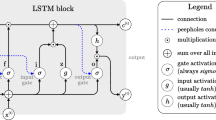
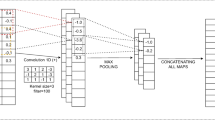
Abstract
Machine lip reading recognizes text content through the speaker's lip motion information. Lip reading has significant research and application value. With the continuous breakthrough of deep learning technology, lip reading research is also developing rapidly, and researchers have published many related studies. This paper studies the development of lip reading in detail, especially the latest research results of lip reading. We focus on the lip reading datasets and their comparison, including some recently released datasets. At the same time, we introduce the feature extraction methods of lip reading and compare various methods in detail. Finally, the future development direction of lip reading is discussed and prospected.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mcgurk, H., Macdonald, J.: Hearing lips and seeing voices. Nature 264(5588), 746–748 (1976)
Potamianos, G., Neti, C., Gravier, G., Garg, A., Senior, A.W.: Recent advances in the automatic recognition of audiovisual speech. Proc. IEEE 91(9), 1306–1326 (2003)
Petajan, E.D.: Automatic lipreading to enhance speech recognition (speech reading). In: University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 1984.
Rabiner, L.R.: A tutorial on hidden Markov models and selected applications in speech recognition. Proc IEEE 77, 257–268 (1989)
Neti, C.: Audio-visual speech recognition. In: Clsp Workshop, vol 2000.
Bayoudh, K., Knani, R., Hamdaoui, F., Mtibaa, A.: A survey on deep multimodal learning for computer vision: advances, trends, applications, and datasets. Vis. Comput. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02166-7
Li, L., Jiadi, Y., Chen, Y., Liu, H., Zhu, Y.M., Kong, L., Li, M.: lip reading-based user authentication through acoustic sensing on smartphones. IEEE/ACM Trans Netw 27(1), 447–460 (2019)
Mathulaprangsan, S., Wang, C.-Y., Kusum A.Z., Tai, T.-C., Wang, J.-C.: A survey of visual lip reading and lip-password verification. In: 2015 International Conference on Orange Technologies (ICOT), vol 2015.
Ding, R., Pang, C., Liu, H.: Audio-Visual Keyword Spotting Based on Multidimensional Convolutional Neural Network. In: 2018 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), vol 2018.
Zhang, Y., Liang, S., Yang, S., Liu, X., Wu, Z., Shan, S., Chen, X.: Unified context network for robust active speaker detection. In: ACM Multimedia 2021, vol 2021.
Stafylakis, T., Tzimiropoulos, G.: Zero-Shot Keyword Spotting for Visual Speech Recognition in-the-Wild. Springer, Cham (2018)
Yao, Y., Wang, T., Du, H., Zheng, L., Gedeon, T.D.: Spotting visual keywords from temporal sliding windows. In: 2019 International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, vol 2019.
Huang, X., Wang, M., Gong, M.: Fine-grained talking face generation with video reinterpretation. Vis. Comput. 37(1), 95–105 (2020)
Fang, Z., Liu, Z., Liu, T., Hung, C.C., Feng, G.: Facial expression GAN for voice-driven face generation. Vis. Comput. 38(3), 1151–1164 (2021)
Mirzaei, M.R., Ghorshi, S., Mortazavi, M.: Audio-visual speech recognition techniques in augmented reality environments. Vis. Comput. 30(3), 245–257 (2014)
Fernandez-Lopez, A., Sukno, F.M.: Survey on automatic lip-reading in the era of deep learning. Image Vis. Comput. 78, 53–72 (2018)
Hao, M., Mamut, M., Yadikar, N., Aysa, A., Ubul, K.: A survey of research on lipreading technology. IEEE Access 8, 204518–204544 (2020)
Oghbaie, M., Sabaghi, A., Hashemifard, K., Akbari M.: Advances and Challenges in Deep Lip Reading. arXiv preprint arXiv:2110.07879 (2021).
Anina, I., Zhou, Z., Zhao, G., Pietikainen, M.: OuluVS2: a multi-view audiovisual database for non-rigid mouth motion analysis. In: 2015 11th IEEE International Conference and Workshops on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG), vol 2015.
Chung, J.S., Zisserman, A. Lip reading in the wild. In: Asian Conference on Computer Vision 2016.
Fox, N.A., O’Mullane, B.A., Reilly, R.B.: VALID: A New Practical Audio-Visual Database, and Comparative Results. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2005)
Movellan, J.R. Visual speech recognition with stochastic networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 7, [NIPS Conference, Denver, Colorado, USA, 1994], vol 1994.
Vanegas, O., Tokuda, K., Kitamura, T.: Location normalization of HMM-based lip-reading: experiments for the M2VTS database. In: International Conference on Image Processing, vol 1999
Yanjun, X., Limin, D., Guoqiang, L., Xin, Z., Zhi, Z.: Chinese auditory visual bimodal database CAVSR1.0. Acta Acoust. A Sinica 25(1), 8 (2000)
Matthews, I., Cootes, T.F., Bangham, J.A., Cox, S., Harvey, R.: Extraction of visual features for lipreading. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 24(2), 198–213 (2002)
Patterson, E.K., Gurbuz, S., Tufekci, Z., Gowdy, J.N.: CUAVE: a new audio-visual database for multimodal human-computer interface research. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, vol 2002
Hazen, T.J., Saenko, K., La, C.H., Glass, J.R.: A segment-based audio-visual speech recognizer: data collection, development, and initial experiments. In: International Conference on Multimodal Interfaces, vol 2004
Fox, N.A.: VALID: a new practical audio-visual database, and comparative results. (2005)
Cooke, M., Barker, J., Cunningham, S., Shao, X.: An audio-visual corpus for speech perception and automatic speech recognition. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 120(5), 2421 (2006)
Cox, S., Harvey, R., Lan, Y.: The challenge of multispeaker lip-reading. In: Proc of International Conference on Auditory-visual Speech Processing, vol 2008.
Zhao, G., Barnard, M., Pietikainen, M.: Lipreading With Local Spatiotemporal Descriptors. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 11(7), 1254–1265 (2009)
Chung, J.s., Senior, A.W., Vinyals, O., Zisserman, A.: Lip reading sentences in the Wild. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), vol 2017.
Afouras, T., Chung, J.S., Senior, A., Vinyals, O., Zisserman, A.: Deep audio-visual speech recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2889052
Afouras, T., Chung, J.S., Zisserman, A.: LRS3-TED: a large-scale dataset for visual speech recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1809.00496, 2018 (2018)
Yang, S., Zhang, Y., Feng, D., Yang, M., Wang, C., Xiao, J., Long, K., Shan, S. and Chen, X.: LRW-1000: a naturally-distributed large-scale benchmark for lip reading in the Wild. In: 2019 14th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2019), vol
Makino, T., Liao, H., Assael, Y,, Shillingford, B., Siohan, O.: Recurrent neural network transducer for audio-visual speech recognition. In: 2019 IEEE Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding Workshop (ASRU), vol 2019.
Zhao, Y., Xu, R., Song, M.: A Cascade Sequence-to-Sequence Model for Chinese Mandarin Lip Reading. In: MMAsia '19: ACM Multimedia Asia, vol 2019.
Prajwal, K.R., Mukhopadhyay, R., Namboodiri, V., Jawahar, C.V.: Learning individual speaking styles for accurate lip to speech synthesis. In: 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), vol 2020.
Chen, X., Du, J., Zhang, H.: Lipreading with DenseNet and resBi-LSTM. Signal Image Video Process 14(5), 981–989 (2020)
Khassanov, Y., Mussakhojayeva, S., Mirzakhmetov, A., Adiye, V.A., Nurpeiissov, M., Varol, H.A.: A crowdsourced open-source Kazakh speech corpus and initial speech recognition baseline. arXiv preprint arXiv:2009.10334 2021.
Egorov, E., Kostyumov, V., Konyk, M., & Kolesnikov, S.: LRWR: large-scale benchmark for lip reading in Russian language. arXiv preprint arXiv:2109.06692 2021.
Lubitz, A., Valdenegro-Toro, M., Kirchner, F.: The VVAD-LRS3 Dataset for Visual Voice Activity Detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2109.13789 (2021).
Messer, K.: XM2VTSDB: the extended m2vts database. Proc. intl. conf. on Audio & Video Based Biometric Person Authentication 1999.
Sanderson, C.: The VidTIMIT database. idiap communication 2004.
Bailly-Bailliére, E., Bengio, S., Thiran, J. P.: The BANCA database and evaluation protocol. In: International Conference on Audio-& Video-based Biometric Person Authentication, vol 2003.
Lee, B., Hasegawajohnson, M., Goudeseune, C., Kamdar, S., Borys, S., Liu, M., Huang, T.: AVICAR: audio-visual speech corpus in a car environment. In: Conf Spoken Language, Jeju, Korea, vol 2011.
Jing, H., Potamianos, G., Connell, J., Neti, C.: Audio-visual speech recognition using an infrared headset. Speech Commun. 44(1–4), 83–96 (2004)
Lucey, P.J., Potamianos, G., Sridharan, S.: Patch-based analysis of visual speech from multiple views. (2008)
Mccool, C., Levy, C., Matrouf, D., Bonastre, J.F., Tresadern, P., Cootes T., Marcel, S., Hadid, A., Pietikainen, M., Matejka, P.: Bi-modal person recognition on a mobile phone: using mobile phone data. In: 2012 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo Workshops, vol 2012.
Rekik, A., Ben-Hamadou, A., Mahdi, W.: A new visual speech recognition approach for rgb-d cameras. In: Campilho, A., Kamel, M. (eds.) International Conference on Image Analysis & Recognition. Springer, Cham (2014)
Laea, B., Tqa, A., Sso, A.: An Arabic visual dataset for visual speech recognition. Procedia Computer Sci. 163, 400–409 (2019)
Liu, M., Wang, L., Lee, K.A., Zhang, H., Zeng, C., Dang, J.: Exploring deep learning for joint audio-visual lip biometrics. arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.08510 2021.
Abdrakhmanova, M., Kuzdeuov, A., Jarju, S., Khassanov, Y., Varol, H.A.: SpeakingFaces: a large-scale multimodal dataset of voice commands with visual and thermal video streams. Sensors 21(10), 3465 (2021)
Chuanzhen, R., Zhenjun, Y., Yongxing, J., Yuan, W., Yu, Y.: Research progress on key technologies of lip recognition. Data acquisition and processing S2): 7, (2012).
Dupont, S., Luettin, J.: Audio-visual speech modeling for continuous speech recognition. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 2(3), 141–151 (2000)
Li, M., Cheung, Y.M.: A novel motion based lip feature extraction for lip-reading. In: International Conference on Computational Intelligence & Security, vol 2008.
Alizadeh, S., Boostani, R., Asadpour, V.: Lip feature extraction and reduction for HMM-based visual speech recognition systems. In: Signal Processing, 2008. ICSP 2008. 9th International Conference on, vol 2008.
Ma, X., Yan, L., Zhong, Q. Lip Feature Extraction Based on Improved Jumping-Snake Model. In: Control Conference (pp. 6928–6933). IEEE, vol
Kass, M., Witkin, A., Terzopoulos, D.: Snakes: active contour models. IJCV 1(4), 321–331 (1988)
Timothy, F.: Active shape models-their training and application. Computer Vis Understand 61(1995).
Chen, J., Tiddeman, B., Zhao, G.: Real-Time Lip Contour Extraction and Tracking Using an Improved Active Contour Model. Springer, Cham (2008)
Cootes, T.F., Edwards, G.J., Taylor, C.J.: Active Appearance Models. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (1998)
Lan, Y., Theobald, B.J., Harvey, R.: View independent computer lip-reading. IEEE Computer Soc (2012)
Lan, Y., Harvey, R., Theobald, B.J.: Insights into machine lip reading. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, vol 2012.
Watanabe, T., Katsurada, K., Kanazawa, Y.: Lip Reading from Multi View Facial Images Using 3D-AAM. 2017.
Aleksic, P.S., Katsaggelos, A.K.: Audio-visual biometrics. Proc. IEEE 94, 2025–2044 (2006)
Stillittano, S., Girondel, V., Caplier, A.: Lip contour segmentation and tracking compliant with lip-reading application constraints. Mach. Vis. Appl. 24(1), 1–18 (2013)
Noda, K., Yamaguchi, Y., Nakadai, K., Okuno, H.G., Ogata, T.: Lipreading using convolutional neural network. Made available by the northern territory library via the publications act 2014.
Garg, A., Noyola, J., Bagadia, S.: Lip reading using CNN and LSTM. InStanford University, 2016.
Lee, D., Lee, J., Kim, K.E.: Multi-view Automatic Lip-Reading Using Neural Network. Asian Conference on Computer Vision 2017.
Nakadai, K.O., Hiroshi, G., Ogata, T., Noda, K., Yamaguchi. Audio-visual speech recognition using deep learning. Applied Intelligence the International Journal of Artificial Intelligence Neural Networks & Complex Problem Solving Technologies 2015.
Zhou, P., Yang, W., Chen, W., Wang, Y., Jia, J.: Modality attention for end-to-end audio-visual speech recognition. In: ICASSP 2019 - 2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), vol 2019.
Saitoh, T., Zhou, Z., Zhao, G., Pietikäinen, M.: Concatenated frame image based CNN for visual speech recognition. In: Asian Conference on Computer Vision, vol 2016.
Lin, M., Chen, Q., Yan, S.: Network in network. Computer Science 2013.
Mesbah, A., Berrahou, A., Hammouchi, H., Berbia, H., Qjidaa, H., Daoudi M.: Lip Reading with Hahn Convolutional Neural Networks. Image and Vision Computing 2019.
Assael, Y.M., Shillingford, B., Whiteson, S., Freitas, N.D.: LipNet: sentence-level lipreading. 2016.
Fung, I., Mak, B.: End-to-end low-resource lip-reading with Maxout CNN and LSTM. 2511–2515, (2018)
Xu, K., Li, D., Cassimatis, N., Wang, X.: LCANet: End-to-end lipreading with Cascaded Attention-CTC. (2018)
Weng, X., Kitani, K.: Learning spatio-temporal features with two-stream deep 3D CNNs for lipreading. In: The 30th British Machine Vision Conference (2019), vol 2019
Wiriyathammabhum P.: SpotFast Networks with Memory Augmented Lateral Transformers for Lipreading. (2020)
Stafylakis, T., Khan, M.H., Tzimiropoulos, G.: Pushing the boundaries of audiovisual word recognition using Residual Networks and LSTMs. Computer Vision & Image Understanding 2018.
Feng, D., Yang, S., Shan, S., Chen, X.: An efficient software for building lip reading models without pains. In: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia & Expo Workshops (ICMEW), IEEE, vol 2021.
Afouras, T., Chung, J.S., Andrew, Z.: My lips are concealed: Audio-visual speech enhancement through obstruction. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.04975 (2019)
Xu, B., Lu, C., Guo, Y., Wang, J.: Discriminative Multi-modality Speech Recognition. (2020)
Luo, M., Yang, S., Shan, S., Chen, X.: Pseudo-convolutional policy gradient for sequence-to-sequence lip-reading. In: IEEE FG, vol 2020.
Xiao, J., Yang, S., Zhang, Y., Shan, S., Chen, X.: Deformation flow based two-stream network for lip reading. In: IEEE FG, vol 2020.
Zhao, X., Yang, S., Shan, S., Chen, X.: Mutual information maximization for effective lip reading. IEEE FG 2020.
Petridis, S., Stafylakis, T., Ma, P., Cai, F., Pantic, M.: End-to-end audiovisual speech recognition. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics,vol 2018.
Petridis, S., Li, Z., Pantic, M.: End-to-end visual speech recognition with LSTMs. In: ICASSP 2017 - 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), vol 2017.
Petridis, S., Wang, Y., Li, Z., Pantic, M.: End-to-end multi-view lipreading. In: British Machine Vision Conference 2017, vol 2017.
Petridis, S., Jie, S., Cetin, D., Pantic, M.: Visual-only recognition of normal, whispered and silent speech. In: ICASSP 2018 - 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP),vol 2018.
Rahmani, M.H., Almasganj, F.: Lip-reading via a DNN-HMM hybrid system using combination of the image-based and model-based features. In: 2017 3rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis (IPRIA), vol 2017.
Wand, M., Schmidhuber, J.: Improving speaker-independent lipreading with domain-adversarial training. Interspeech 2017, (2017)
Wand, M., Schmidhuber, J., Vu, N.T.: Investigations on end- to-end audiovisual fusion. In: ICASSP 2018 - 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), vol 2018.
Moon, S., Kim, S., Wang, H.: Multimodal transfer deep learning with applications in audio-visual recognition. (2014)
Chung, J.S., Andrew, Z.: Out of time: automated lip sync in the wild. In: Asian Conference on Computer Vision, vol 2017.
Chung, J.S., Zisserman, A.: Learning to lip read words by watching videos. Computer Vis. Image Understand. 173, 76–85 (2018)
Oliveira, D., Mattos, A.B., Morais, E.: Improving viseme recognition with GAN-based muti-view mapping. In: International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, vol
Jha, A., Namboodiri, V.P., Jawahar, C.V.: Word spotting in silent lip videos. In: 2018 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), vol 2018.
Zhao, Y., Xu, R., Wang, X., Hou, P., Tang, H., Song, M.: Hearing lips: improving lip reading by distilling speech recognizers. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2020.
Zhang, X., Gong, H., Dai, X., Yang, F., Liu, M.: Understanding pictograph with facial features: end-to-end sentence-level lip reading of Chinese. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artific. Intell. 33, 9211–9218 (2019)
Assael, Y.M., Shillingford, B., Whiteson, S., Freitas, N.D.: LipNet: End-to-End Sentence-level Lipreading. arXiv preprint arXiv:1611.01599 2016.
Torfi, A., Iranmanesh, S.M., Nasrabadi, N., Dawson, J.: 3D Convolutional Neural Networks for Cross Audio-Visual Matching Recognition. IEEE Access 99, 1–1 (2017)
Shillingford, B., Assael, Y., Hoffman, M.W., Paine, T., Freitas, N.D.: Large-Scale Visual Speech Recognition. In: Interspeech 2019, vol 2019.
Kumar, Y., Jain, R., Salik, K.M., Shah, R.R., Yin, Y., Zimmermann, R.: Lipper: synthesizing thy speech using multi-view lipreading. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artific. Intell. 33, 2588–2595 (2019)
Kai, X., Li, D., Cassimatis, N., Wang, X.: LCANet: End-to-end lipreading with cascaded attention-CTC. In: 2018 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2018),vol 2018.
Liu, J., Ren, Y., Zhao, Z., Zhang, C., Yuan, J. FastLR: non-autoregressive lipreading model with integrate-and-fire. (2020)
Themos, S., Georgios T.: Combining residual networks with LSTMs for lipreading. Interspeech 2017.
Stafylakis, T., Tzimiropoulos, G.: Deep word embeddings for visual speech recognition. IEEE 2017.
Petridis, S., Stafylakis, T., Ma, P., Tzimiropoulos, G., Pantic M.: Audio-Visual speech recognition with a hybrid CTC/attention architecture. In: 2018 IEEE Spoken Language Technology Workshop (SLT), vol 2018.
Sterpu, G., Saam, C., Harte, N.: Attention-based Audio-Visual Fusion for Robust Automatic Speech Recognition. 2018.
Chenhao W. Multi-grained spatio-temporal modeling for lip-reading. InThe 30th British Machine Vision Confer-ence (2019), vol 2019
Sterpu, G., Saam, C., Harte N.: Should we hard-code the recurrence concept or learn it instead? Exploring the Transformer architecture for Audio-Visual Speech Recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:2005.09297 (2020)
Ma, P., Petridis, S., Pantic M.: End-to-end Audio-visual Speech Recognition with Conformers. (2021)
Ma, P., Martinez, B., Petridis, S., Pantic M.:Towards practical lipreading with distilled and efficient models. ICASSP 2021–2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP 2021)
Tamura, S., Seko, T., Hayamizu, S.: Integration of deep bottleneck features for audio-visual speech recognition. In: Proceedings of the Sixteenth annual conference of the international speech communication association, pp 1–6, (2014)
Wand, M., Koutník, J., Schmidhuber, J.: lipreading with long short-term memory. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, vol 2016
Petridis, S., Wang, Y., Li, Z., Pantic M.: End-to-end audiovisual fusion with LSTMs. In: International Conference on Auditory-visual Speech Processing, vol 2017
Funding
This study was funded by the Scientific Research Key Project of Hebei Provincial Department of Education (Grant No.ZD2020161) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (Grant No.F2021409007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Author Gangqiang Pu declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Huijuan Wang declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pu, G., Wang, H. Review on research progress of machine lip reading. Vis Comput 39, 3041–3057 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-022-02511-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-022-02511-4