Abstract
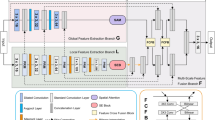
Medical image segmentation has the priori guiding significance for clinical diagnosis and treatment. In the past ten years, a large number of experimental facts have proved the great success of deep convolutional neural networks in various medical image segmentation tasks. However, the convolutional networks seem to focus too much on the local image details, while ignoring the long-range dependence. The Transformer structure can encode long-range dependencies in image and learn high-dimensional image information through the self-attention mechanism. But this structure currently depends on the database scale to give full play to its excellent performance, which limits its application in medical images with limited database size. In this paper, the characteristics of CNNs and Transformer are integrated to propose a dual encoding–decoding structure of the X-shaped network (X-Net). It can serve as a good alternative to the traditional pure convolutional medical image segmentation network. In the encoding phase, the local and global features are simultaneously extracted by two types of encoders, convolutional downsampling, and Transformer and then merged through jump connection. In the decoding phase, a variational auto-encoder branch is added to reconstruct the input image itself in order to weaken the impact of insufficient data. Comparative experiments on three medical image datasets show that X-Net can realize the organic combination of Transformer and CNNs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhu, Z., Wei, H., Hu, G., Li, Y., Qi, G., Mazur, N.: A novel fast single image dehazing algorithm based on artificial multiexposure image fusion. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 70, 1–23 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2020.3024335
Tu, Z., Xie, W., Qin, Q., Poppe, R., Veltkamp, R.C., Li, B., Yuan, J.: Multi-stream cnn: learning representations based on human-related regions for action recognition. Pattern Recogn. 79, 32–43 (2018)
Chen, Y., Tu, Z., Kang, D., Bao, L., Zhang, Y., Zhe, X., Chen, R., Yuan, J.: Model-based 3d hand reconstruction via self-supervised learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 10451–10460 (2021)
Havaei, M., Davy, A., Warde-Farley, D., Biard, A., Courville, A., Bengio, Y., Pal, C., Jodoin, P., Larochelle, H.: Brain tumor segmentation with deep neural networks. medical image analysis (2017)
Muthukrishnan, R., Radha, M.: Edge detection techniques for image segmentation. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Technol. 3(6), 259 (2011)
Yu-Qian, Z., Wei-Hua, G., Zhen-Cheng, C., Jing-Tian, T., Ling-Yun, L.: Medical images edge detection based on mathematical morphology. In: 2005 IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology 27th Annual Conference, pp. 6492–6495 (2006). IEEE
Naylor, P., Laé, M., Reyal, F., Walter, T.: Nuclei segmentation in histopathology images using deep neural networks. In: 2017 IEEE 14th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2017), pp. 933–936 (2017). IEEE
Gibson, E., Giganti, F., Hu, Y., Bonmati, E., Bandula, S., Gurusamy, K., Davidson, B., Pereira, S.P., Clarkson, M.J., Barratt, D.C.: Automatic multi-organ segmentation on abdominal ct with dense v-networks. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 37(8), 1822–1834 (2018)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-assisted Intervention, pp. 234–241 (2015). Springer
Valanarasu, J.M.J., Oza, P., Hacihaliloglu, I., Patel, V.M.: Medical transformer: gated axial-attention for medical image segmentation. Preprint arXiv:2102.10662 (2021)
Jin, Q., Meng, Z., Sun, C., Cui, H., Su, R.: Ra-unet: a hybrid deep attention-aware network to extract liver and tumor in ct scans. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 8, 1471 (2020)
Feng, S., Zhao, H., Shi, F., Cheng, X., Wang, M., Ma, Y., Xiang, D., Zhu, W., Chen, X.: Cpfnet: context pyramid fusion network for medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 39(10), 3008–3018 (2020)
Chen, L.-C., Papandreou, G., Kokkinos, I., Murphy, K., Yuille, A.L.: Deeplab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 40(4), 834–848 (2017)
Brown, T.B., Mann, B., Ryder, N., Subbiah, M., Kaplan, J., Dhariwal, P., Neelakantan, A., Shyam, P., Sastry, G., Askell, A., et al.: Language models are few-shot learners. Preprint arXiv:2005.14165 (2020)
Devlin, J., Chang, M.-W., Lee, K., Toutanova, K.: Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. Preprint arXiv:1810.04805 (2018)
Ott, M., Edunov, S., Grangier, D., Auli, M.: Scaling neural machine translation. Preprint arXiv:1806.00187 (2018)
Shao, T., Guo, Y., Chen, H., Hao, Z.: Transformer-based neural network for answer selection in question answering. IEEE Access 7, 26146–26156 (2019)
Pappagari, R., Zelasko, P., Villalba, J., Carmiel, Y., Dehak, N.: Hierarchical transformers for long document classification. In: 2019 IEEE Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding Workshop (ASRU), pp. 838–844 (2019). IEEE
Dosovitskiy, A., Beyer, L., Kolesnikov, A., Weissenborn, D., Zhai, X., Unterthiner, T., Dehghani, M., Minderer, M., Heigold, G., Gelly, S., et al.: An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. Preprint arXiv:2010.11929 (2020)
Zheng, S., Lu, J., Zhao, H., Zhu, X., Luo, Z., Wang, Y., Fu, Y., Feng, J., Xiang, T., Torr, P.H., et al: Rethinking semantic segmentation from a sequence-to-sequence perspective with transformers. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6881–6890 (2021)
Touvron, H., Cord, M., Douze, M., Massa, F., Sablayrolles, A., Jégou, H.: Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 10347–10357 (2021). PMLR
Tu, Z., Li, H., Zhang, D., Dauwels, J., Li, B., Yuan, J.: Action-stage emphasized spatiotemporal vlad for video action recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 28(6), 2799–2812 (2019)
Tu, Z., Xie, W., Dauwels, J., Li, B., Yuan, J.: Semantic cues enhanced multimodality multistream cnn for action recognition. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 29(5), 1423–1437 (2018)
Liu, S., Wang, S., Liu, X., Gandomi, A.H., Daneshmand, M., Muhammad, K., de Albuquerque, V.H.C.: Human memory update strategy: a multi-layer template update mechanism for remote visual monitoring. IEEE Trans. Multimed. (2021)
Zhu, Z., Luo, Y., Qi, G., Meng, J., Li, Y., Mazur, N.: Remote sensing image defogging networks based on dual self-attention boost residual octave convolution. Remote Sens. 13(16), 3104 (2021)
Liu, S., Wang, S., Liu, X., Lin, C.-T., Lv, Z.: Fuzzy detection aided real-time and robust visual tracking under complex environments. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 29(1), 90–102 (2020)
Kingma, D.P., Welling, M.: Auto-encoding variational bayes. Preprint arXiv:1312.6114 (2013)
Patil, D.D., Deore, S.G.: Medical image segmentation: a review. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Mob. Comput. 2(1), 22–27 (2013)
Guerrout, E.-H., Mahiou, R., Ait-Aoudia, S.: Medical image segmentation on a cluster of pcs using markov random fields. Int. J. New Comput. Arch. Appl. 3(1), 35–44 (2013)
Cui, W., Wang, Y., Lei, T., Fan, Y., Feng, Y.: Local region statistics-based active contour model for medical image segmentation. In: 2013 Seventh International Conference on Image and Graphics, pp. 205–210 (2013). IEEE
Li, B.N., Chui, C.K., Chang, S., Ong, S.H.: Integrating spatial fuzzy clustering with level set methods for automated medical image segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 41(1), 1–10 (2011)
Saha, P.K., Udupa, J.K., Odhner, D.: Scale-based fuzzy connected image segmentation: theory, algorithms, and validation. Comput. Vis. Image Understanding 77(2), 145–174 (2000)
Long, J., Shelhamer, E., Darrell, T.: Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3431–3440 (2015)
Xiao, X., Lian, S., Luo, Z., Li, S.: Weighted res-unet for high-quality retina vessel segmentation. In: 2018 9th International Conference on Information Technology in Medicine and Education (ITME), pp. 327–331 (2018). IEEE
Li, X., Chen, H., Qi, X., Dou, Q., Fu, C.-W., Heng, P.-A.: H-denseunet: hybrid densely connected unet for liver and tumor segmentation from ct volumes. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 37(12), 2663–2674 (2018)
Çiçek, Ö., Abdulkadir, A., Lienkamp, S.S., Brox, T., Ronneberger, O.: 3d u-net: learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotation. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-assisted Intervention, pp. 424–432 (2016). Springer
Chen, J., Lu, Y., Yu, Q., Luo, X., Adeli, E., Wang, Y., Lu, L., Yuille, A.L., Zhou, Y.: Transunet: Transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation. Preprint arXiv:2102.04306 (2021)
Caicedo, J.C., Goodman, A., Karhohs, K.W., Cimini, B.A., Ackerman, J., Haghighi, M., Heng, C., Becker, T., Doan, M., McQuin, C., et al.: Nucleus segmentation across imaging experiments: the 2018 data science bowl. Nat. Methods 16(12), 1247–1253 (2019)
Naylor, P., Laé, M., Reyal, F., Walter, T.: Segmentation of nuclei in histopathology images by deep regression of the distance map. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 38(2), 448–459 (2018)
Jha, D., Smedsrud, P.H., Riegler, M.A., Halvorsen, P., de Lange, T., Johansen, D., Johansen, H.D.: Kvasir-seg: A segmented polyp dataset. In: International Conference on Multimedia Modeling, pp. 451–462 (2020). Springer
Funding
This work is jointly funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61803061, 61906026, 6217021768; Innovation research group of universities in Chongqing; Innovative project of shapingba district, Chongqing, Jcd202135; Funding: Chongqing Kewei Joint Medical Research Project, 2020GDRC019, 2021MSXM337; the Chongqing Natural Science Foundation under Grant cstc2020jcyjmsxm X0577, cstc2020jcyj-msxmX0634; “Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Circle” innovation funding of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission KJCXZD2020028; Special key project of Chongqing technology innovation and application development cstc2019jscx-zdztzx0068; the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation 2020M670111ZX; and Special Fund for Young and Middle-aged Medical Top Talents of Chongqing ZQNYXGDRCGZS2019005.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Wang, Z., Yin, L. et al. X-Net: a dual encoding–decoding method in medical image segmentation. Vis Comput 39, 2223–2233 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02328-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02328-7