deep features to improve the discrimination of similar scenes. Another property is that the generated sparser main global descriptors can greatly reduce the retrieval time of multi-dimensional features. Second, we innovatively implement the efficient association of 3D point with the 2D features generated by its projection regions. Preserving the associations of the pixels in some key areas of the image, the precise and quick large-scale indoor localization can be realized. The experimental results show that EfiLoc can achieve good positioning accuracy and is of better robustness to the environment of weak textures and similar scenes compared with current state-of-the-art vision-based solutions.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xiao, J., Zhou, Z., Yi, Y., et al.: A survey on wireless indoor localization from the device perspective. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 49(2), 25 (2016)
Hu, J., Liu, D., Yan, Z., et al.: Experimental analysis on weight K-nearest neighbor indoor fingerprint positioning. IEEE Internet Things J. 6(1), 891–897 (2018)
Shah, R., Aditya D., and Narayanan, P.J.: Multistage SfM: A coarse-to-fine approach for 3d reconstruction. arXiv preprint arXiv:1512.06235 (2015)
Sattler, T., Zhou, Q., Pollefeys, M., et al. Understanding the limitations of cnn based absolute camera pose regression. In: IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3302–3312 (2019)
Yin, Z., Wu, C., Yang, Z., et al.: Peer-to-peer indoor navigation using smartphones. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 35(5), 1141–1153 (2017)
Xu, H., Yang, Z., Zhou, Z., et al.: Enhancing wifi-based localization with visual clues. In: Proceedings of the 2015 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing, pp. 963–974. ACM (2015)
Wu, C., Yang, Z., Xiao, C.: Automatic radio map adaptation for indoor localization using smartphones. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 17(3), 517–528 (2017)
Wu, C., Yang, Z., Liu, Y.: Wireless Indoor Localization: A Crowdsourcing Approach. Springer (2018)
Xu, J., Yang, Z., Chen, H., et al.: Embracing spatial awareness for reliable WiFi-based Indoor location systems. In: 2018 IEEE 15th International Conference on Mobile Ad Hoc and Sensor Systems (MASS), pp. 281–289. IEEE (2018)
Liu, Z., Zhang, L., Liu, Q., et al.: Fusion of magnetic and visual sensors for indoor localization: infrastructure-free and more effective. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 19(4), 874–888 (2016)
Dong, J., Xiao, Y., Noreikis, M.: et al. imoon: Using smartphones for image based indoor navigation. In: Proceedings of the 13th ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems, pp. 85–97. ACM (2015)
Lu, G., Song, J.: 3D Image-based Indoor localization joint with WiFi positioning. In: Proceedings of the 2018 ACM on International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval, pp. 465–472. ACM (2018)
Dong, J., Noreikis, M., Xiao, Y., et al.: Vinav: a vision-based indoor navigation system for smartphones. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 18(6), 1461–1475 (2018)
Xompero, A., Lanz, O., Cavallaro, A. Multi-camera matching of spatio-temporal binary features. In: 2018 21st International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), pp. 1519–1526. IEEE (2018)
Xu, H., Yang, Z., Zhou, Z., et al. Indoor localization via multi-modal sensing on smartphones. In: Proceedings of the 2016 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing, pp. 208–219. ACM (2016)
Redžić, M.D., Laoudias, C., Kyriakides, I.: Image and WLAN bimodal integration for Indoor user localization. IEEE Trans. Mobile Comput. 19(5), 1109–1122 (2019)
Zheng, Y., Shen, G., Li, L., et al.: Travi-navi: self-deployable indoor navigation system. IEEE/ACM Trans. Network. 25(5), 2655–2669 (2017)
Guo, B., Han, Q., Chen, H., et al.: The emergence of visual crowdsensing: challenges and opportunities. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 19(4), 2526–2543 (2017)
Lowe, D.G.: Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vision 60(2), 91–110 (2004)
Guclu, O., Can, A.B.: Integrating global and local image features for enhanced loop closure detection in RGB-D SLAM systems. Vis. Comput. 36(6), 1271–1290 (2020)
He, M., Zhu, C., Huang, Q., et al.: A review of monocular visual odometry. Vis. Comput. 36(5), 1053–1065 (2020)
Niu, Q., Li, M., He, S., et al.: Resource-efficient and automated image-based indoor localization. ACM Trans. Sensor Netw. 15(2), 1–31 (2019)
Gu, F., Niu, J., Duan, L.: WAIPO: a fusion-based collaborative indoor localization system on smartphones. IEEE/ACM Trans. Network. 25(4), 2267–2280 (2017)
Kasap, Z., Magnenat-Thalmann, N.: Building long-term relationships with virtual and robotic characters: the role of remembering. Vis. Comput. 28(1), 87–97 (2012)
Huitl R., Schroth, G., Hilsenbeck S., Schweiger F., Steinbach, E.: TUMindoor dataset (2012) http://www.navvis.de/dataset
Yin, X., Ma, L., Tan, X.: A PCLR-GIST algorithm for fast image retrieval in visual indoor localization system. In: 2018 IEEE 87th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), pp. 1–5. IEEE (2018)
Ma, L., Xue, H., Jia, T., et al. A fast C-GIST based image retrieval method for vision-based Indoor localization. In: 2017 IEEE 85th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), pp. 1–5. IEEE (2017)
Azzi, C., Asmar, D.C., Fakih, A.H., et al. Filtering 3D keypoints using GIST for accurate image-based localization. In: Wilson, R.C., Hancock, E.R., Smith, W.A.P. (eds.) Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), pp. 127.1–127.12. BMVA Press (2016)
Cao, S., Snavely, N.: Graph-based discriminative learning for location recognition. In: Proceedings of the ieee conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 700–707 (2013)
Schlegel, D., Colosi, M., Grisetti, G.: Proslam: Graph SLAM from a programmer’s perspective. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 1–9. IEEE (2018)
Micusik, B., Wildenauer, H.: Descriptor free visual indoor localization with line segments. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3165–3173 (2015)
Gopalan, R.: Hierarchical sparse coding with geometric prior for visual geolocation. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 2432–2439 (2015)
Lu, G., Yan, Y., Ren, L., Saponaro, P., Sebe, N., Kambhamettu, C.: Where am I in the dark: exploring active transfer learning on the use of indoor localization based on thermal imaging. Neurocomputing 173, 83–92 (2016)
Toft, C., Stenborg, E., Hammarstrand, L., et al.: Semantic match consistency for long-term visual localization. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 383–399 (2018)
Taira, H., Okutomi, M., Sattler, T., et al.: InLoc: Indoor visual localization with dense matching and view synthesis. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7199–7209 (2018)
Yi, K.M., Trulls, E., Lepetit, V., et al.: Lift: Learned invariant feature transform. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 467–483. Springer, Cham (2016)
Li, X., Larson, M., Hanjalic, A.: Pairwise geometric matching for large-scale object retrieval. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5153–5161 (2015)
Saurer, O., Baatz, G., Köser, K., et al.: Image based geo-localization in the alps. Int. J. Comput. Vision 116(3), 213–225 (2016)
Chen, Y., Chen, R., Liu, M., et al.: Indoor visual positioning Aided by CNN based image retrieval: training-Free, 3D modeling-free. Sensors 18(8), 2692 (2018)
Ghofrani, A., Toroghi, R.M., Tabatabaie, S.M.: ICPS-net: An end-to-end RGB-based Indoor camera positioning system using deep convolutional neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.06219 (2019)
Yang, G., Liang, Y.: An Indoor localization method of image matching based on deep learning. In: 2018 International Conference on Mechanical, Electronic, Control and Automation Engineering (MECAE), pp. 103–108. Atlantis Press (2018)
Kendall, A., Cipolla, R.: Geometric loss functions for camera pose regression with deep learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5974–5983 (2017)
Tang, Z., Peng, X., Geng, S., et al.: Quantized densely connected u-nets for efficient landmark localization. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 339–354 (2018)
Zhao, J., Frumkin, N., Ishwar, P., et al.: CNN-based Indoor occupant localization via active scene illumination. In: IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 2636–2640. IEEE (2019)
David, C., Andrew, O., Noah, S., Dan, H.: Discrete-continuous optimization for large-scale structure from motion. In: CVPR, pp. 3001–3008 (2011)
Snavely, N., Seitz, S.M., Szeliski, R.: Photo tourism: exploring photo collections in 3D. ToG 25(3), 835–846 (2006)
Sattler, T., Leibe, B., Kobbelt, L.: Efficient & effective prioritized matching for large-scale image-based localization. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39(9), 1744–1756 (2016)
Sattler, T., Leibe, B., Kobbelt, L. Fast image-based localization using direct 2d-to-3d matching. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 667–674 (2011)
Sattler, T., Havlena, M., Radenovic, F., et al.: Hyperpoints and fine vocabularies for large-scale location recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2102–2110 (2015)
Zhang, W., Xiao, C.: PCAN: 3D attention map learning using contextual information for point cloud based retrieval. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 12436–12445 (2019)
Lim, H., Sinha, S.N., Cohen, M.F., et al.: Real-time image-based 6-dof localization in large-scale environments. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1043–1050. IEEE (2012)
Wang, X., Huang, Q., Celikyilmaz, A,. et al.: Reinforced cross-modal matching and self-supervised imitation learning for vision-language navigation. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6629–6638 (2019)
Brachmann, E., Rother, C.: Learning less is more-6d camera localization via 3d surface regression. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4654–4662 (2018)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556 (2014)
Shahjalal, M., Hossan, M., et al.: An implementation approach and performance analysis of image sensor based multilateral indoor localization and navigation system. Wireless Commun. Mobile Comput. 2018, 768–780 (2018)
Laoudias, C., Moreira, A., Kim, S., et al.: A survey of enabling technologies for network localization, tracking, and navigation. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 20(4), 3607–3644 (2018)
Szegedy, C., Liu, W., Jia, Y., et al.: Going deeper with convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1–9 (2015)
Opdenbosch, D.V., et al.: Camera-based Indoor positioning using scalable streaming of compressed binary image signatures. In: International Conference on Image Processing, pp. 2804–2808. IEEE (2014)
Cao, Y., Wang, C., Li, Z., et al.: Spatial-bag-of-features. In: The Twenty-Third IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp.13–18 (2010)
Kanzow, C., Yamashita, N., Fukushima, M.: Levenberg–Marquardt methods with strong local convergence properties for solving nonlinear equations with convex constraints. JAMC 173, 375–397 (2004)
Li, X., Ylioinas, J., Verbeek, J., et al.: Scene coordinate regression with angle based reprojection loss for camera relocalization. In: European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) Workshops, pp. 229–245 (2018)
Sarlin, P.E., Cadena, C., Siegwart, R, et al.: From coarse to fine: Robust hierarchical localization at large scale. In: IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 12716–12725 (2019)
Vasudevan, S., Chauhan, N., Sarobin, V., et al.: Image-based recommendation engine using VGG model. In: Advances in Communication and Computational Technology, pp. 257–265. Springer, Singapore (2020)
Xu, R., Wunsch, D.: Survey of clustering algorithms. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw 16(3), 645–678 (2005)
Fu, Y., Yan, Q., Liao, J., et al.: Real-time dense 3D reconstruction and camera tracking via embedded planes representation. Vis. Comput. 36(10), 2215–2226 (2020)
Lu, F., Zhou, B., Zhang, Y., et al.: Real-time 3D scene reconstruction with dynamically moving object using a single depth camera. Vis. Comput. 34(6), 753–763 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work is partially supported by The National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFB0502201) and The National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), Grant No. 61971316.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, N., Ai, H. EfiLoc: large-scale visual indoor localization with efficient correlation between sparse features and 3D points. Vis Comput 38, 2091–2106 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02270-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02270-8