Abstract
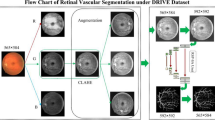
Retinal vessel segmentation can obtain rich ocular information which is important for the diagnosis of fundus diseases. To address the problems of existing segmentation methods such as poor capillary segmentation and incorrect segmentation of pathological information, an AFNet vessel segmentation network combining location attention, semantic aggregation module and multi-scale feature fusion module is proposed. Add positional attention to the feature codec block of the network for modeling global dependencies and reducing intra-class inconsistencies, the multiscale feature fusion module is used in the last layer of the coding part to extract multiscale feature information to solve the difficult problem of large variation of retinal vessel width and size, and the designed semantic aggregation module can fully utilize the contextual semantic information to improve the segmentation accuracy of capillaries. Extensive experiments are conducted on three publicly available fundus image databases DRIVE, STARE and CHASE_DB1, and the results show that AFNet can effectively improve the accuracy of retinal vessel segmentation and achieve better comprehensive performance compared with other methods.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheung, C.Y.-L., Ikram, M.K., Chen, C., Wong, T.Y.: Imaging retina to study dementia and stroke. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 57, 89–107 (2017)
Fraser-Bell, S., Symes, R., Aze, A.V.: Hypertensive eye disease: a review. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 45(1), 45–53 (2017)
Lee, H., Lee, M., Chung, H., Kim, H.C.: Quantificationofretinalvessel tortuosity in diabetic retinopathy using optical coherence tomography angiography. Retina 38(5), 976–985 (2018)
Akil, H., Huang, A.S., Francis, B.A., Sadda, S.R., Chopra, V.: Retinal vessel density from optical coherence tomography angiography to differ-entiate early glaucoma, pre-perimetric glaucoma and normal eyes. PLoS ONE 12(2), e0170476 (2017)
Singh, N.P., Srivastava, R.: Retinal blood vessels segmentation by using Gumbel probability distribution function based matched filter. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 129, 45–50 (2016)
Karn, P.K., Biswal, B., Samantaray, S.R.: Robust retinal blood vessel segmentation using hybrid active contour model. IET Image Process. 13(3), 440–450 (2019)
Wang, W., Zhang, J., Wu, W., Zhou, S.: An automatic approach for retinal vessel segmentation by multi-scale morphology and seed point tracking. J. Med. Imag. Health Inf. 8(2), 262–274 (2018)
Uslu, F., Bharath, A.A.: A recursive Bayesian approach to describe retinal vasculature geometry. Pattern Recognit. 87, 157–169 (2019)
Tuba, E., Mrkela, L., Tuba, M.: Retinal blood vessel segmentation by support vector machine classification. In: Present at the 27th Int. Conf. Radioelektronika (RADIOELEKTRONIKA). (2017)
Jin, Q., Meng, Z., Pham, T.D., Chen, Q., Wei, L., Su, R.: DUNet: a deformable network for retinal vessel segmentation. Knowl.-Based Syst. 178, 149–162 (2019)
Wang, C., Zhao, Z., Ren, Q., Xu, Y., Yu, Y.: Dense U-net based on patch-based learning for retinal vessel segmentation. Entropy 21(2), 168 (2019)
Guo, S., Wang, K., Kang, H., Zhang, Y., Gao, Y., Li, T.: BTS-DSN: deeply supervised neural network with short connections for reti-nal vessel segmentation. Int. J. Med. Inf. 126, 105–113 (2019)
Feng, S., Zhuo, Z., Pan, D.: CcNet: a cross-connected convolutional network for segmenting retinal vessels using multi-scale features. Neuro-Comp. 392, 268–2767 (2020)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015)
Jie, H., Li, S., Gang, S.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: CVPR, pp. 7132–7141. (2018).
Jongchan, P., Sanghyun, W., Joon-Young, L., I.S.K. Bam: bottleneck attention module. arXiv preprint: http://arxiv.org/abs/1807.06514. (2018)
Sanghyun, W., Jongchan, P., Joon-Young, L., In, S.K.: Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 3–19. (2018)
Wang, B, Qiu, S., He, H. (2019) Dual encoding U-Net for retinal vessel segmentation. In: Shen D. et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 11764. Springer, Cham (2019)
Wu, Y., Xia, Y., Song, Y., Zhang, D., Liu, D., Zhang, C., Cai, W.: Vessel-Net: retinal vessel segmentation under multi-path supervision. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention -MICCAI 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 11764. Springer, Cham (2019)
Zhang, S., Fu, H., Yan, Y., Zhang, Y., Wu, Q., Yang, M., Tan, M.: Attention guided network for retinal image segmentation. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention -MICCAI 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 11764. Springer, Cham (2019)
Lyu, C., Hu, G., Wang, D.: Attention to fine-grained information: hierarchical multi-scale network for retinal vessel segmentation. Vis. Comput. 2020(8), 1–11 (2020)
Zhao, H., Shi, J., Qi, X., Wang, X., Jia, J.: Pyramid scene parsing network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 2881–2890. (2017)
Liu, J.-J., Hou Q., Cheng, M.-M., Feng, J., Jiang, J.: A Simple Pooling-Based Design for Real-Time Salient Object Detection. (2019).arXiv: http://arxiv.org/abs/1904.09569
Gu, Z., et al.: CE-Net: context encoder network for 2D medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 38(10), 2281–2292 (2019)
Yu, C., Wang, J., Peng, C., Gao, C., Yu, G., Sang, N.: Learning a discriminative feature network for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and pattern Recognition, pp. 1857–1866. (2018)
Chen, L.-C., Yang, J., Wang, W.X., Yuille, A.L.: Attention to scale: Scale-aware semantic image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 3640–3649. (2016)
Sun, W., Wu, T.: Learning Spatial Pyramid Attentive Pooling in Image Synthesis and Image-to-Image Translation. arXiv: http://arxiv.org/abs/1901.06322. (2019)
Li, X., Wang, W., Hu, X., Yang, J.: Selective kernel networks. arXiv: http://arxiv.org/abs/1903.06586. (2019)
Hou, Q., Zhou, D., Feng, J.: Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 13713–13722. (2021)
Alom, M.Z., Hasan, M., Yakopcic, C., et al.: Recurrent residual convolutional neural network based on U-Net (R2U-Net) for medical image segmentation. arXiv preprint: http://arxiv.org/abs/1802.06955. (2018)
Jin, Q., Meng, Z., Pham, T.D., et al.: DUNet: a deformable network for retinal vessel segmentation. (2018)
Li, L., Verma, M., Nakashima, Y., et al.: Iternet: Retinal image segmentation utilizing structural redundancy in vessel networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, pp. 3656–3665. (2020)
Xianjing, M., Li Jing, Lu., Yu, X.G.: Fundus i magesblood vessel segmentation basedon improved S- egNet. Comput. Eng. Des. 41(11), 3148–3153 (2020)
Yang, T., Wu, T., Li, L., et al.: SUD-GAN: deep convol ution generative adversarial network combined with short connection and dense block for retinal vessel segmentation. J. Digit. Imag. 2020, 1–12 (2020)
Raz, F.M., Remagnino, P., Hoppe, A., et al.: An ensemble classification-based approach applied to retinal blood vessel segmentation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 59(9), 2538–2548 (2012)
Li, X., Hao, C., Qi, X., et al.: H-DenseUNet: hybrid densely connected UNet for liver and liver tumor segmentation from CT volumes. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 2017, 1–1 (2017)
Wang W, Zhong J, Wu H, et al.: Rvseg-net: An efficient feature pyramid cascade network for retinal vessel segmentation. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Springer, Cham, pp.796–805. (2020)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 12171114) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61100150).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest in the submission.
Ethical approval
We would like to state that this work is original research that has not been published before and is not considered for publication elsewhere.
Humans or animal rights
The paper does not include any studies of humans or animals.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Lingxi Peng, Shaohu Peng Co-first authors
The original online version of this article was revised: Author name in article note was not corrects.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D., Peng, L., Peng, S. et al. Retinal vessel segmentation by using AFNet. Vis Comput 39, 1929–1941 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-022-02456-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-022-02456-8