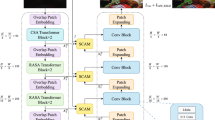
Abstract
Due to the images obtained in lowlight environments often showing low contrast, low brightness and artifacts, it is difficult to distinguish the details of these images for people. In the field of images fusion and target tacking, lowlight images cannot be processed better. In this paper, we proposed an end-to-end lowlight image enhancement network, which uses modules stacking methods and attention modules. Firstly, the method of module stacking was applied to extract the different features of images, and then the features are fused on the channel dimension. Finally, the final image was reconstructed with a series of convolutions. In particular, our loss function consists of two parts: the first part of the loss function was calculated using L1 loss, L2 loss and the gradient loss, and VGG network was utilized to calculate the second part. Furthermore, we verified the effectiveness of the model via a large number of comparative experiments, and illustrated the comparison results through quantitative and qualitative methods. We additionally show the performance of our network on lowlight video enhancement, which also has better results than the other methods.















Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Guo, T., Xu, X.: Salient object detection from low contrast images based on local contrast enhancing and non-local feature learning. Visual Comput. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-020-01964-9
Hou, R., Zhou, D., Nie, R., Liu, D., Xiong, L., Guo, Y., Yu, C.: VIF-Net: an unsupervised framework for infrared and visible image fusion. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 6, 640–651 (2020)
Chen, G., Qin, H.: Class-discriminative focal loss for extreme imbalanced multiclass object detection towards autonomous driving. Visual Comput. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02067-9
Liu, Y., Zhou, D., Nie, R., Hou, R., Ding, Z.: Construction of high dynamic range image based on gradient information transformation. IET Image Process. 14(7), 1233–1239 (2020)
Wang, C., He, C., Xu, M.: Fast exposure fusion of detail enhancement for brightest and darkest regions. Visual Comput. 37(5), 1233–1243 (2021)
Ibrahim, H., Kong, N.S.P.: Brightness preserving dynamic histogram equalization for image contrast enhancement. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 53(4), 1752–1758 (2007)
Sheet, D., Garud, H., Suveer, A., Mahadevappa, M., Chatterjee, J.: Brightness preserving dynamic fuzzy histogram equalization. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 56(4), 2475–2480 (2010)
Pizer, S.M., Amburn, E.P., Austin, J.D., Cromartie, R., Geselowitz, A., Greer, T., ter Haar Romeny, B., Zimmerman, J.B., Zuiderveld, K.: Adaptive histogram equalization and its variations. Comput. Vis. Graph. Image Process. 39(3), 355–368 (1987)
Land, E.H.: The retinex theory of color vision. Sci. Am. 237(6), 108–129 (1977)
Jobson, D.J., Rahman, Z.U., Woodell, G.A.: A multiscale retinex for bridging the gap between color images and the human observation of scenes. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 6(7), 965–976 (1997)
Shen L., Yue Z., Feng F., Chen Q., Liu S., Ma J.: MSR-net: lowlight image enhancement using deep convolutional network. arXiv:1711.02488 (2017)
Zhang Y., Zhang J., Guo X.: Kindling the darkness: a practical lowlight image enhancer. In: 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia 2019, pp. 1632–1640. ACM, Nice, France (2019)
Li, M., Zhou, D., Nie, R., Xie, S., Liu, Y.: AMBCR: lowlight image enhancement via attention guided multi-branch construction and Retinex theory. IET Image Proc. 15(9), 2020–2038 (2021)
Garces, E., Munoz, A., Lopez-Moreno, J., Gutierrez, D.: Intrinsic images by clustering. Comput. Graph. Forum 31(4), 1415–1424 (2012)
Janner, M., Wu, J., Kulkarni, T.D., Yildirim, I., Tenenbaum, J.B.: Self-supervised intrinsic image decomposition. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 30, 5937–5947 (2017)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Berlin (2015)
Pizer, S.M., Zimmerman, J.B., Staab, E.V.: Adaptive grey level assignment in CT scan display. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 8(2), 300–305 (1984)
Kim, Y.T.: Contrast enhancement using brightness preserving bi-histogram equalization. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 43(1), 1–8 (1997)
Wang, Y., Chen, Q., Zhang, B.: Image enhancement based on equal area dualistic sub-image histogram equalization method. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 45(1), 68–75 (1999)
Chen, S.D., Ramli, A.R.: Minimum mean brightness error bi-histogram equalization in contrast enhancement. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 49(4), 1310–1319 (2003)
Wang, C., Ye, Z.: Brightness preserving histogram equalization with maximum entropy: a variational perspective. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 51(4), 1326–1334 (2005)
Pathak S. S., Dahiwale P., Padole G.: A combined effect of local and global method for contrast image enhancement. In: IEEE International Conference on Engineering and Technology (ICETECH), 2015. IEEE, Coimbatore, India (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICETECH.2015.7275011
Zhang, X., Feng, R., Li, X., Yuan, Z.: Block adjustment-based radiometric normalization by considering global and local differences. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2020.3031398
Abdullah-Al-Wadud, M., Kabir, M.H., Dewan, M.A., Chae, O.: A dynamic histogram equalization for image contrast enhancement. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 53(2), 593–600 (2007)
Jobson, D.J., Rahman, Z., Woodell, G.A.: Properties and performance of a center/surround retinex. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 6(3), 451–462 (1997)
Wei, C., Wang, W., Yang, W., Liu, J.: Deep retinex decomposition for lowlight enhancement. In: British Machine Vision Conference 2018. Amazon, Newcastle, UK (2018)
Dong, X., Wang, G., Pang, Y., Li, W., Lu, Y.: Fast efficient algorithm for enhancement of low lighting video. In: IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, 2011. IEEE, Barcelona, Spain (2011)
Wang, S., Zheng, J., Hu, H.M., Li, B.: Naturalness preserved enhancement algorithm for non-uniform illumination images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 22(9), 3538–3548 (2013)
Fu, X., Zeng, D., Huang, Y., Liao, Y., Ding, X., Paisley, J.: A fusion-based enhancing method for weakly illuminated images. Signal Process. 129, 82–96 (2016)
Fu, X., Zeng, D., Huang, Y., Zhang, X., Ding, X.: A weighted variational model for simultaneous reflectance and illumination estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2016, pp. 2782–2790. IEEE, Las Vegas, USA (2016)
Ying, Z., Li, G., Gao, W.: A bio-inspired multi-exposure fusion framework for lowlight image enhancement. arXiv:1711.00591 (2017)
Tao, L., Zhu, C., Xiang, G., Li, Y., Jia, H., Xie, X: LLCNN: a convolutional neural network for lowlight image enhancement. In: IEEE Visual Communications and Image Processing 2017, pp. 1–4. IEEE, St. Petersburg, USA (2017)
Lore, K.G., Akintayo, A., Sarkar, S.: LLNet: a deep autoencoder approach to natural lowlight image enhancement. Pattern Recognit. 61(SI), 650–662 (2017)
Chen, C., Chen, Q., Xu, J., Koltun, V.: Learning to see in the dark. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2018, pp. 3291–3300. IEEE, Salt Lake City, USA (2018)
Li, C., Guo, J., Porikli, F., Pang, Y.: LightenNet: a convolutional neural network for weakly illuminated image enhancement. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 104, 15–22 (2018)
Lv, F., Lu, F., Wu, J., Lim, C.: MBLLEN: lowlight image/video enhancement using CNNs. In: British Machine Vision Conference. BMVA Press, Newcastle, UK (2018)
Jiang, Y., Gong, X., Liu, D., Cheng, Y., Fang, C., Shen, X., Yang, J., Zhou, P., Wang, Z.: EnlightenGAN: deep light enhancement without paired supervision. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 30, 2340–2349 (2021)
Goodfellow, I., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B., Warde-Farley, D., Ozair, S., Courville, A., Bengio, Y.: Generative adversarial networks. arXiv:1406.2661 (2014)
Guo, C., Li, C., Guo, J., Loy, C., Hou, J., Kwong, S., Cong, R.: Zero-reference deep curve estimation for lowlight image enhancement. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2020, pp. 1780–1789. IEEE, USA (2020)
Ulyanov, D., Vedaldi, A., Lempitsky, V.: Deep Image Prior, arXiv:1711.10925 (2017)
Zhang, Y., Di, X., Zhang, B., Wang, C.: Self-supervised image enhancement network: training with lowlight images only. arXiv:2002.11300 (2020)
Jin, X., Xu, C., Feng, J., Wei, Y., Xiong, J., Yan, S.: Deep learning with s-shaped rectified linear activation units. In: 30th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 2016, pp. 1737–1743. AAAI Press, Phoenix, USA
He K., Zhang X., Ren S., Sun J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2016, pp. 770–778. IEEE, Las Vegas, USA (2016)
Woo, S., Park, J., Lee, J., Kweon, I.S.: CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 11211, pp. 3–19. Springer, Munich (2018)
Wang, Z., Bovik, A.C., Sheikh, H.R., Simoncelli, E.P.: Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 13(4), 600–612 (2004)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In: 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations 2015. ICLR, San Diego, USA (2015)
Abadi, M., Barham, P., Chen, J., et al.: Tensorflow: a system for large-scale machine learning. In: Proceedings of the 12th USENIX Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation 2016, pp. 265–283. USENIX Association, Savannah, USA (2016)
Damera-Venkata, N., Kite, T.D., Geisler, W.S., Evans, B.L., Bovik, A.C.: Image quality assessment based on a degradation model. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 9(4), 636–650 (2000)
Sheikh, H.R., Bovik, A.C.: Image information and visual quality. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 15(2), 430–444 (2006)
Sheikh, H.R., Bovik, A.C., de Veciana, G.: An information fidelity criterion for image quality assessment using natural scene statistics. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 14(12), 2117–2128 (2005)
Hensel, M., Ramsauer, H., Unterthiner, T., Nessler, B., Hochreiter S.: GANs trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local Nash equilibrium. In: 31st Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Long Beach, USA (2017)
Zhang, R., Isola, P., Efros, A.A., Shechtman, E., Wang, O.: The unreasonable effectiveness of deep features as a perceptual metric. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, pp. 586–595 (2018)
Cai, J., Gu, S., Zhang, L.: Learning a deep single image contrast enhancer from multi-exposure images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 27(4), 2049–2062 (2018)
Li, X., Wang, W., Hu, X., Yang, J.: Selective kernel networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2019, pp. 510–519. IEEE, Long Beach, USA (2019)
Hu, J., Shen, L., Albanie, S., Sun, G., Wu, E.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 42(8), 2011–2023 (2020)
Zhong, J., Kleijn, W.B., Hu, X.: Camera control in multi-camera systems for video quality enhancement. IEEE Sens. J. 14(9), 2955–2966 (2014)
Baker, S., Scharstein, D., Lewis, J.P., Roth, S., Black, M.J., Szeliski, R.: A database and evaluation methodology for optical flow. Int. J. Comput. Vision 92(1), 1–31 (2011)
Huang, L., Zhao, X., Huang, K.: Got-10k: a large high-diversity benchmark for generic object tracking in the wild. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 43(5), 1562–1577 (2021)
Liang, Y., He, F., Zeng, X.: 3D mesh simplification with feature preservation based on whale optimization algorithm and differential evolution. Integr. Comput.-Aided Eng. 27(4), 417–435 (2020)
Chen, Y., He, F., Li, H., Zhang, D., Wu, Y.: A full migration BBO algorithm with enhanced population quality bounds for multimodal biomedical image registration. Appl. Soft Comput. 93, 106335 (2020)
Zhang, S., He, F.: DRCDN: learning deep residual convolutional dehazing networks. Visual Comput. 36(9), 1797–1808 (2020)
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank the editors and the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments. Besides, this work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 62066047, 61966037, 61463052 and 61365001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest to this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Zhao, L., Zhou, D. et al. AEMS: an attention enhancement network of modules stacking for lowlight image enhancement. Vis Comput 38, 4203–4219 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02289-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02289-x